Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Mar 24, 2025; 16(3): 101766
Published online Mar 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.101766
Published online Mar 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.101766
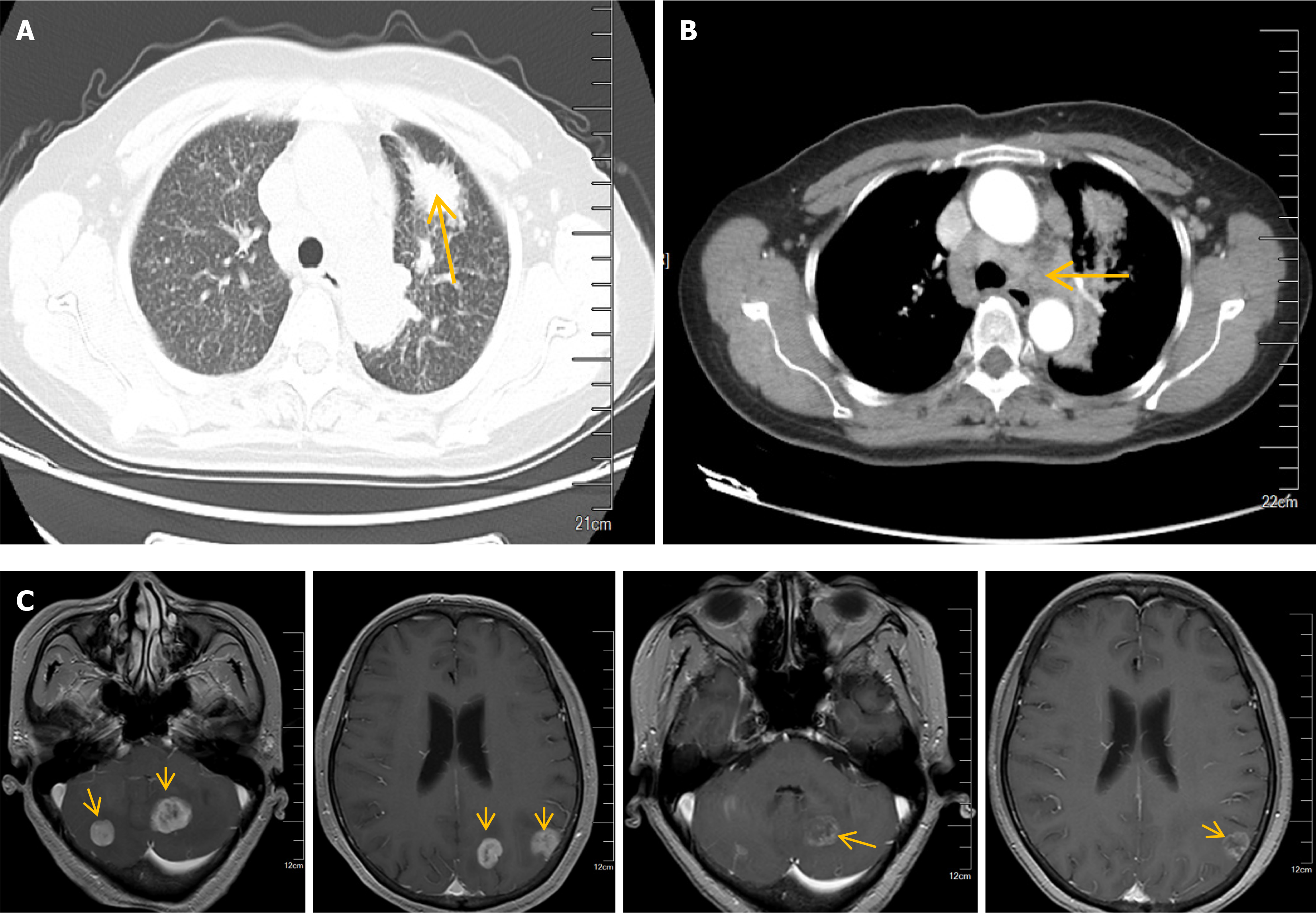
Figure 1 Lung adenocarcinoma with lung hilum, lymph nodes in mediastinum and brain metastases.
A: A mass in the left upper lobe (arrow) with blurred boundaries; B: Enlarged lymph nodes (arrow) in both pulmonary hilum and mediastinum; C: Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain suggested multiple abnormal signals (arrows) in the left occipital lobe, bilateral parietal lobes, bilateral cerebellum, and cerebellar vermis.
