Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Oct 10, 2014; 5(4): 693-704
Published online Oct 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.693
Published online Oct 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.693
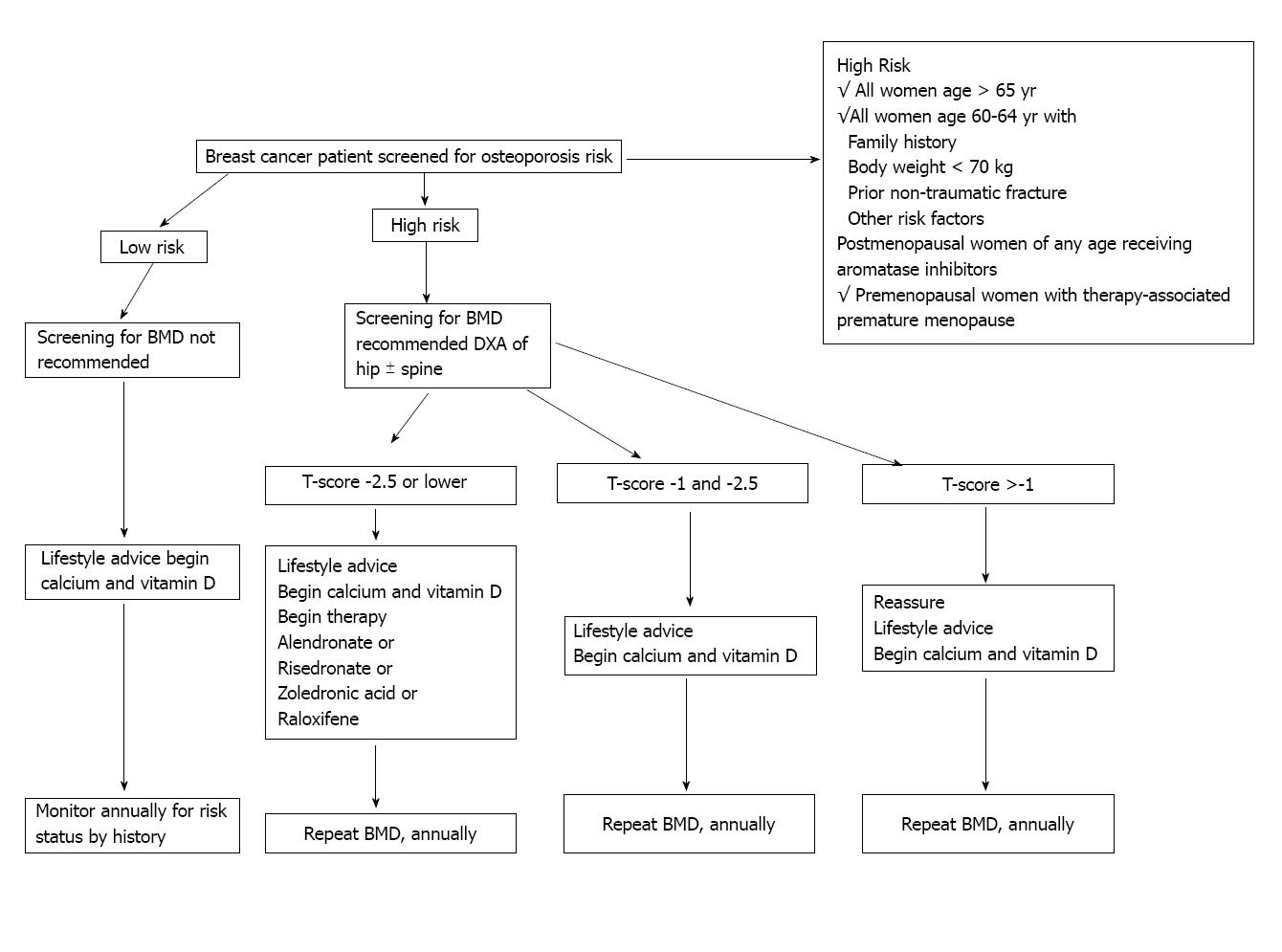
Figure 1 Recommended management strategy for patients with diagnosed nonmetastatic breast cancer[97].
