Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Oncol. Jul 10, 2011; 2(7): 299-302
Published online Jul 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i7.299
Published online Jul 10, 2011. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i7.299
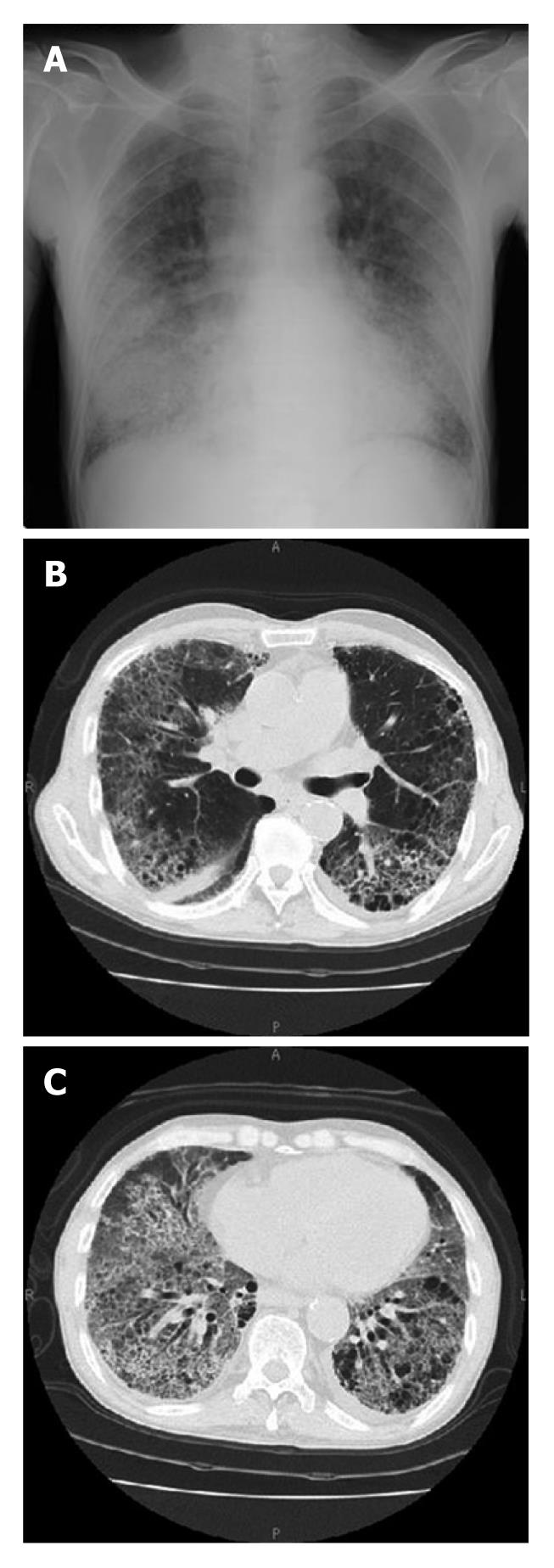
Figure 1 Chest radiograph and computed tomography findings on admission.
Chest radiograph (A) showed bilateral interstitial shadows mainly in the middle to lower lung field on both sides. Chest computed tomography (B, C) revealed diffuse interstitial lesions with thickening of the alveolar septa, bilateral airspace consolidation, and ground glass opacity.
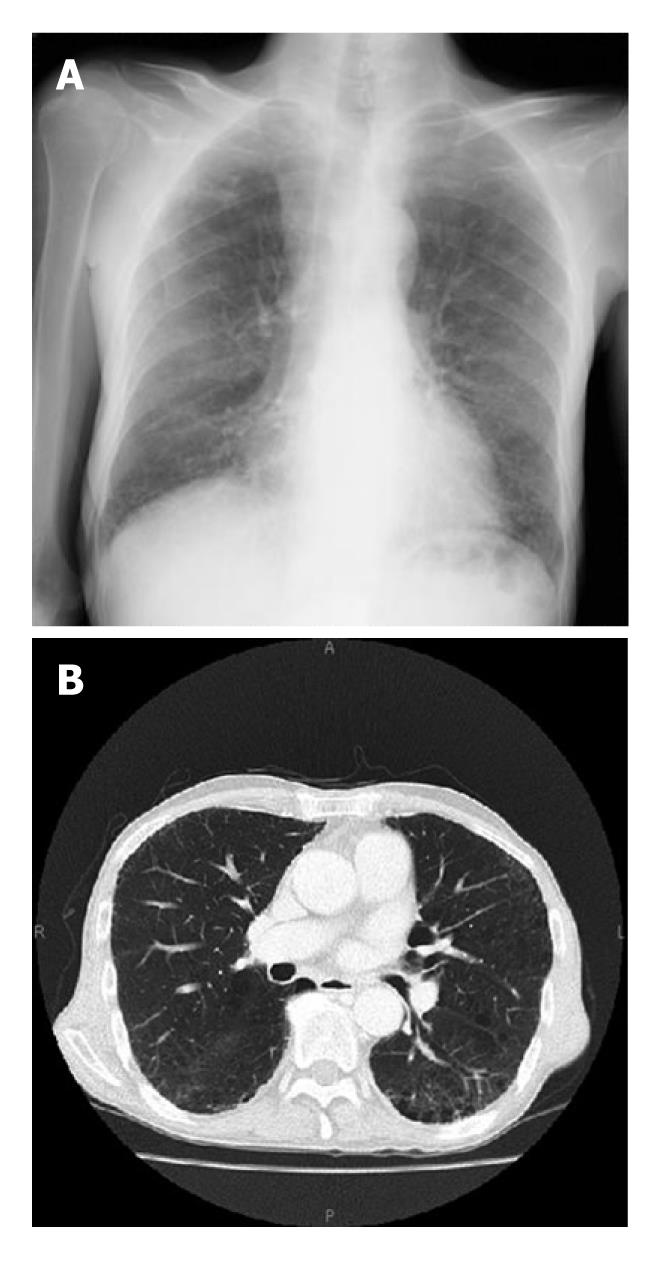
Figure 2 Chest radiograph and computed tomography findings 16 d after initiating steroid therapy.
Chest radiograph (A) and computed tomography (B) findings were substantially improved 16 d after initiating steroid pulse therapy.
- Citation: Yamane H, Kinugawa M, Umemura S, Shiote Y, Kudo K, Suwaki T, Kamei H, Takigawa N, Kiura K. An oral fluoropyrimidine agent S-1 induced interstitial lung disease: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2011; 2(7): 299-302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v2/i7/299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v2.i7.299