Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. Feb 10, 2011; 2(2): 73-79
Published online Feb 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i2.73
Published online Feb 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i2.73
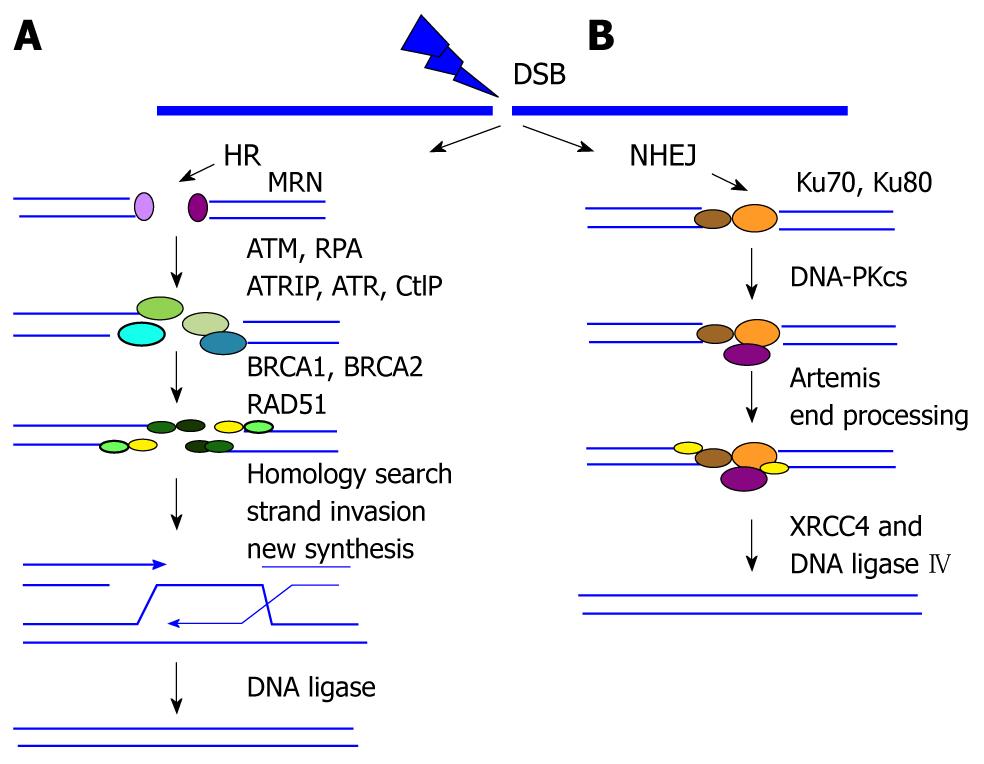
Figure 1 DNA double strand break repair pathways.
A: Homologous recombination (HR) repair. MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex recognizes and senses double strand breaks (DSBs). This complex activates ATM kinase, which in turn initiates the full DNA damage response, particularly in the heterochromatin regions of chromosomes. CtIP-mediated nuclease activity is required for the end resection from 5' to 3', which leads to the formation of single-strand DNA (ssDNA). The exposed ssDNA is coated with DNA replication protein A (RPA) and activates the Ataxia Telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) response to facilitate HR repair. Then RAD51 nucleoprotein filament is assembled, which replaces RPA-coated ssDNA, performs homology sequence searching, and mediates strand invasion. DSBs are restored by branch migration of this joint DNA molecule, DNA synthesis, ligation, and resolution of Holliday junctions; B: Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair. The two broken ends are processed and ligated directly by the action of the end-binding KU70/80 complex and DNA-PKcs followed by XRCC4-ligase4.
- Citation: Peng G, Lin SY. Exploiting the homologous recombination DNA repair network for targeted cancer therapy. World J Clin Oncol 2011; 2(2): 73-79
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v2/i2/73.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v2.i2.73