Published online Apr 12, 2012. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v3.i4.63
Revised: February 2, 2012
Accepted: March 12, 2012
Published online: April 12, 2012
A 70-year-old man was referred to our hospital due to abnormal liver function. A tumor of 92 mm × 61 mm was detected on ultrasound screening of the left liver lobe. Although the tumor was suspected to be intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma, he had chronic heart disease and was unable to undergo surgery. Therefore, he was followed without further testing. No increase in tumor serum markers or tumor size was observed for the subsequent 7 years. We continued to suspect intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma, and we decided to perform a tumor biopsy. Tumor biopsy findings indicated intrahepatic bile duct adenoma (BDA), which is a rare benign epithelial liver tumor typically ranging from 1 mm to 20 mm. We herein report a case of very large BDA followed for 7 years.
- Citation: Koga F, Tanaka H, Takamatsu S, Baba S, Takihara H, Hasegawa A, Yanagihara E, Inoue T, Nakano T, Ueda C, Ono W. A case of very large intrahepatic bile duct adenoma followed for 7 years. World J Clin Oncol 2012; 3(4): 63-66
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v3/i4/63.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v3.i4.63
Intrahepatic bile duct adenoma (BDA) is a rare, benign epithelial liver tumor that typically ranges in size from 1 mm to 20 mm[1]. BDA is mainly found incidentally at laparotomy or autopsy[1-5]. Here, we report a case of very large BDA (about 90 mm in diameter) that was followed for 7 years.
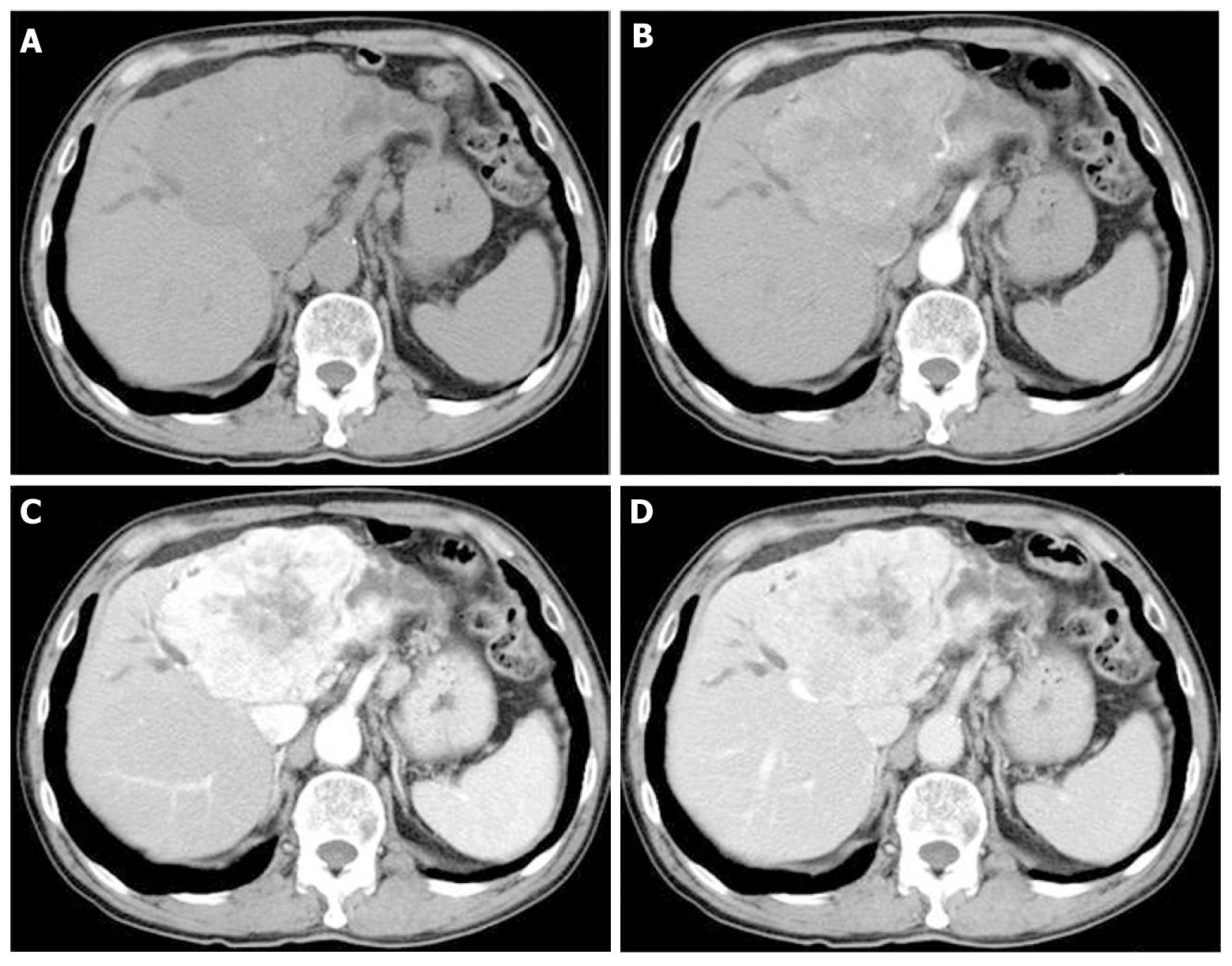
A 70-year-old man was referred to our hospital due to liver dysfunction (Table 1). Although no liver failure was shown, mild increased serum ALP and γ-GTP were observed. A tumor of 92 mm × 61 mm was observed on ultrasound screening of the left liver lobe. Unenhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) showed a tumor of the same size with dilation of the peripheral bile duct, while dynamic contrast-enhanced