This management strategy is largely based on influence from results in non-breast cancer populations. BMD: Bone mass density; DEXA: Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry bone scan. Reprinted with permission. © (2003) American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
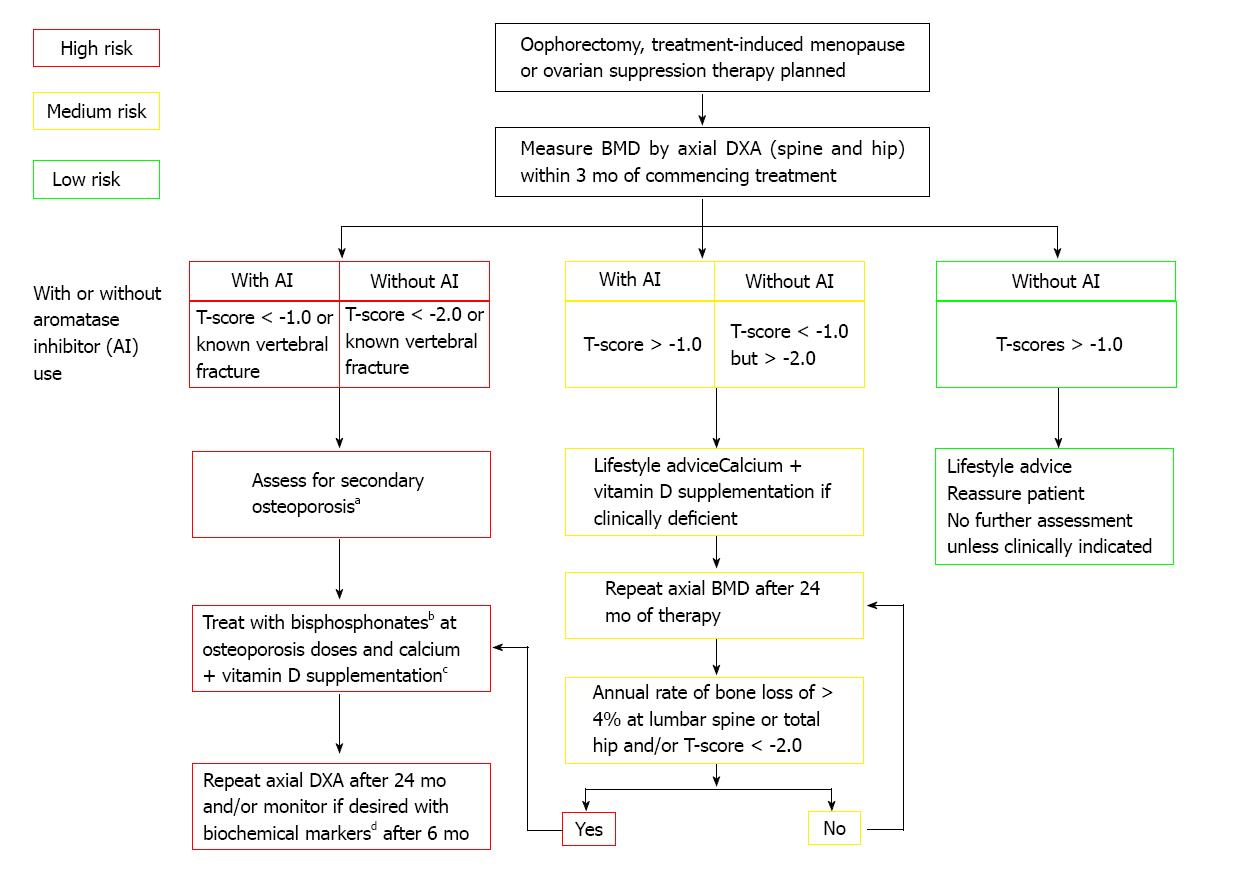
Figure 2 Adjuvant treatment associated with ovarian suppression/failure with or without concomitant aromatase inhibitor use in women who experience premature menopause[92].
aErythrocyte sedimentation rate, full blood count, bone and liver function (calcium phosphate, alkaline phosphatase, albumin, AST/γGT), serum creatinine, endomysial antibodies, serum thyroid stimulating hormone; bAlendronate 70 mg per week, risedronate 35 mg per week, ibandronate (150 mg po monthly or 3 mg iv 3-monthly), zoledronic acid 4 mg iv 6-monthly; cTo be given as ≥ 1 g of calcium + ≥ 800 IU of vitamin D; dBiochemical markers such as serum C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen or urinary N-telopeptide of type I collagen. Reprinted with permission. © (2008) Elsevier.
