Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2024; 15(12): 1501-1506
Published online Dec 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i12.1501
Published online Dec 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i12.1501
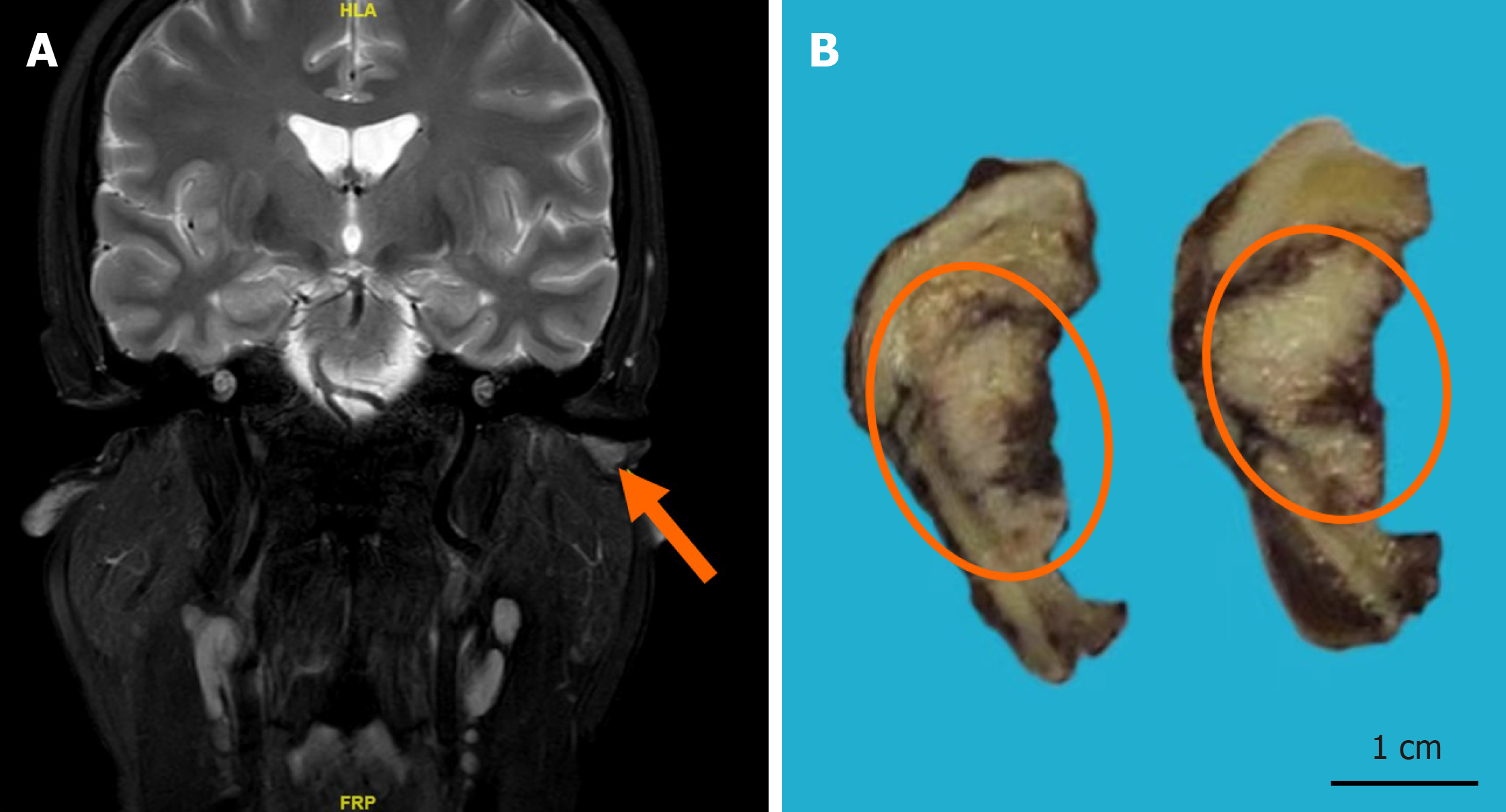
Figure 1 The magnetic resonance imaging and macroscopic view of the tumor.
A: magnetic resonance enhanced scan of the inner ear canal showing a space-occupying lesion in the left external auditory canal (orange arrow); B: Macroscopic view of the tumor (orange circle).
