Published online Jun 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i6.520
Peer-review started: April 10, 2021
First decision: July 6, 2021
Revised: October 24, 2021
Accepted: May 21, 2022
Article in press: May 21, 2022
Published online: June 24, 2022
Processing time: 437 Days and 23.6 Hours
Although PNENs generally have a better prognosis than pancreatic cancers, some PNENs display malignant behavior including lymph node (LN) metastasis. Complete tumor resection can be the only potentially curative treatment for patients with resectable PNENs. However, the indications for LN dissection are still controversial. Over the last decade, minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopic pancreatic surgery (LPS) has been increasingly performed for pancreatic tumors including PNENs.
To investigate the risk factors for LN metastasis in PNENs and to select appropriate patients for limited surgery by LPS.
From April 2001 to December 2019, 92 patients underwent pancreatic resection for PNENs at Kumamoto University Hospital. Finally, 82 patients were enrolled in this study. Using perioperative factors, we examined the predictive factors for LN metastasis in PNENs.
Among the 82 patients, the percentage of LN metastasis according to the pathological findings was 12% (10/82 cases). The median tumor size was 12 mm (range: 5-90 mm). The median tumor size in the LN-positive group (37 mm) was significantly larger than that in the LN-negative group (12 mm) (P = 0.0001). Multivariate analyses revealed that larger tumor size (≥ 20 mm) was an inde
Larger tumor size (≥ 20 mm) is an independent risk factor for LN metastasis in PNENs. In smaller PNENs (≤ 10 mm), we may be able to choose limited surgery without LN dissection.
Core Tip: Among the 82 patients, the percentage with lymph node (LN) metastasis according to the pathological findings was 12% (10/82 cases). The median tumor size was 12 mm (range: 5-90 mm). The median tumor size in the LN-positive group (37 mm) was significantly larger than that in the LN-negative group (12 mm) (P = 0.0001). Multivariate analyses revealed that large tumor size (≥ 20 mm) was an independent risk factor for LN metastasis. In patients with small tumors (≤ 10 mm), LN metastasis was not found. In conclusion, large tumor size (≥ 20 mm) is an independent risk factor for LN metastasis in PNENs. In smaller PNENs (≤ 10 mm), we may be able to choose limited surgery without LN dissection.
- Citation: Nakao Y, Hayashi H, Yamashita YI, Takashi O, Matsumura K, Uemura N, Kitamura F, Itoyama R, Yusa T, Taki K, Miyata T, Higashi T, Nakagawa S, Okabe H, Imai K, Baba H. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Clin Oncol 2022; 13(6): 520-528
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v13/i6/520.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i6.520
Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs) are relatively rare and represent 1%-2% of all pancreatic neoplasms[1]. Although patients with PNENs generally have better prognosis than those with pancreatic cancers, some PNENs display malignant behavior including local invasion, lymph node (LN) metastasis, and distant metastasis[2]. The natural history of PNENs is not fully understood because of their relative rarity, and therefore, it is difficult to predict the malignant potential of PNENs precisely.
Complete tumor resection can be the only potentially curative treatment for patients with resectable PNENs. However, optimal surgical management procedures have not yet been established[3,4]. Especially, the indications for LN dissection are still controversial, especially in early PNENs. This is partly caused by the difficulty of predicting LN metastasis. Therefore, it is important to establish appropriate indications for LN dissection to treat PNENs.
Over the last decade, minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopic pancreatic surgery (LPS) has been increasingly performed for pancreatic tumors including PNENs[5-7]. Non-comparative studies have shown that LPS for pancreatic tumors is safe and equivalently effective to open pancreatic surgery (OPS)[8-10]. In well-selected groups of patients with pancreatic lesions, LPS provides good peri and post operative outcomes, such as reduced intraoperative blood loss, and postoperative pain and length of postoperative day[8,10-13]. As a limited type of LPS, laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy and excisional resection for PNENs has also been performed in selected cases[7,14,15]. However, the indications for limited surgery by LPS for patients with PNENs remain unclear.
The aims of this study are to investigate the risk factors for LN metastasis in PNENs and to select appropriate patients for limited LPS.
