Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 10, 2012; 3(6): 82-91
Published online Jun 10, 2012. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v3.i6.82
Published online Jun 10, 2012. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v3.i6.82
Figure 1 Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha mRNA expression level determination via semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction in the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep3B under aerobic and hypoxic conditions (0.
1% O2 for 24 h) without or with cytokine stimulation (interleukin-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha or transforming growth factor-beta) under both aeration conditions examined. β-actin was used as a loading control. Bar graphs show band intensities after densitometric evaluation. Representative experiment of three different experiments. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha.
Figure 2 Western blotting analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha protein expression under hypoxia or cytokine stimulation (interleukin-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha or transforming growth factor-beta) in nuclear extracts of the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep3B.
Treatment with 100 μmol/L DFO under aerobic conditions served as a positive control. One representative Western blotting of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) protein with β-tubulin as a loading control and quantification of the results via densitometry. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta.
Figure 3 Western blotting of carbonic anhydrase 9 protein expression in whole-cell lysates of the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep3B during hypoxia or cytokine stimulation (interleukin-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha or transforming growth factor-beta) with densitometric quantification of carbonic anhydrase 9 protein expression and β-actin as loading control.
Representative experiment of three different experiments. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; CA9: Carbonic anhydrase 9.
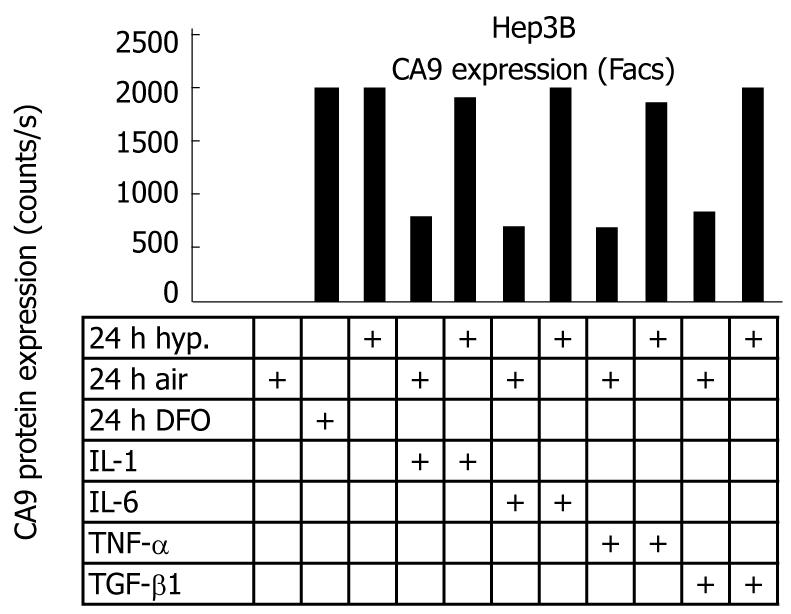
Figure 4 Representative carbonic anhydrase 9 flow cytometry with suspensions of known aerobic and hypoxic cell populations (0.
1% O2 for 24 h) or cytokine stimulation under both aeration conditions. Suspensions of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines during hypoxia or cytokine stimulation [interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) or transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)] were incubated with the anti-carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) antibody M75 and a fluorescein-isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody.
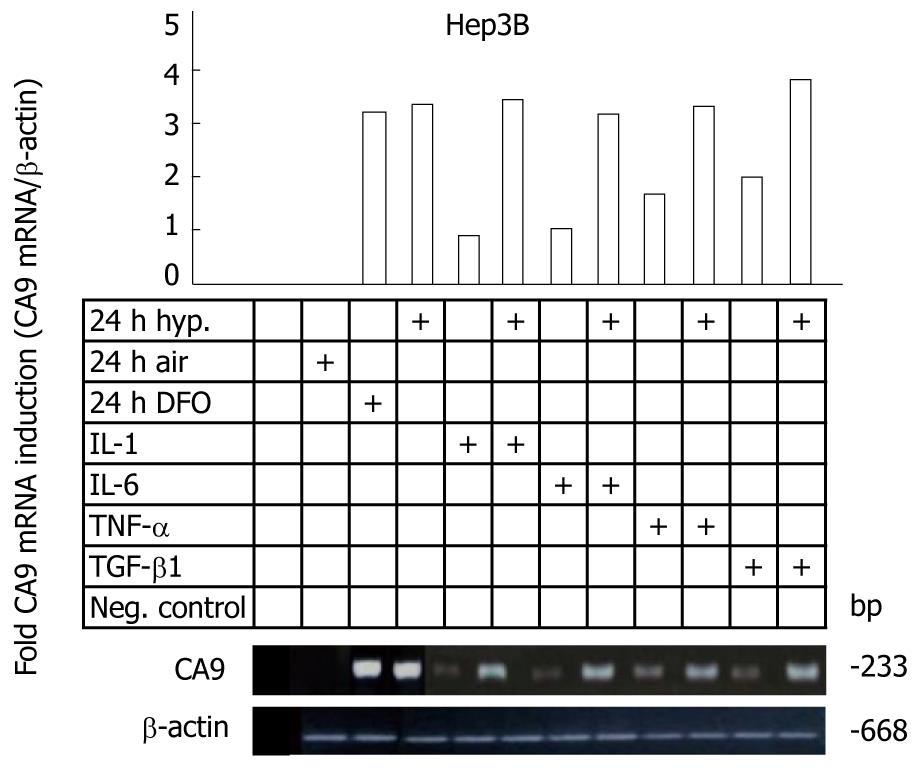
Figure 5 Regulation of hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase 9 mRNA level via semiquantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction in vitro in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep3B under aerobic and hypoxic conditions (0.
