Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 10, 2014; 5(3): 248-262
Published online Aug 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.248
Published online Aug 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.248
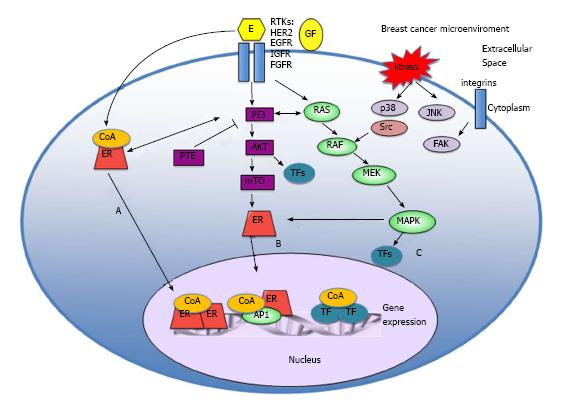
Figure 1 Estrogen receptor action at molecular level.
A: Ligand dependent activation: in classic estrogen signaling, ligand-bound ER activates gene expression-either through direct binding of dimeric ER to specific DNA response elements in complexes including co-activators, or function as a coregulator through protein - protein interactions with other transcription factors to facilitate binding to serum response elements and activation of transcription; B: Ligand independent activation: the ER can also be activated by ligand independent fashion, as a consequence of signaling events downstream of membrane receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs); C: Non-genomic mechanisms: signaling can be mediated through non-genomic mechanisms by ER that is localized at the cell membrane or in the cytoplasm. ER: Estrogen receptor; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; FGFR: Fibroblast growth factor receptor; IGF-1R: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
- Citation: Zhao M, Ramaswamy B. Mechanisms and therapeutic advances in the management of endocrine-resistant breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(3): 248-262
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i3/248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.248