CT revealed heterogeneous enhancement in the venous phase (Figure 1). Although the tumor was suspected to be intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma, he had chronic heart disease and was unable to undergo surgery. Therefore, he was followed without further testing. No increase in serum tumor markers, such as CEA and CA19-9, or in tumor size was observed during the subsequent 7 years.
| WBC | 7000/uL | BS | 100 mg/dL |
| Neutro | 60.9% | CRP | 0.72 mg/dL |
| Eosin | 3.6% | Na | 139 mEq/L |
| Baso | 0.5% | K | 4.5 mEq/L |
| Mono | 9.1% | Cl | 103 mEq/L |
| Lympho | 25.9% | CEA | 2.5 ng/mL |
| RBC | 413 × 104/uL | CA19-9 | 46 U/mL |
| Hb | 12.8 g/dL | Alb | 4.2 g/dL |
| Ht | 41.2% | BUN | 20.8 mg/dL |
| Plt | 19.8 × 104/uL | Cr | 1.07 mg/dL |
| TP | 8.4 g/dL | D-Bil | 0.1 mg/dL |
| T-Bil | 0.9 mg/dL | ALT | 12 IU/L |
| AST | 22 IU/L | ALP | 360 U/L |
| PT | 56% | γ-GTP | 168 IU/L |
| ChE | 274 U/L | ||
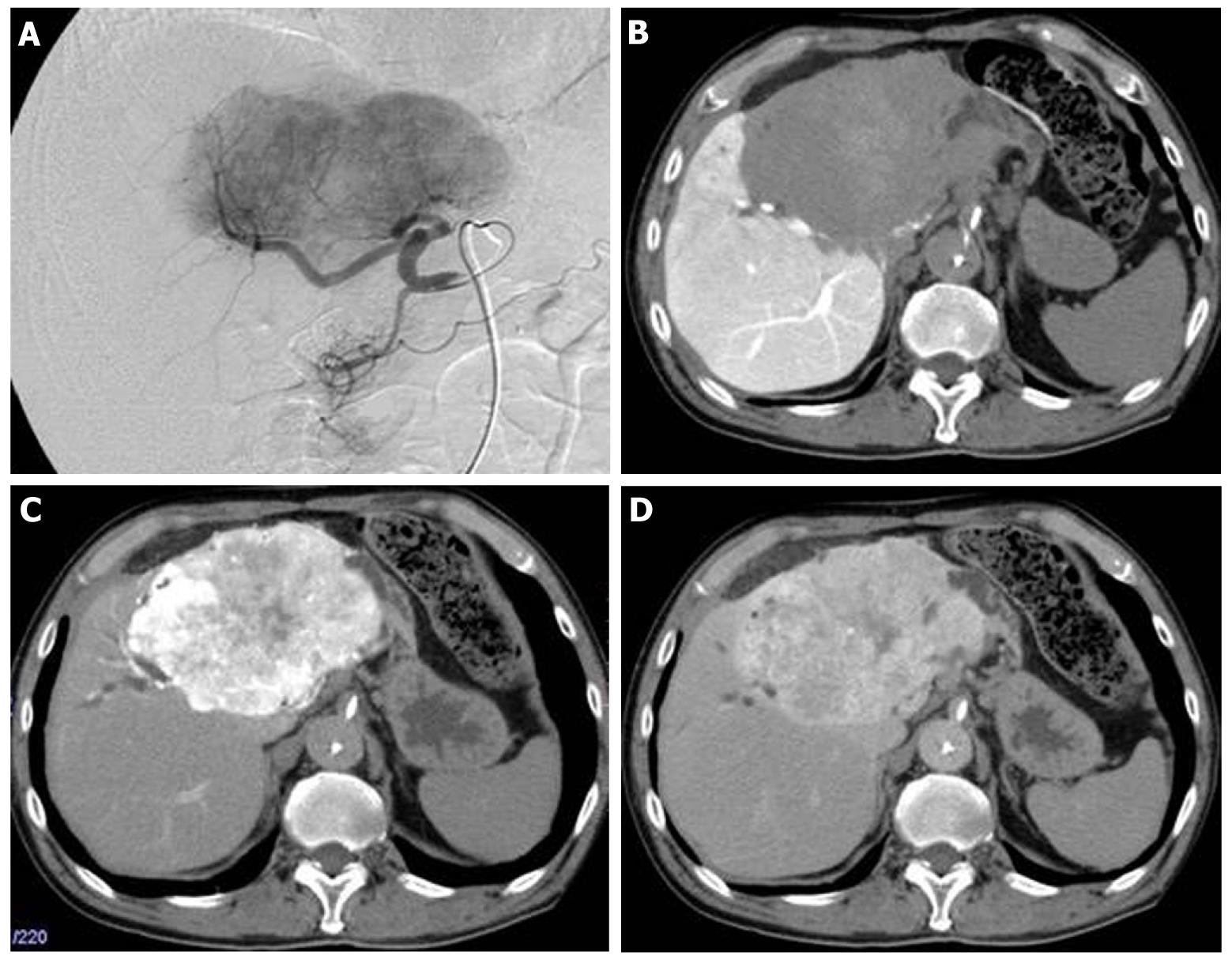
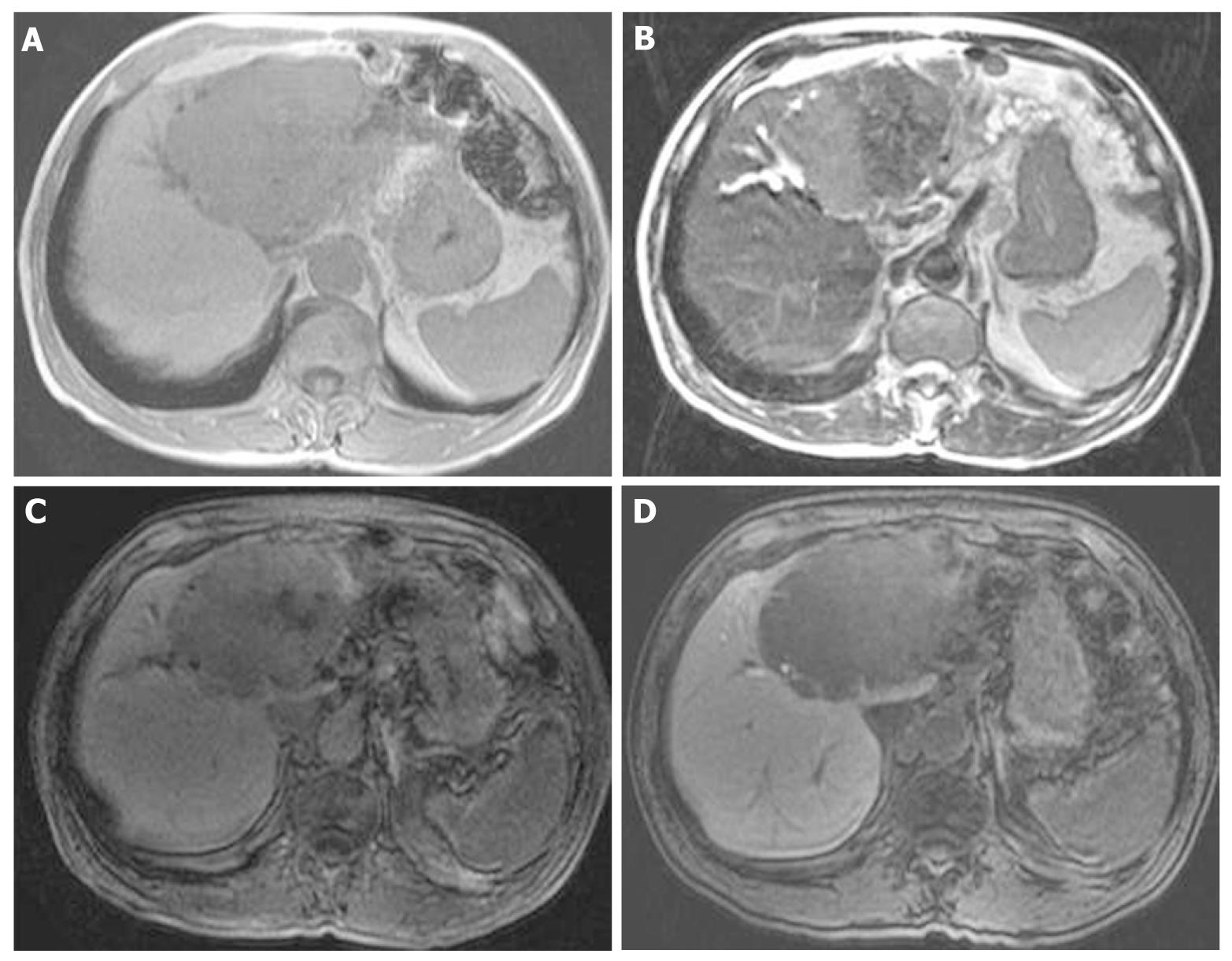
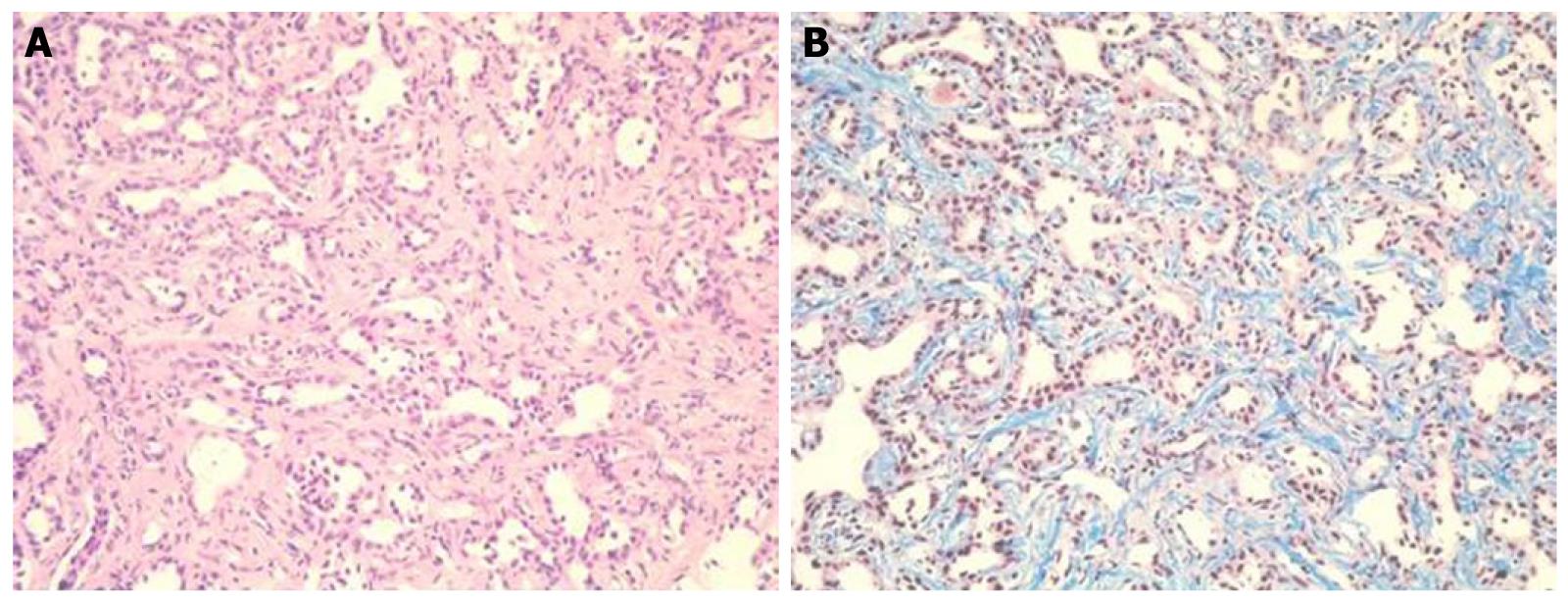
At that point, hepatic arterial angiography, abdominal CT angiography, gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced abdominal magnatic resonance image (MRI) and tumor biopsy were performed in order to confirm the diagnosis of intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. Hepatic arterial angiography and CT angiography showed a hypervascular tumor of the left liver lobe with an enhancement effect persisting into the late phase, suggesting that this tumor had rich fibrous tissues (Figure 2). MRI confirmed that the tumor showed heterogeneous high intensity on T2-weighted images (Figure 3B) and low intensity on T1-weighted images (Figure 3A). Contrast-enhanced EOB MRI revealed that this tumor had relative hypointensity in comparison with the normal liver parenchyma on equilibrium and hepatobiliary phase (Figure 3C and D). Biopsy findings showed that the tumor consisted of small heterogeneous tubular ducts with fibrous tissues, without cell atypia or mitotic activity. Thus, diagnosis was confirmed as BDA (Figure 4).