From April 2001 to December 2019, 92 patients underwent pancreatic resection for PNENs at Kumamoto University Hospital. Of them, 10 patients (11%) were excluded from this analysis because of distant metastases and coexisting tumors other than PNENs. Finally, 82 patients were enrolled in this study. The patients were identified retrospectively from a prospectively maintained database, and additional data were obtained by reviewing each patient’s medical records. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before treatment, and this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kumamoto University (number 1291).
Before treatment, all patients underwent routine diagnostic laboratory tests and imaging modalities including enhanced computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). The final diagnoses were confirmed pathologically using resected specimens. Tumors were classified as functional PNENs according to the clinical signs and symptoms of hormonal excess and increased levels of corresponding serum peptides and hormones. Tumors were classified as non-functional if they were not associated with distinct clinical manifestations or hormonal alterations[16]. Surgical procedures were selected based on each tumor’s location and extent and the patient’s general condition. Pancreatic resection was considered the first-choice treatment for patients with PNENs.
After treatment, all of the patients underwent regular follow-up examinations including routine laboratory tests and imaging studies including EUS, CT, or MRI to detect any pancreatic recurrence or distant metastasis, as described previously[17]. When tumor recurrence was confirmed, various treatment modalities were selected, including repeat surgery, chemotherapy, or a combination of these methods, according to tumor location and patient condition.
Continuous variables were expressed as median (range). Continuous and categorical variables were compared using Mann-Whitney U and χ2 tests, respectively. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, with comparisons using the log rank test. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of surgery until death or last follow-up. Variables in which the P value for LN metastasis was < 0.05 in univariate analysis were subjected to subsequent multivariate analysis by stepwise backward elimination procedures. All statistical analyses were performed using JMP® version 13.1 (SAS institute, Cary, NC, United States). All P values were two-sided, and P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
The 82 patients’ demographic and clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. There were 41 male and 41 female patients, with a median age of 59 years (range, 18-81 years). Thirty five patients (43%) had symptoms at the first consultation. Preoperative contrast-enhanced CT showed that the majority of patients had tumors with hyper enhanced pattern (72 patients, 88%). Of the 31 patients (38%) who had functional PNENs, the most frequent type of functional PNEN was insulinoma (26 patients, 32%), followed by glucagonoma (2, 2.5%), gastrinoma (2, 2.5%), and VIPoma (1, 1%). There were 51 patients (62%) who had non-functional PNENs. Their 2017 WHO classifications were: G1, 70 (85%); G2, 9 (11%); and G3 or NEC, 3 (4%). Fourteen patients (17%) had multiple tumors, and the median tumor size was 12 mm (range, 5-90 mm). Among the 82 patients, 23 (28%) received pancreatoduodenectomy (PD), 38 (46%) received distal pancreatectomy, 2 (2.5%) received PD + DP, and 19 (23%) received enucleation or partial pancreatectomy.