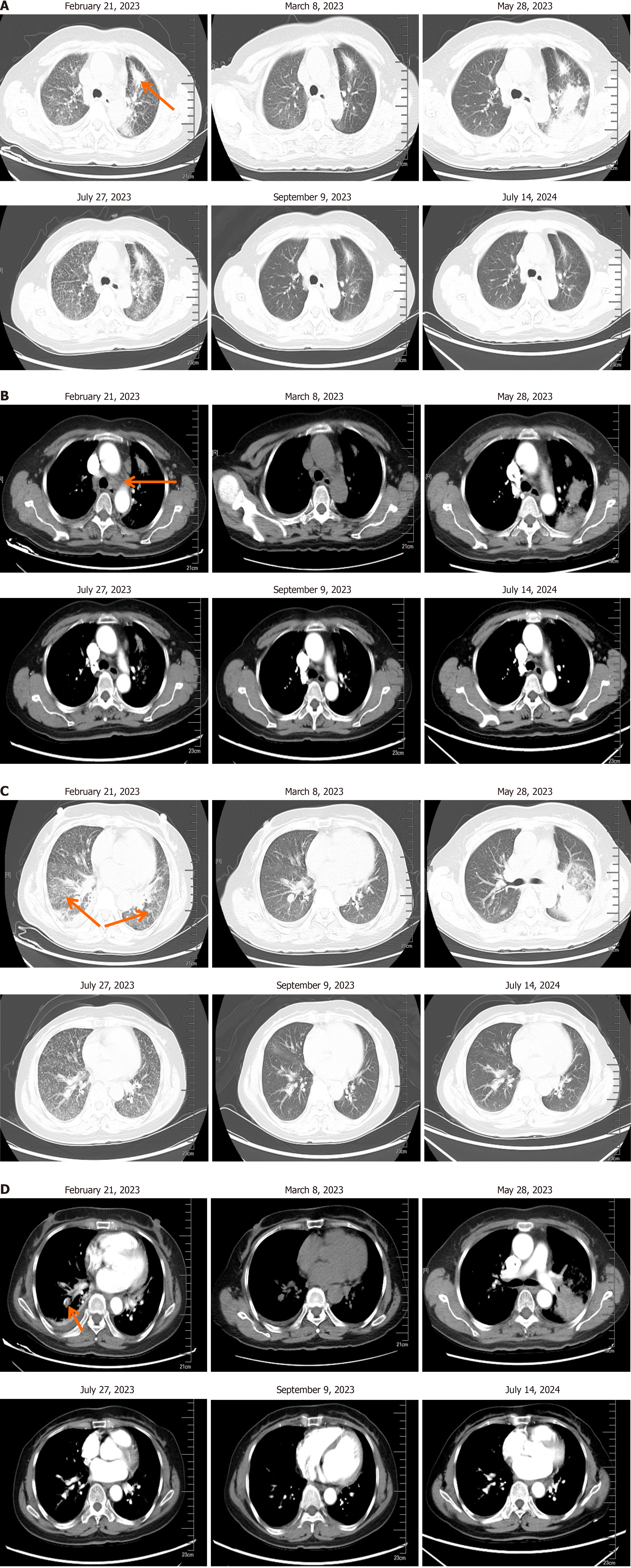
Figure 2 Changes in lung lesions before and after medication.
A: Changes during the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma (arrow indicates the mass in the left upper lobe); B: Changes during the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma and mediastinal lymph node metastasis (arrow indicates enlarged lymph nodes); C: Inflammation in lung tissues (arrows). D: Pulmonary vasculature changes before and after medication, regular use of anticoagulant drugs and thrombosis disappearance (arrow indicates pulmonary vasculature).
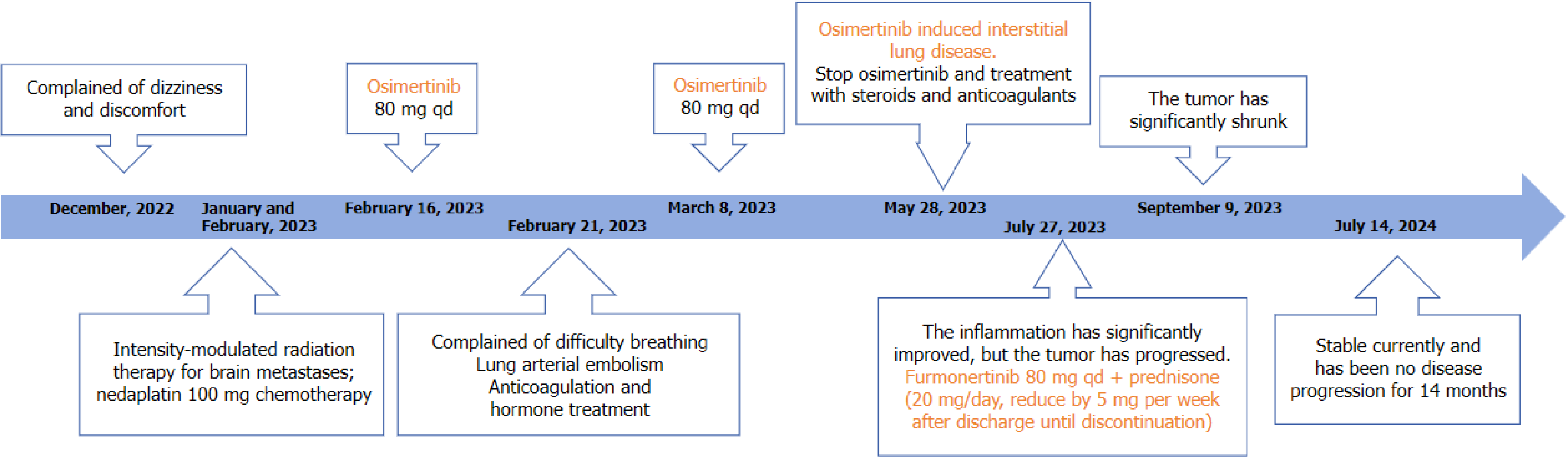
Figure 3 Treatment regimen.
qd: Per day.
- Citation: Wei FF, Zhang J, Jia Z, Yao ZC, Chen CQ. Furmonertinib re-challenge for epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinoma after osimertinib-induced interstitial lung disease: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(3): 101766
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i3/101766.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.101766