1% O2 for 24 h) with or without cytokine stimulation (interleukin-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha or transforming growth factor-beta) under both aeration conditions and β-actin as loading control. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; CA9: Carbonic anhydrase 9.
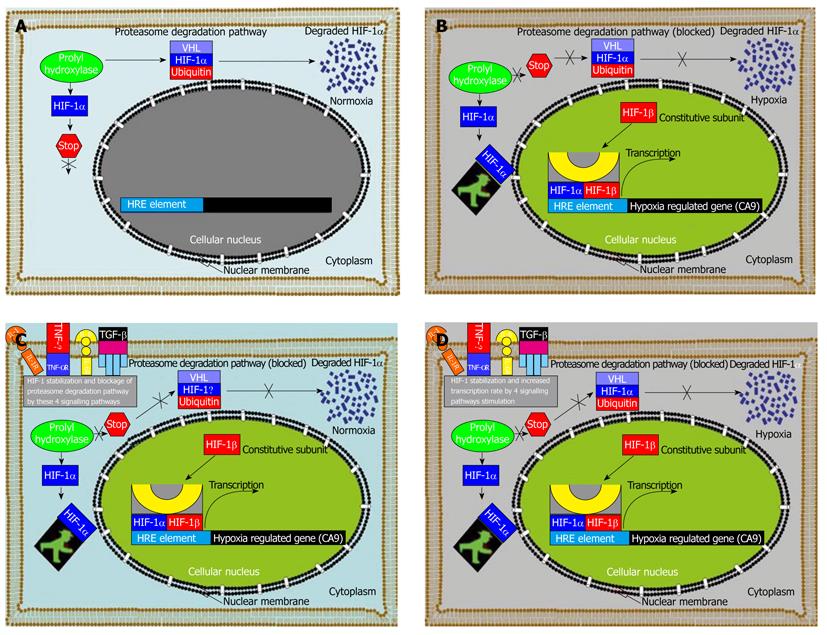
Figure 6 Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha induced regulation of hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase 9 expression in human tumor cells without or with stimulation.
A: Under normoxic conditions in the tumour cell microenvironment, hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) is rapidly degraded via the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor gene product (pVHL) - mediated proteasome pathway; B: Following a shift in tumour environment aeration conditions from normoxic to hypoxic aeration conditions, HIF-1α subunit becomes stable and translocates into the cellular nucleus and interacts with co-activators of which its transcription machinery consists if e.g. p300/CBP to modulate the transcriptional activity of numerous hypoxia inducible genes, such as carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) in our case, and about 61 other hypoxia induced genes[51]; C: When the cells are stimulated under normoxia with either interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) or transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), the transcription factor HIF-1α subunit becomes stable despite the oxygenation status of the tumour environment and translocates into the cellular nucleus and interacts with co-activators of which its transcription machinery consists of e.g. p300/CBP to modulate the transcriptional activity of CA9 with a similar expression to that under hypoxia; D: Experimental stimulation with either IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α or TGF-β1 under hypoxia increases the CA9 level to almost double the expression rate under hypoxic conditions with the stimulation of these cytokines due to increased HIF-1α translocation into the nucleus and increased binding rate to the hypoxia response element element within the CA9 promoter region.
-
Citation: Kockar F, Yildrim H, Sagkan RI, Hagemann C, Soysal Y, Anacker J, Hamza AA, Vordermark D, Flentje M, Said HM. Hypoxia and cytokines regulate carbonic anhydrase 9 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
in vitro . World J Clin Oncol 2012; 3(6): 82-91 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v3/i6/82.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v3.i6.82