| Variables | Total (n = 82) | N- (n = 72) | N+ (n = 10) | P value | |
| Age, median (range) | 59 (18-81) | 58 (18-80) | 63 (18-81) | 0.65 | |
| Gender (male/female) | 41/41 | 35/37 | 6/4 | 0.50 | |
| Tumor size, median, mm (range) | 12 (5-90) | 12 (5-90) | 37 (12-75) | 0.0001 | |
| Tumor number (single/multiple) | 68/14 | 59/13 | 9/1 | 0.50 | |
| Tumor location (Ph/Pb/Pt/Ph and Pt) | 32/23/25/2 | 23/22/25/2 | 9/1/0/0 | 0.15 | |
| Symptoms (yes/no) | 35/47 | 31/41 | 4/6 | 0.85 | |
| CT Enhancement (hyper/hypo) | 72/10 | 64/8 | 8/2 | 0.17 | |
| Type of PNEN, n (%) | NS | ||||
| Insulinoma | 26 (32) | 26 | 0 | ||
| Gastrinoma | 2 (2.5) | 1 | 1 | ||
| Glucagonoma | 2 (2.5) | 2 | 0 | ||
| VIPoma | 1 (1) | 1 | 0 | ||
| Non functional | 51 (62) | 42 | 9 | ||
| WHO classification 2017, n (%) | 0.0009 | ||||
| NET G1 | 70 (85) | 66 | 4 (6%) | ||
| NET G2 | 9 (11) | 5 | 4 (44%) | ||
| NET G3/NEC | 3 (4) | 1 | 2 (67%) | ||
| Surgical procedure, n (%) | NS | ||||
| Pancreatoduodenectomy (PD) | 23 (28) | 15 | 8 | ||
| Distal pancreatectomy (DP) | 38 (46) | 37 | 1 | ||
| PD + DP | 2 (2.5) | 2 | 0 | ||
| Enucleation/partial pancreatectomy | 19 (23) | 18 | 1 | ||
Among the 82 patients, 10 (12%) were identified as having LN metastasis. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the 10 patients with LN metastasis were compared with those of the 72 patients without LN metastasis (Table 1). LN metastases of PNENs were positively associated with pathological grade: 6%, 44%, and 67% of cases with LN metastases were classified as G1, G2, and G3/NEC, respectively (P = 0.0009). In the LN metastasis-positive group, tumor