Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2024; 15(12): 1507-1513
Published online Dec 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i12.1507
Published online Dec 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i12.1507
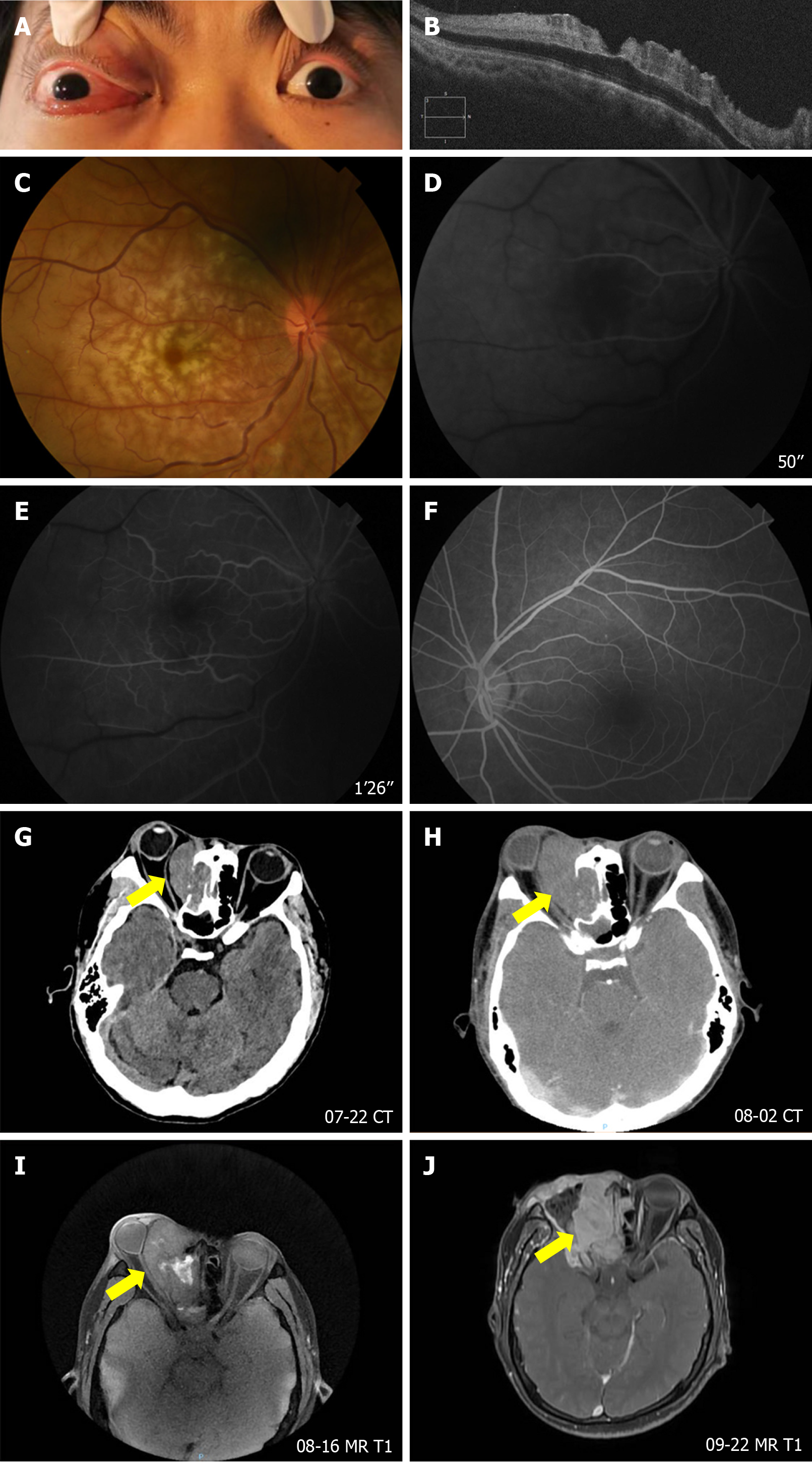
Figure 1 Imaging examination.
A: The patient exhibited notable protrusion of the right eyeball; B: Optical coherence tomography revealed diffuse edema and thickening of the inner retinal layer in the right eye; C: Fundus examination revealed twisted retinal blood vessels, gray-white retinal edema, and a cherry-red spot in the macula of the right eye; D and E: Fundus fluorescein angiography revealed a significant delay in retinal arterial and venous filling in the right eye, indicative of central retinal artery occlusion; F: There was no obvious abnormality in fundus fluorescein angiography of the left eye; G and H: Computed tomography revealed a soft tissue density shadow and outward protrusion in the right sinus-orbital-frontal region, encroaching upon the right medial rectus muscle and optic nerve, with progressive enlargement over time; I: The first postoperative enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed an irregular signal shadow on the right side with indistinct boundaries; T1-weighted image (T1WI) demonstrated mixed high signal intensity; J: The second postoperative enhanced MRI revealed the absence of the right eyeball and an irregular mixed T1WI signal shadow, with an expanded lesion range compared with previous findings. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; CT: Computed tomography.