Although the actual incidence of BDA is unknown, it is a rare, benign and asymptomatic tumor of the liver, and is typically found incidentally[1-5]. Most BDAs are subcapsular, ranging from 1 mm to 20 mm in diameter[1]. However, in the present case, the tumor was very large, at 90 mm in diameter. Therefore, we initially suspected tumor intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma, and believed the patient to be end-stage. Thus, we followed him without treatment over a 7-year follow-up period.
Although various abdominal imaging approaches have been reported, most BDAs show hypervascular characteristics consisting of prolonged enhancement[6-9]. Our case showed the same findings as in these reports, and it was suggested that the delayed or prolonged enhancement on dynamic CT and MRI was due to the fibrous stroma within the tumor[8]. However, it has also been reported that the differential diagnosis between BDA and malignant tumor is very difficult using radiological methods[10]. In addition, although we obtained liver biopsy samples from some areas of the tumor, there may have been sampling errors due to the large tumor size and heterogeneous enhanced pattern. Therefore, we believe that this patient requires further follow-up.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of a very large BDA, and we confirmed no changes in size over a 7-year follow-up period. Although rare, BDA should be considered in the differential diagnosis of hepatic hypervascular tumors.
Peer reviewer: Naoya Sakamoto, MD, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, 1-5-45 Yushima, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8519, Japan
S- Editor Yang XC L- Editor A E- Editor Yang XC
| 1. | Allaire GS, Rabin L, Ishak KG, Sesterhenn IA. Bile duct adenoma. A study of 152 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12:708-715. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Edmondson HA. Tumors of the liver and intrahepatic bile duct. Washington DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology 1958; 19-29. |
| 3. | Craig JR, Peters RL, Edmondson HA. Tumors of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts. Washington DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology 1989; 56-62. |
| 4. | Tajima T, Honda H, Kuroiwa T, Yoshimitsu K, Irie H, Aibe H, Taguchi K, Shimada M, Masuda K. Radiologic features of intrahepatic bile duct adenoma: a look at the surface of the liver. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999;23:690-695. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Cho C, Rullis I, Rogers LS. Bile duct adenomas as liver nodules. Arch Surg. 1978;113:272-274. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Kobayashi T, Matsui O, Takashima T. A case of bile duct adenoma (Japanese). In Abdominal Radiology Study Group of Japan, eds. Atlas of diagnostic abdominal imaging, vol. 1. Osaka, Japan: Nihon Schering 1993; 26-27. |
| 7. | Maeda E, Uozumi K, Kato N, Akahane M, Inoh S, Inoue Y, Beck Y, Goto A, Makuuchi M, Ohtomo K. Magnetic resonance findings of bile duct adenoma with calcification. Radiat Med. 2006;24:459-462. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Honda H, Onitsuka H, Yasumori K, Hayashi T, Ochiai K, Gibo M, Adachi E, Matsumata T, Masuda K. Intrahepatic peripheral cholangiocarcinoma: two-phased dynamic incremental CT and pathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1993;17:397-402. [PubMed] |
| 9. | Kim YS, Rha SE, Oh SN, Jung SE, Shin YR, Choi BG, Byun JY, Jung ES, Kim DG. Imaging findings of intrahepatic bile duct adenoma (peribiliary gland hamartoma): a case report and literature review. Korean J Radiol. 2010;11:560-565. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Kawakatsu M, Vilgrain V, Zins M, Vullierme M, Belghiti J, Menu Y. Radiologic features of papillary adenoma and papillomatosis of the biliary tract. Abdom Imaging. 1997;22:87-90. [PubMed] |