size was significantly larger than that in the negative group (median, 12 vs 37, P = 0.0001). Univariate analysis showed that the following three factors were related to LN metastasis: tumor size ≥ 20 mm [Odds Ratio (OR) 31.5, P < 0.0001], WHO 2017 classification ≥ G2 (OR 20.1, P = 0.0001), and non-functional type of PNEN (OR 6.43, P = 0.035). Multivariate logistic regression analyses revealed that tumor size ≥ 20 mm was an independent risk factor for LN metastasis (OR 16.8, P = 0.0062) (Table 2).
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
| Odds ratio | P value | Odds ratio | 95%CI | P value | |
| Age ≥ 60 | 0.54 | 0.40 | |||
| Gender (male) | 0.63 | 0.50 | |||
| Symptoms (yes) | 1.13 | 0.85 | |||
| CT Enhancement (hyper) | 4 | 0.17 | |||
| Tumor number (multiple) | 1.98 | 0.50 | |||
| Tumor size (≥ 20 mm) | 31.5 | < 0.0001 | 16.8 | 2.15-35.4 | 0.0062 |
| WHO classification 2017 (≥ G2) | 20.1 | 0.0001 | NS | ||
| Type of PNEN (non functional) | 6.43 | 0.035 | NS | ||
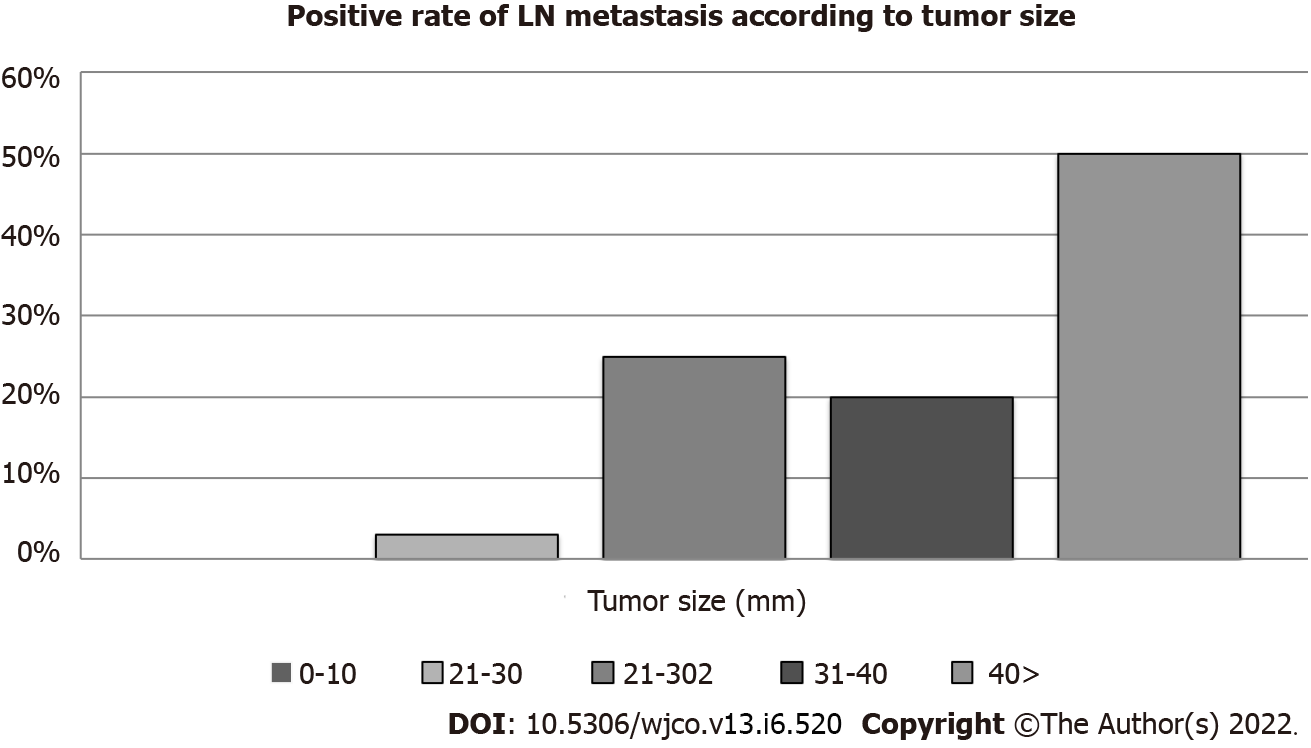
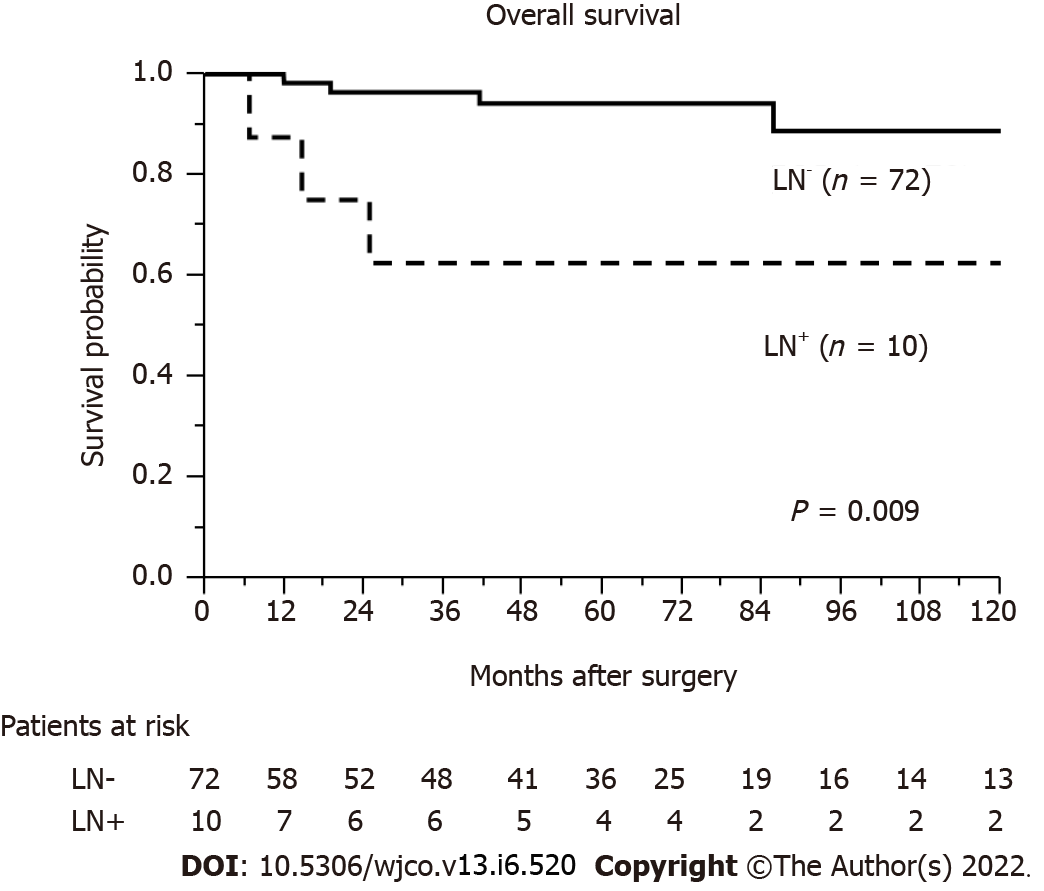
Figure 1 shows the rate of LN metastasis according to tumor size. The rates of LN metastasis according to tumor size were as follows: 0% (0/29 cases, ≤ 10 mm group), 3% (1/31 cases, 11 mm-20 mm group), 25% (2/8 cases, 21-30 mm group), 50% (3/6 cases, 31-40 mm group), and 50% (4/8 cases, > 40 mm group) (Figure 1). The median length of follow-up after surgery was 51.8 months (range, 0.4-224.2). The cumulative OS rate after surgery for patients with no LN metastasis was significantly higher than that for those with LN metastasis (P = 0.009) (Figure 2).