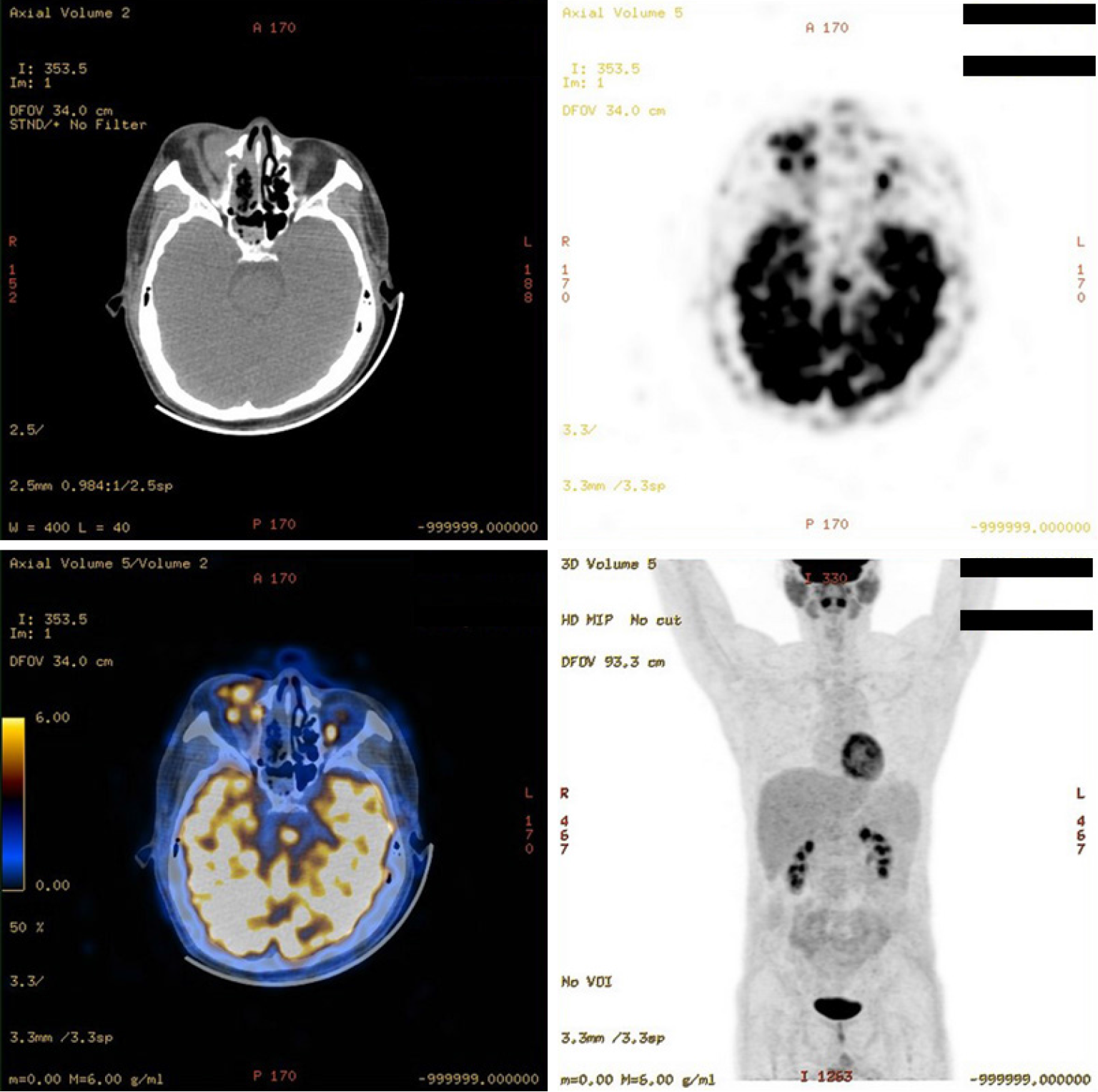
Figure 2 Positron emission tomography/computed tomography examination.