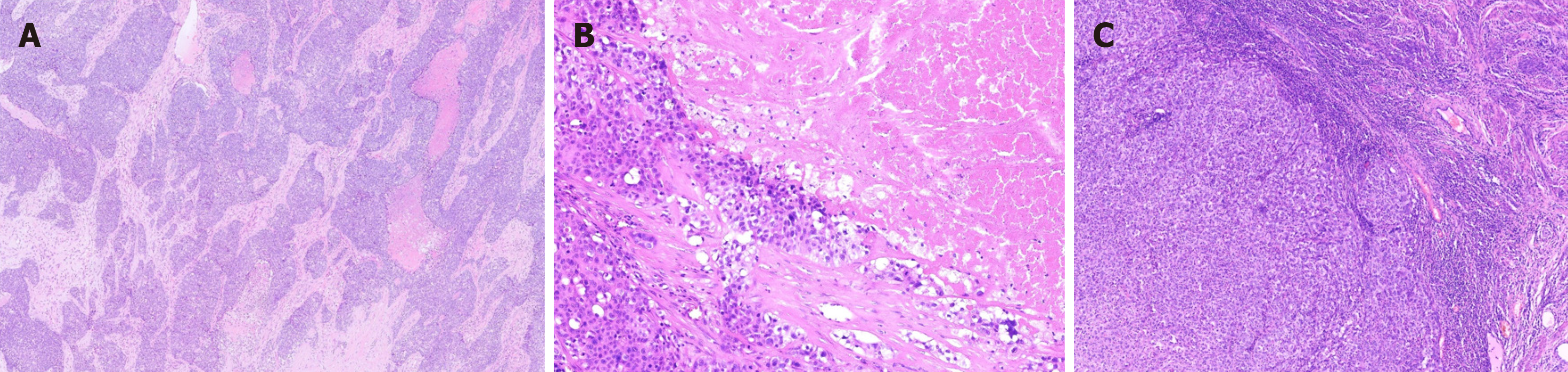
Figure 2 Histological examination of the tumor.
A: Histological analysis showed the tumor manifested as an endophytic papillary carcinoma resembling transitional epithelium with inverted nest-like proliferation patterns; B: The basal cells exhibited fence-like arrangements, interspersed with extensive areas of necrosis; C: Inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils, were considerably present in both the epithelial and stromal layers.
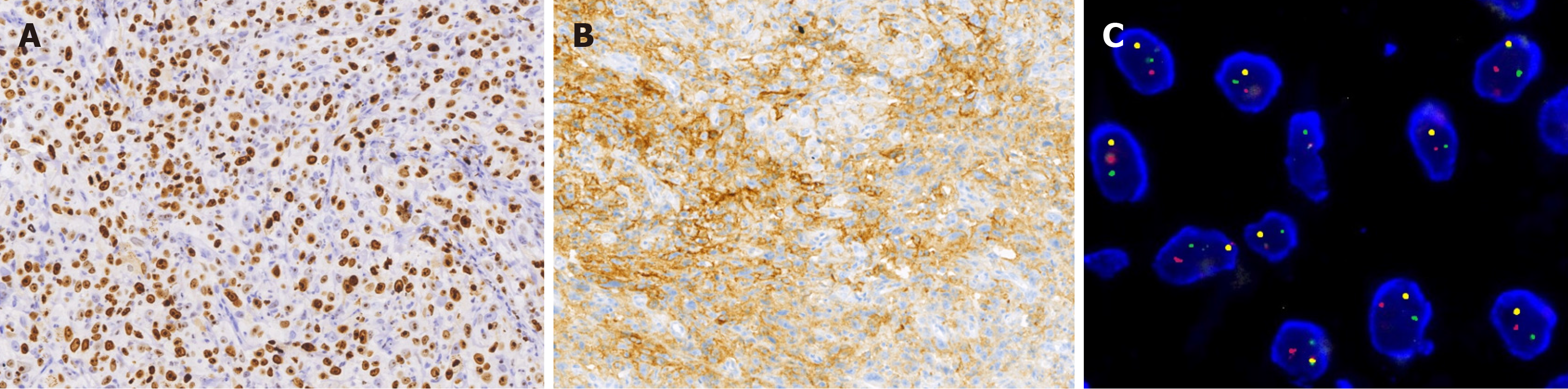
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining and fluorescence in situ hybridization testing of the tumor.