PNENs are rare tumors[1]. The oncological history is not yet fully understood due to their often-lazy course, because it is not easy to find correct diagnosis and treatment. Furthermore, PNENs have wide variety biological behaviors, such as benign tumors and malignant status[18]. Because of the heterogeneity of PNENs, it is very difficult both to construct the effective clinical treatment policy systems and to confirm the surgical method for cure.
Some reports have associated LN metastasis with shorter OS[3,19-25], while others have found that LN status did not affect survival[26-29]. LN metastasis is positively correlated with pathological grade, with 15%-20%, 30%-40%, and > 50% of patients with LN metastasis classified as G1, G2, and G3, respectively[30]. In our study, we also reported that the LN metastasis-positive group of PNENs had poor OS after surgery. Further, we reported that LN metastases of PNENs are positively associated with pathological grade, with 6%, 44%, and 67% of patients with LN metastases classified as G1, G2, and G3/NEC, respectively (P = 0.0009; Table 1). Therefore, patients with PNENs and LN metastasis have poor prognosis and high malignant potential. However, previous reports have not clearly shown that to omit LN dissection may increase the possibility of recurrence. Some previous studies shows that local LN metastases of PNENs have oncologic effects[30,31]. A past study related with non-functional G1 PNENs who underwent surgery of pancreas reported that LN metastases of PNENs do not adversely affect oncological outcomes and do not require routine local lymphadenectomy[32]. Partelli et al[33] reported that a lot of insulinomas (well-differentiated) and non-functional PNENs located in the distal pancreas are very small, rarely associated with LN metastases, and there is no radiographic evidence of positive of LN metastases. Thus, the significance of LN metastasis in patients with PNENs is very complicated, and the indications for regional LN dissection are still controversial.
Previous studies have focused on the associations of LN metastasis or and/or prognosis with tumor size[17,21,34-39]. Although LN metastasis has been seen even in patients with tumors < 10 mm, LN metastasis occurs more often in patients with large tumors than in those with smaller ones. In our study, there were no cases of LN metastasis in patients with tumors ≤ 10 mm. LN metastases of PNENs were positively associated with tumor size, being present in 0%, 3%, 25%, and 50% of patients with primary tumors ≤ 10 mm, 11-20 mm, 21-30 mm, and > 30 mm, respectively. If we can predict the presence of LN metastasis according to tumor size, we can select appropriate patients for limited LPS.
