Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 10, 2014; 5(5): 806-823
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.806
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.806
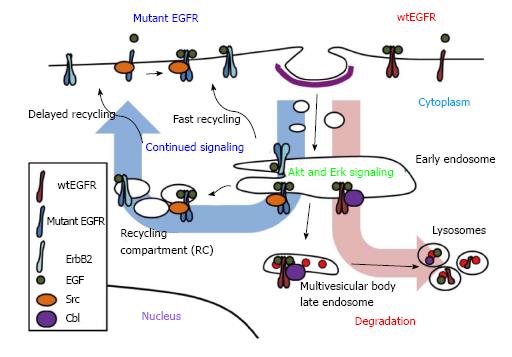
Figure 1 Model of mutant epidermal growth factor receptor endocytic trafficking.
Upon ligand binding, activated wtEGFR becomes internalized and localized to endosomes. Internalized EGFR has been linked to Erk and Akt activation. Depending on type of ligand bound, ligand concentration, dimerization partner, mutational statuses and/or availability of other regulators, wtEGFR may recycle to cell surface or be sorted to lysosomes. EGFR bound to EGF is mostly targeted for lysosomes, where it becomes degraded. Sorting of ligand-induced wtEGFR to lysosome is mediated by E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl which remains attached to receptor throughout endocytosis. Mutant EGFR, however, escapes ligand-induced downregulation through decreased interaction with Cbl, enhanced dimerization with ErbB2, which prefers recycling pathway, and/or constitutive interaction with Src, which antagonizes Cbl. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
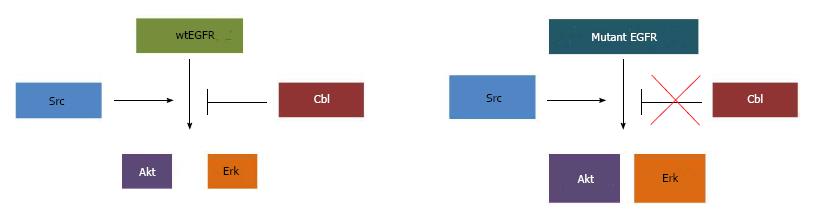
Figure 2 Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor vs wt-epidermal growth factor receptor signaling.
While wtEGFR signaling to Akt and Erk is subjected to Cbl-mediated degradation, mutant EGFR cooperates with Src to exaggerate signaling through downstream effectors. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
- Citation: Chung BM, Tom E, Zutshi N, Bielecki TA, Band V, Band H. Nexus of signaling and endocytosis in oncogenesis driven by non-small cell lung cancer-associated epidermal growth factor receptor mutants. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(5): 806-823
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i5/806.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.806