A: Immunohistochemical staining showing tumor cells positive for AFF2 (EnVision method, medium magnification); B: Immunohistochemical staining showing tumor cells positive for programmed death-ligand 1 (EnVision method, medium magnification); C Fluorescence in situ hybridization testing revealing disruption within the DEK gene structure.
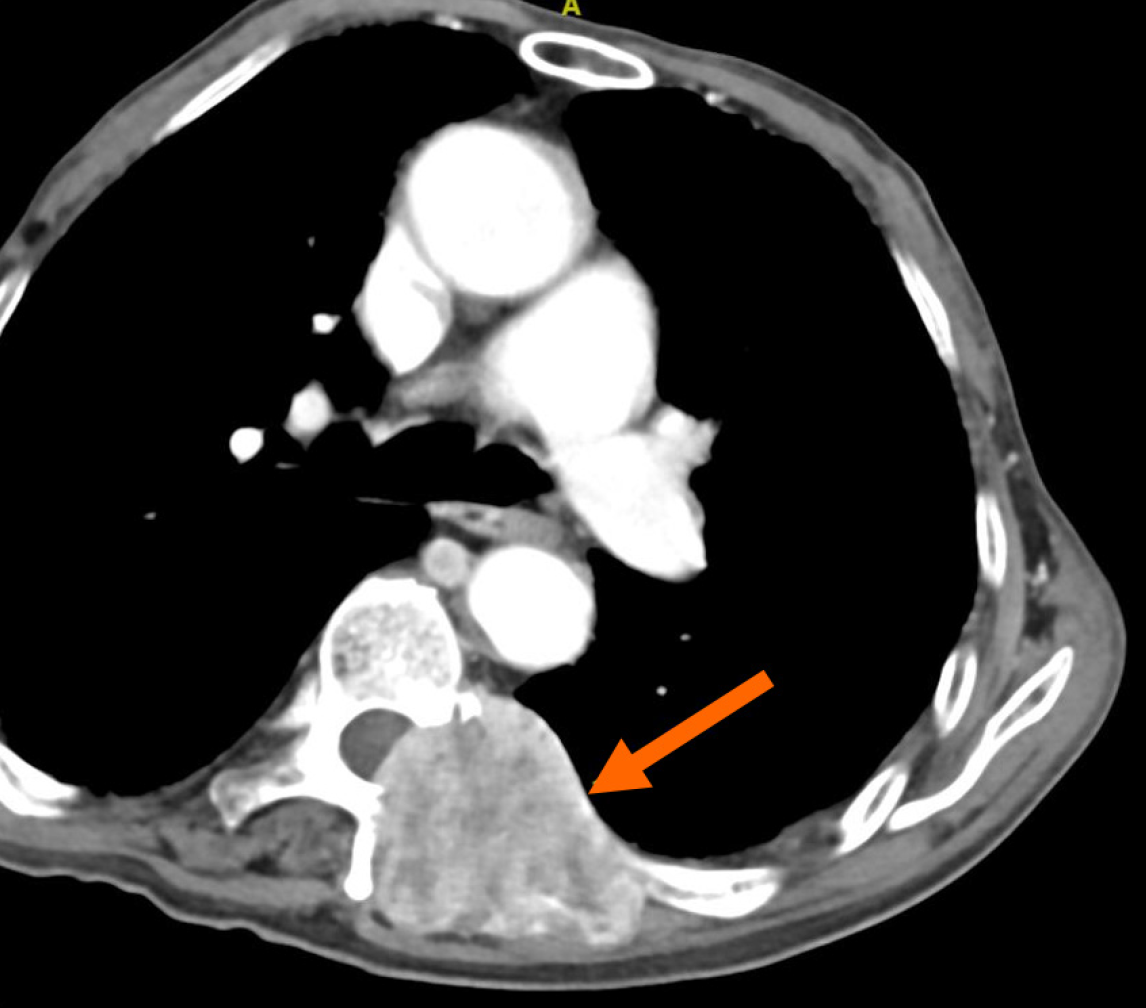
Figure 4 Computed tomography scan of metastatic lesions.
The computed tomography scan shows thoracic vertebral metastatic lesions (orange arrow).
- Citation: Sun YW, Zhou Y, Liu XY, Shen DH. DEK::AFF2 fusion-associated middle ear non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(12): 1501-1506
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i12/1501.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i12.1501