Over the last decade, the use of laparoscopy in pancreatic surgery has increased significantly, and previously almost all open surgery can now be performed in a minimally invasive method. In general, these minimally invasive surgery should be limited to high-volume centers with extensive experience in pancreatic surgery with open surgery. Patients with small-sized PNENs in the body and tail of the pancreas are particularly well suited for minimally invasive surgery, and the laparoscopic procedures gives better result than open surgical method[40,41]. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy have the potential to be superior to the open surgical method in patients with benign tumors, resulting in less operative bleeding, shorter postoperative days, and equivalent rates of complications[13]. According to the review by 11 studies, which involve 906 PNENs patients, of whom 22% and 78% underwent LPS and OPS, respectively, it reported that overall complication rate of laparoscopic method was significantly lower (38% vs 46%, P < 0.001) and the postoperative days in hospital is shorter (P < 0.001)[40]. LPS is now considered to be a safe approach for PNENs and should be included in the patient’s surgical equipment. Many surgeons have reported that the rates of overall complication in small or benign tumors were lower with LPS than OPS. Although in the cases of patients with malignant PNENs, we need advanced surgical skills, LPS was not associated with compromised oncologic resection and provided benefits including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stay, and shorter postoperative recovery period. Thus, it is important to investigate the risk factors of LN metastases in PNENs and to select appropriate patients for limited LPS. Our results offer certain recommendations in this regard.
However, this study had several limitations, including its retrospective design, the small number of subjects, and the lack of data on certain pathologic variables (especially the Ki-67 indices and mitotic rates) for all patients. The number of examined LNs was not sufficient, and data on the number of positive LNs were not available for all PNENs. Therefore, further research regarding advanced PNENs is required.
In conclusion, larger tumor size (≥ 20 mm) is an independent risk factor for LN metastasis in PNENs. In smaller PNENs (≤ 10 mm), we may be able to choose limited surgery without LN dissection.
The indications for lymph node (LN) dissection are still controversial.
Over the last decade, minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopic pancreatic surgery (LPS) has been increasingly performed for pancreatic tumors including pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs).
The aim of this study was to investigate the risk factors for LN metastasis in PNENs and to select appropriate patients for limited surgery by LPS.
From April 2001 to December 2019, 92 patients underwent pancreatic resection for PNENs at Kumamoto University Hospital. Finally, 82 patients were enrolled in this study. Using perioperative factors, we examined the predictive factors for LN metastasis in PNENs.
Among the 82 patients, the percentage of LN metastasis according to the pathological findings was 12% (10/82 cases). The median tumor size was 12 mm (range: 5-90 mm). The median tumor size in the LN-positive group (37 mm) was significantly larger than that in the LN-negative group (12 mm) (P = 0.0001). Multivariate analyses revealed that large tumor size (≥ 20 mm) was an independent risk factor for LN metastasis (odds ratio 16.8, P = 0.0062). In patients with small tumors (≤ 10 mm), LN metastasis was not found.
Large tumor size (≥ 20 mm) is an independent risk factor for LN metastasis in PNENs. In smaller PNENs (≤ 10 mm), we may be able to choose limited surgery without LN dissection.
In smaller PNENs (≤ 10 mm), we may be able to choose limited surgery without LN dissection.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Sun Y, China S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: Kerr C P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE, Abdalla EK, Fleming JB, Vauthey JN, Rashid A, Evans DB. One hundred years after "carcinoid": epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063-3072. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3022] [Cited by in RCA: 3242] [Article Influence: 190.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Halfdanarson TR, Rabe KG, Rubin J, Petersen GM. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): incidence, prognosis and recent trend toward improved survival. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:1727-1733. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 663] [Cited by in RCA: 620] [Article Influence: 36.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Fischer L, Bergmann F, Schimmack S, Hinz U, Prieß S, Müller-Stich BP, Werner J, Hackert T, Büchler MW. Outcome of surgery for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Br J Surg. 2014;101:1405-1412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kleine M, Schrem H, Vondran FW, Krech T, Klempnauer J, Bektas H. Extended surgery for advanced pancreatic endocrine tumours. Br J Surg. 2012;99:88-94. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Asbun HJ, Stauffer JA. Laparoscopic vs open pancreaticoduodenectomy: overall outcomes and severity of complications using the Accordion Severity Grading System. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;215:810-819. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 287] [Cited by in RCA: 295] [Article Influence: 22.