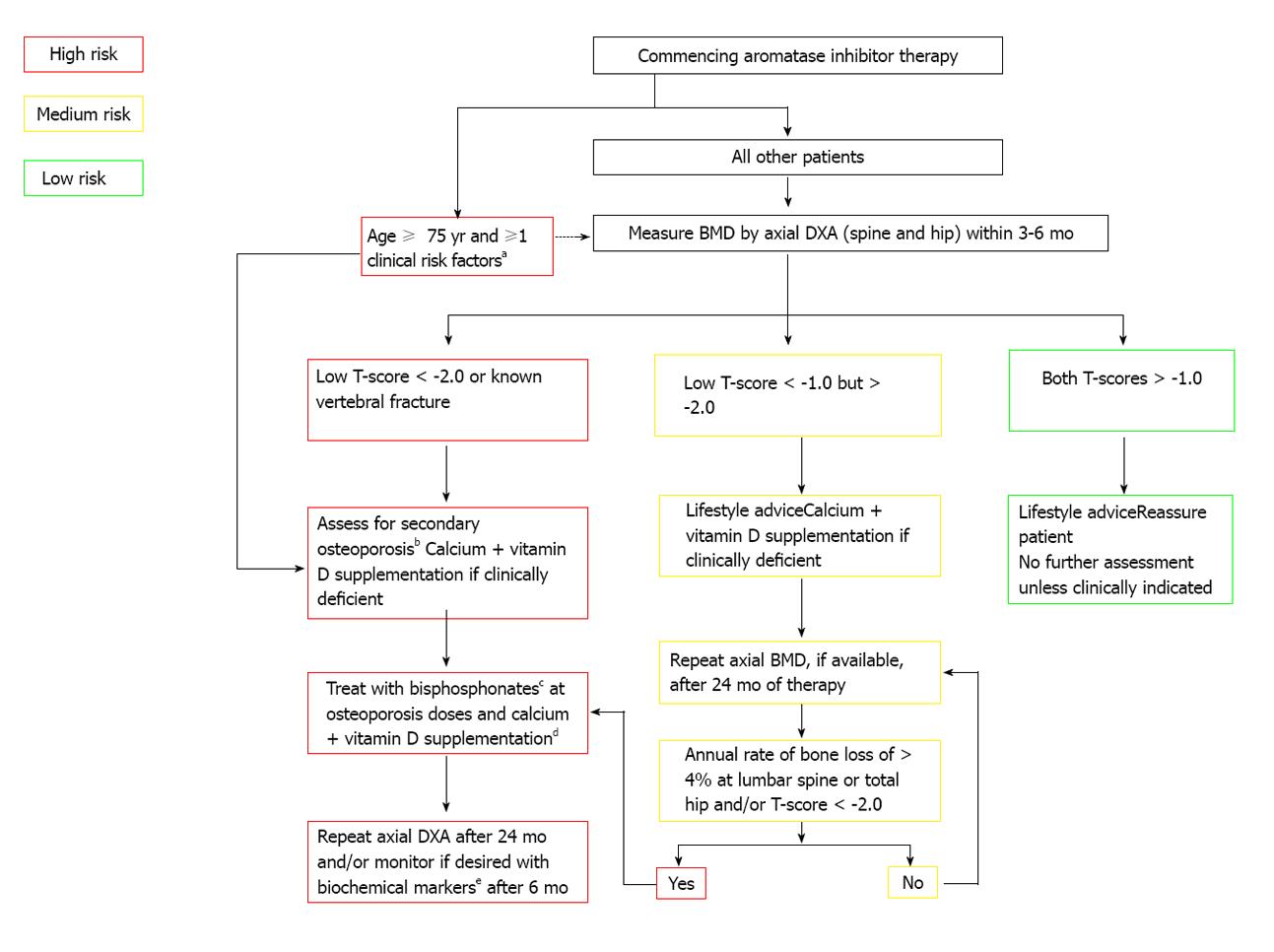
Figure 3 Postmenopausal adjuvant treatment with aromatase inhibitors[92].
aPrevious low-trauma fracture after age 50, parental history of hip fracture, alcohol intake of ≥ 4 units/day, diseases associated with secondary osteoporosis, prior corticosteroids for > 6 mo, low BMI (< 22); bErythrocyte sedimentation rate, full blood count, bone and liver function (calcium phosphate, alkaline phosphatase, albumin, AST/γGT), serum creatinine, endomysial antibodies, serum thyroid stimulating hormone; cAlendronate 70 mg per week, risedronate 35 mg per week, ibandronate (150 mg po monthly or 3 mg iv 3-monthly), zoledronic acid 4 mg iv 6-monthly; dTo be given as ≥ 1 g of calcium + ≥ 800 IU of vitamin D; eBiochemical markers such as serum C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen or urinary N-telopeptide of type I collagen. Reprinted with permission. © (2008) Elsevier.
- Citation: Casey PM, Faubion SS, MacLaughlin KL, Long ME, Pruthi S. Caring for the breast cancer survivor’s health and well-being. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(4): 693-704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i4/693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.693