Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Mar 24, 2025; 16(3): 101686
Published online Mar 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.101686
Published online Mar 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.101686
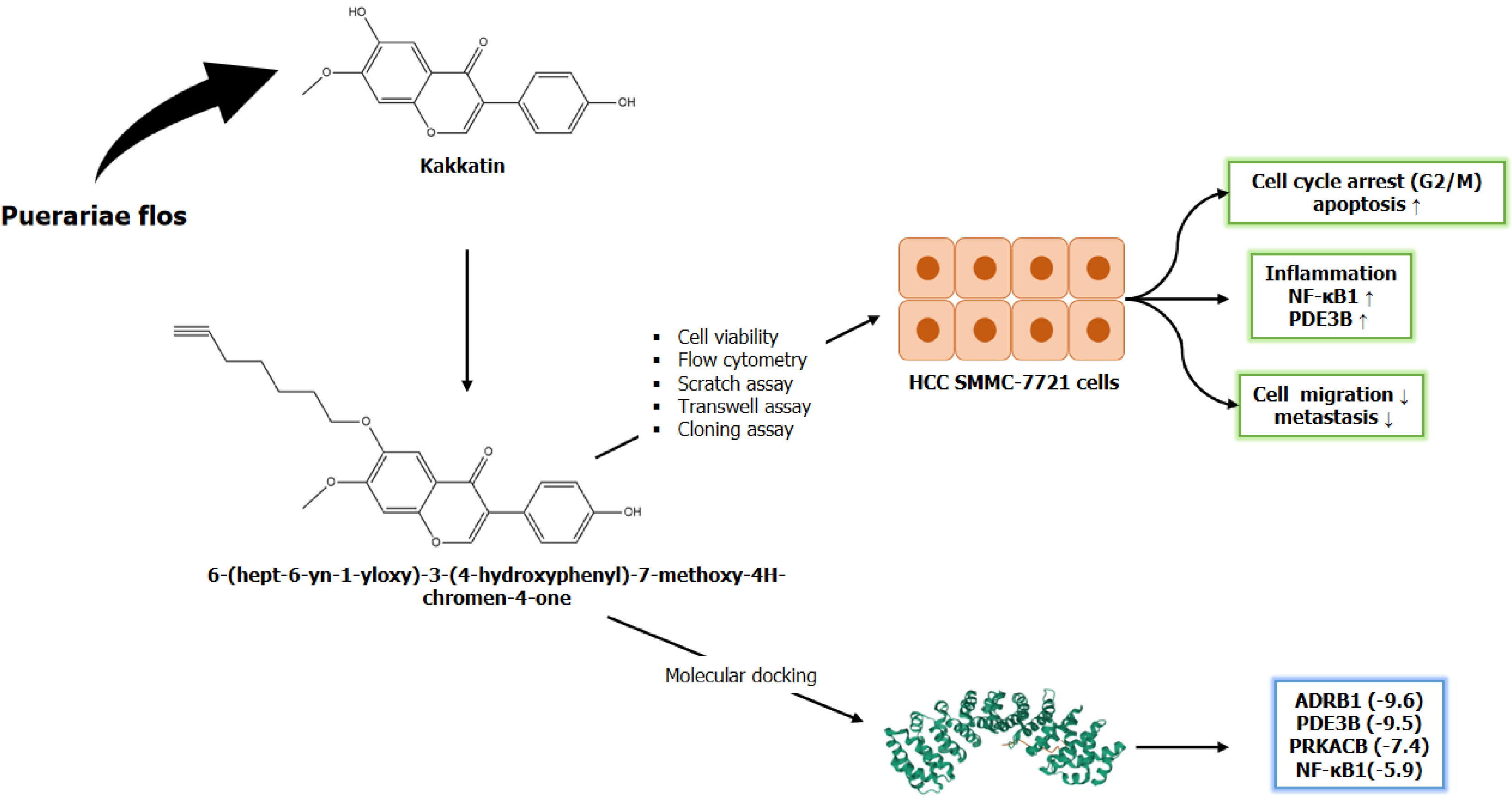
Figure 1 Intervention of 6-(hept-6-yn-1-yloxy)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-4H-chromen-4-one, a kakkatin derivative, induces the activation of the apoptotic pathway and inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and metastasis in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SMMC-7221.
A kakkatin derivative formed by the introduction of a competing group, hept-6-yn-1-yl ethane sulphonate, to the phenolic hydroxyl group of the kakkatin structure was explored for its antitumor activity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) SMMC-7221 cells. Binding energy (kcal/mol) of 6-(hept-6-yn-1-yloxy)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-4H-chromen-4-one with phosphodiesterase 3B (PDE3B), adrenoceptor beta 1 (ADRB1), protein kinase cyclic adenosine 3,5-monophosphate-activated catalytic subunit beta (PRKACB), and nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 (NF-κB1) was checked by molecular docking. Real-time reverse transcriptase-PCR was performed to validate upregulation of NF-κB1 and PDE3B expression, which in turn inhibit cancer cell invasion, migration, and HCC progression.
- Citation: Chahal S, Patial V. Therapeutic potential of kakkatin derivatives against hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(3): 101686
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i3/101686.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.101686