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Cuschieri A, Jakimowicz JJ, van Spreeuwel J. Laparoscopic distal 70% pancreatectomy and splenectomy for chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1996;223:280-285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 154] [Cited by in RCA: 154] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Gagner M, Pomp A, Herrera MF. Early experience with laparoscopic resections of islet cell tumors. Surgery. 1996;120:1051-1054. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 312] [Cited by in RCA: 307] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Venkat R, Edil BH, Schulick RD, Lidor AO, Makary MA, Wolfgang CL. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy is associated with significantly less overall morbidity compared to the open technique: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2012;255:1048-1059. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 429] [Cited by in RCA: 388] [Article Influence: 29.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | DiNorcia J, Schrope BA, Lee MK, Reavey PL, Rosen SJ, Lee JA, Chabot JA, Allendorf JD. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy offers shorter hospital stays with fewer complications. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:1804-1812. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 85] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Nakamura M, Nakashima H. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy and pancreatoduodenectomy: is it worthwhile? J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013;20:421-428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 112] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Aly MY, Tsutsumi K, Nakamura M, Sato N, Takahata S, Ueda J, Shimizu S, Redwan AA, Tanaka M. Comparative study of laparoscopic and open distal pancreatectomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2010;20:435-440. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Jusoh AC, Ammori BJ. Laparoscopic versus open distal pancreatectomy: a systematic review of comparative studies. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:904-913. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 117] [Cited by in RCA: 114] [Article Influence: 8.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Nigri GR, Rosman AS, Petrucciani N, Fancellu A, Pisano M, Zorcolo L, Ramacciato G, Melis M. Metaanalysis of trials comparing minimally invasive and open distal pancreatectomies. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:1642-1651. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 128] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Shirota T, Nagakawa Y, Sahara Y, Takishita C, Hijikata Y, Hosokawa Y, Nakajima T, Osakabe H, Katsumata K, Tsuchida A. Surgical resection of neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas (pNETs) by minimally invasive surgery: the laparoscopic approach. Gland Surg. 2018;7:12-19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Assalia A, Gagner M. Laparoscopic pancreatic surgery for islet cell tumors of the pancreas. World J Surg. 2004;28:1239-1247. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Han X, Xu X, Jin D, Wang D, Ji Y, Lou W. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis-related factors of resectable pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a retrospective study of 104 cases in a single Chinese center. Pancreas. 2014;43:526-531. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Taki K, Hashimoto D, Nakagawa S, Ozaki N, Tomiyasu S, Ohmuraya M, Arima K, Kaida T, Higashi T, Sakamoto K, Sakata K, Okabe H, Nitta H, Hayashi H, Chikamoto A, Beppu T, Takamori H, Hirota M, Baba H. Significance of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Surg Today. 2017;47:1104-1110. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Dimou AT, Syrigos KN, Saif MW. Neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas: what's new. Highlights from the "2010 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium". Orlando, FL, USA. January 22-24, 2010. JOP. 2010;11:135-138. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Boninsegna L, Panzuto F, Partelli S, Capelli P, Delle Fave G, Bettini R, Pederzoli P, Scarpa A, Falconi M. Malignant pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour: lymph node ratio and Ki67 are predictors of recurrence after curative resections. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:1608-1615. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 121] [Cited by in RCA: 128] [Article Influence: 9.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Hashim YM, Trinkaus KM, Linehan DC, Strasberg SS, Fields RC, Cao D, Hawkins WG. Regional lymphadenectomy is indicated in the surgical treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs). Ann Surg. 2014;259:197-203. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 215] [Cited by in RCA: 198] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Tsutsumi K, Ohtsuka T, Mori Y, Fujino M, Yasui T, Aishima S, Takahata S, Nakamura M, Ito T, Tanaka M. Analysis of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) based on the tumor size and hormonal production. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:678-685. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Postlewait LM, Ethun CG, Baptiste GG, Le N, McInnis MR, Cardona K, Russell MC, Sarmiento JM, Kooby DA, Staley CA, Maithel SK. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Preoperative factors that predict lymph node metastases to guide operative strategy. J Surg Oncol. 2016;114:440-445. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Fendrich V, Langer P, Celik I, Bartsch DK, Zielke A, Ramaswamy A, Rothmund M. An aggressive surgical approach leads to long-term survival in patients with pancreatic endocrine tumors. Ann Surg. 2006;244:845-51; discussion 852. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 121] [Cited by in RCA: 108] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Ballian N, Loeffler AG, Rajamanickam V, Norstedt PA, Weber SM, Cho CS. A simplified prognostic system for resected pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. HPB (Oxford). 2009;11:422-428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Brunner SM, Weber F, Werner JM, Agha A, Farkas SA, Schlitt HJ, Hornung M. Neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas: a retrospective single-center analysis using the ENETS TNM-classification and immunohistochemical markers for risk stratification. BMC Surg. 2015;15:49. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Parekh JR, Wang SC, Bergsland EK, Venook AP, Warren RS, Kim GE, Nakakura EK. Lymph node sampling rates and predictors of nodal metastasis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor resections: the UCSF experience with 149 patients. Pancreas. 2012;41:840-844. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Wong J, Fulp WJ, Strosberg JR, Kvols LK, Centeno BA, Hodul PJ. Predictors of lymph node metastases and impact on survival in resected pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a single-center experience. Am J Surg. 2014;208:775-780. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Gratian L, Pura J, Dinan M, Roman S, Reed S, Sosa JA. Impact of extent of surgery on survival in patients with small nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:3515-3521. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Kazanjian KK, Reber HA, Hines OJ. Resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: results of 70 cases. Arch Surg. 2006;141:765-9; discussion 769. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Tsutsumi K, Ohtsuka T, Fujino M, Nakashima H, Aishima S, Ueda J, Takahata S, Nakamura M, Oda Y, Tanaka M. Analysis of risk factors for recurrence after curative resection of well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors based on the new grading classification. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21:418-425. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Birnbaum DJ, Turrini O, Ewald J, Barbier L, Autret A, Hardwigsen J, Brunet C, Moutardier V, Le Treut YP, Delpero JR. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: A multivariate analysis of factors influencing survival. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40:1564-1571. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Yoo YJ, Yang SJ, Hwang HK, Kang CM, Kim H, Lee WJ. Overestimated Oncologic Significance of Lymph Node Metastasis in G1 Nonfunctioning Neuroendocrine Tumor in the Left Side of the Pancreas. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e1404. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Partelli S, Gaujoux S, Boninsegna L, Cherif R, Crippa S, Couvelard A, Scarpa A, Ruszniewski P, Sauvanet A, Falconi M. Pattern and clinical predictors of lymph node involvement in nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NF-PanNETs). JAMA Surg. 2013;148:932-939. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Nomura N, Fujii T, Kanazumi N, Takeda S, Nomoto S, Kasuya H, Sugimoto H, Yamada S, Nakao A. Nonfunctioning neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors: our experience and management. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009;16:639-647. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Kim MJ, Choi DW, Choi SH, Heo JS, Park HJ, Choi KK, Jang KT, Sung JY. Surgical strategies for non-functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Surg. 2012;99:1562-1568. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Kuo EJ, Salem RR. Population-level analysis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors 2 cm or less in size. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:2815-2821. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 146] [Cited by in RCA: 173] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Kishi Y, Shimada K, Nara S, Esaki M, Hiraoka N, Kosuge T. Basing treatment strategy for non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors on tumor size. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:2882-2888. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Conrad C, Kutlu OC, Dasari A, Chan JA, Vauthey JN, Adams DB, Kim M, Fleming JB, Katz MH, Lee JE. Prognostic Value of Lymph Node Status and Extent of Lymphadenectomy in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Confined To and Extending Beyond the Pancreas. J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;20:1966-1974. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Jiang Y, Jin JB, Zhan Q, Deng XX, Shen BY. Impact and Clinical Predictors of Lymph Node Metastases in Nonfunctional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128:3335-3344. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Drymousis P, Raptis DA, Spalding D, Fernandez-Cruz L, Menon D, Breitenstein S, Davidson B, Frilling A. Laparoscopic versus open pancreas resection for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB (Oxford). 2014;16:397-406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | DiNorcia J, Lee MK, Reavey PL, Genkinger JM, Lee JA, Schrope BA, Chabot JA, Allendorf JD. One hundred thirty resections for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: evaluating the impact of minimally invasive and parenchyma-sparing techniques. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:1536-1546. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |