Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Oncol. Mar 24, 2022; 13(3): 168-185
Published online Mar 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i3.168
Published online Mar 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i3.168
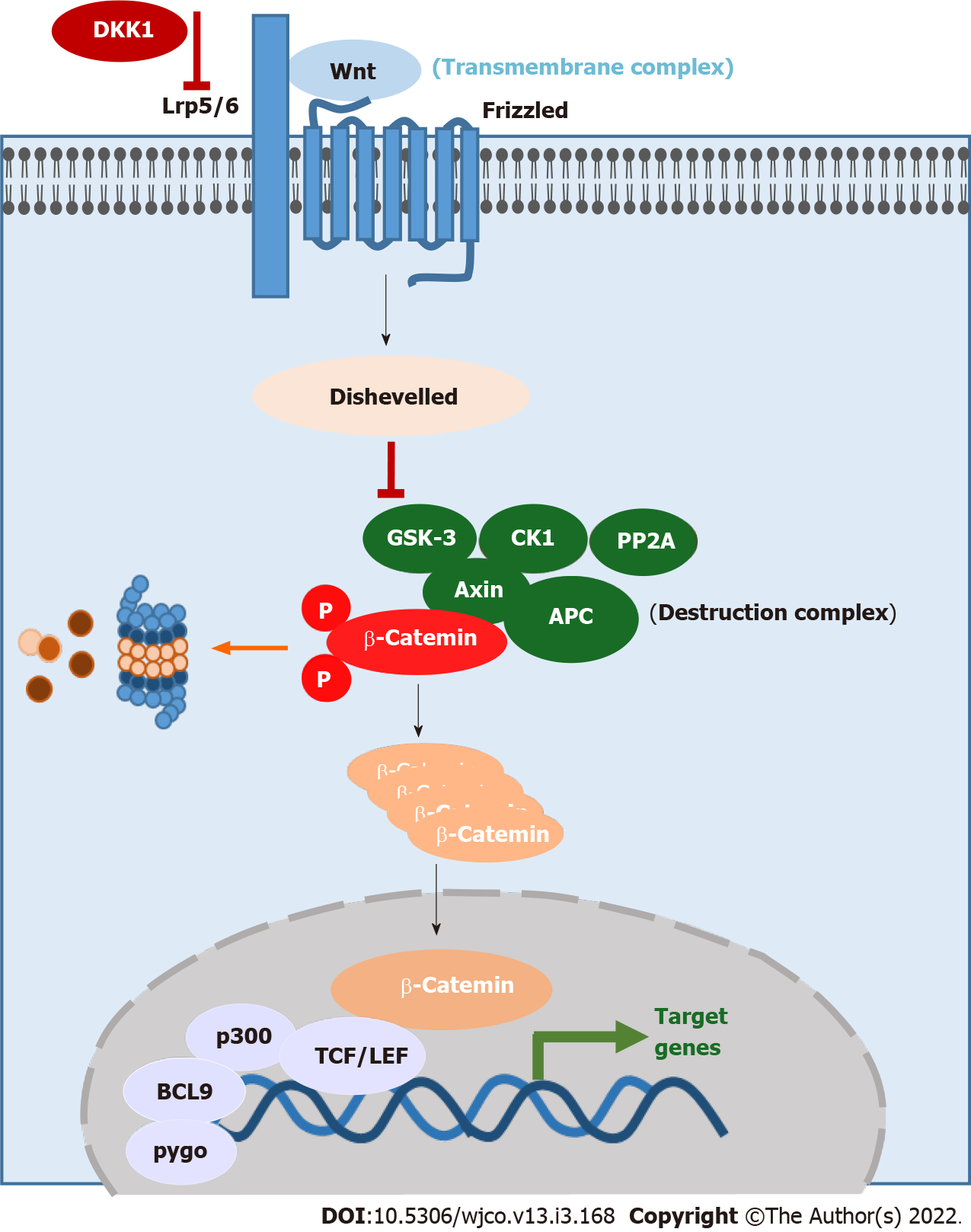
Figure 1 Wnt signaling pathway.
Activated Wnt signaling pathway: Wnt ligand binds to the transmembrane complex and activates Disheveled, which turns down the destruction complex. β-catenin accumulates in the cytoplasm and translocates in the nucleus, where it acts with several cofactors as a transcription factor. Inactivated Wnt signaling pathway: β-catenin is phosphorylated by the destruction complex and gets degraded. Dkk1: Dickkopf 1; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase-3; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; PP2A: Protein phosphatase 2A; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; BCL9: B-cell lymphoma 9.
- Citation: Swoboda J, Mittelsdorf P, Chen Y, Weiskirchen R, Stallhofer J, Schüle S, Gassler N. Intestinal Wnt in the transition from physiology to oncology. World J Clin Oncol 2022; 13(3): 168-185
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v13/i3/168.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i3.168