A right orbital and frontal lesion demonstrating increased glucose metabolism had invaded the local frontal bone as well as part of the right residual ethmoidal orbital plate. A nodule in the right residual ethmoidal sinus, also indicating heightened glucose metabolism, was suspected to be a residual tumor. No significant increases in fluorodeoxyglucose metabolism were detected in other areas of the body.
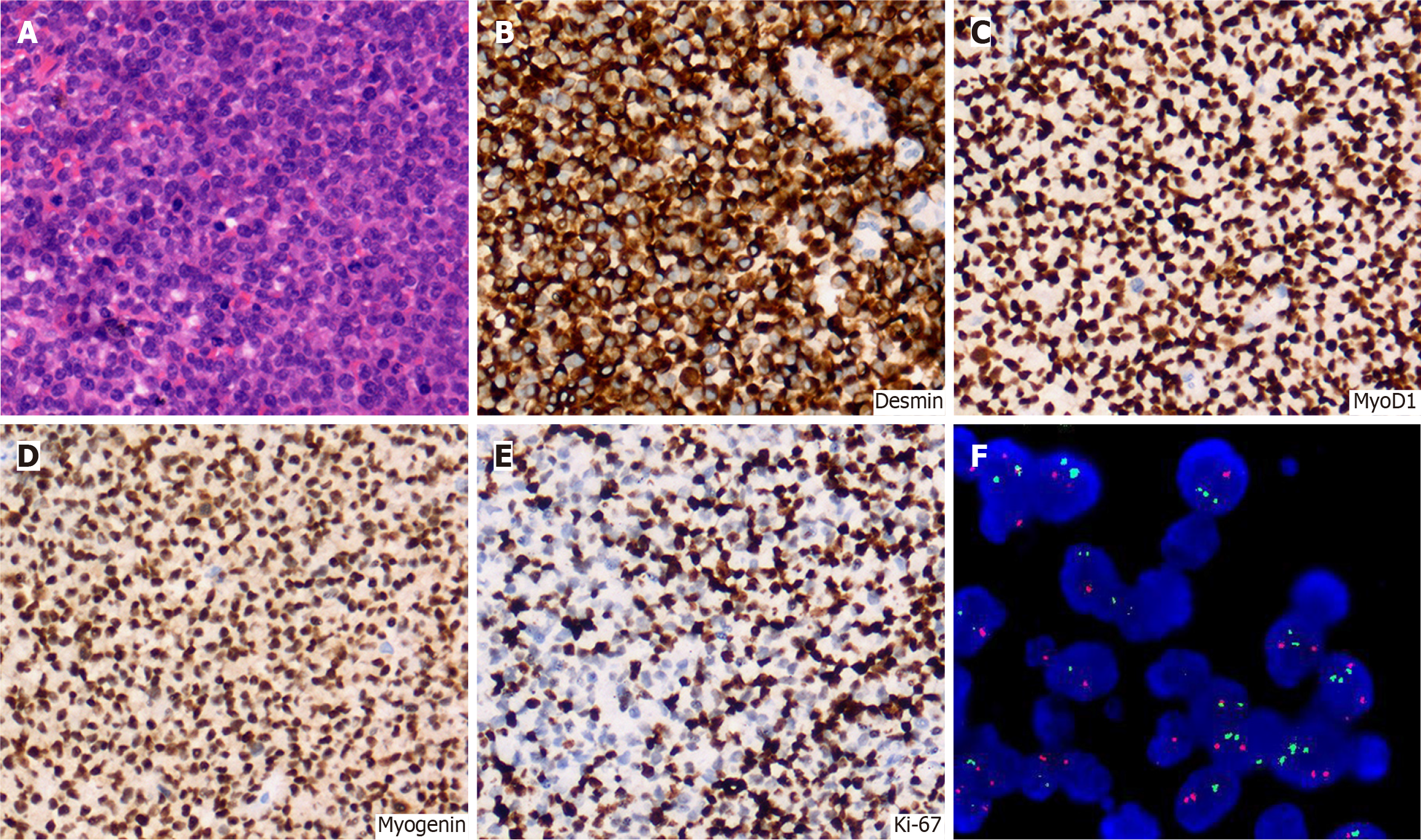
Figure 3 Pathological examination.
A: Histopathological biopsy revealed small blue round cells; B: The immunohistochemistry results were positive for desmin; C-E: MyoD1 (C), myogenin (D) and Ki-67 (E); F: Fluorescence in situ hybridization confirmed the presence of EWSR1 gene breakage.
- Citation: Ma Y, Jia B, He XJ, Cai YX, Chen JY, Zhong JX. Orbital and sinus rhabdomyosarcoma with concurrent central retinal artery occlusion: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(12): 1507-1513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i12/1507.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i12.1507