Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Oncol. Mar 24, 2023; 14(3): 117-130
Published online Mar 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i3.117
Published online Mar 24, 2023. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i3.117
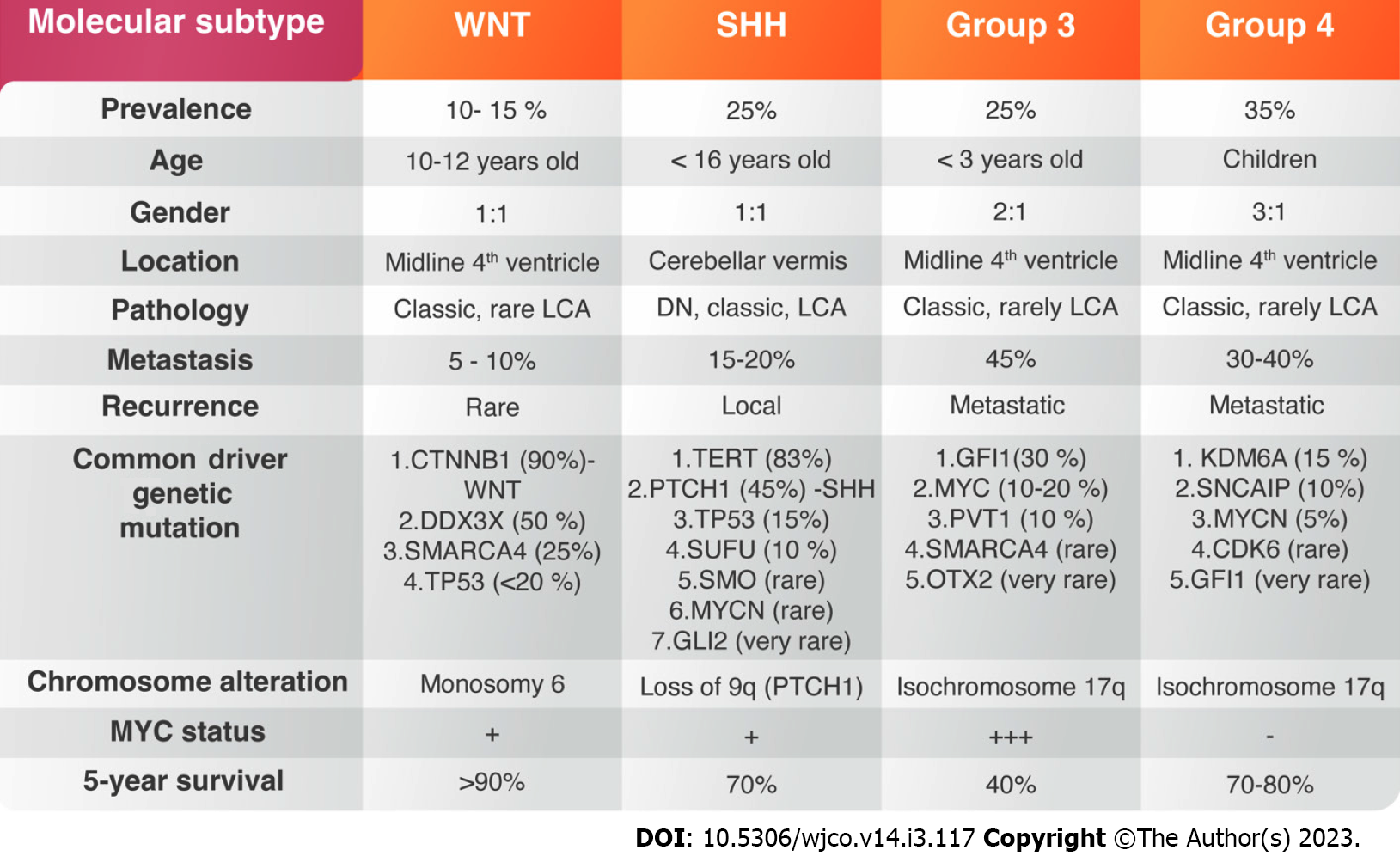
Figure 1 Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma based on 2021 World Health Organization classification of central nervous system tumours.
SHH: Sonic-hedgehog; MYC: Myelocytomatosis oncogene; LCA: Life cycle assessment; WNT: Wingless.
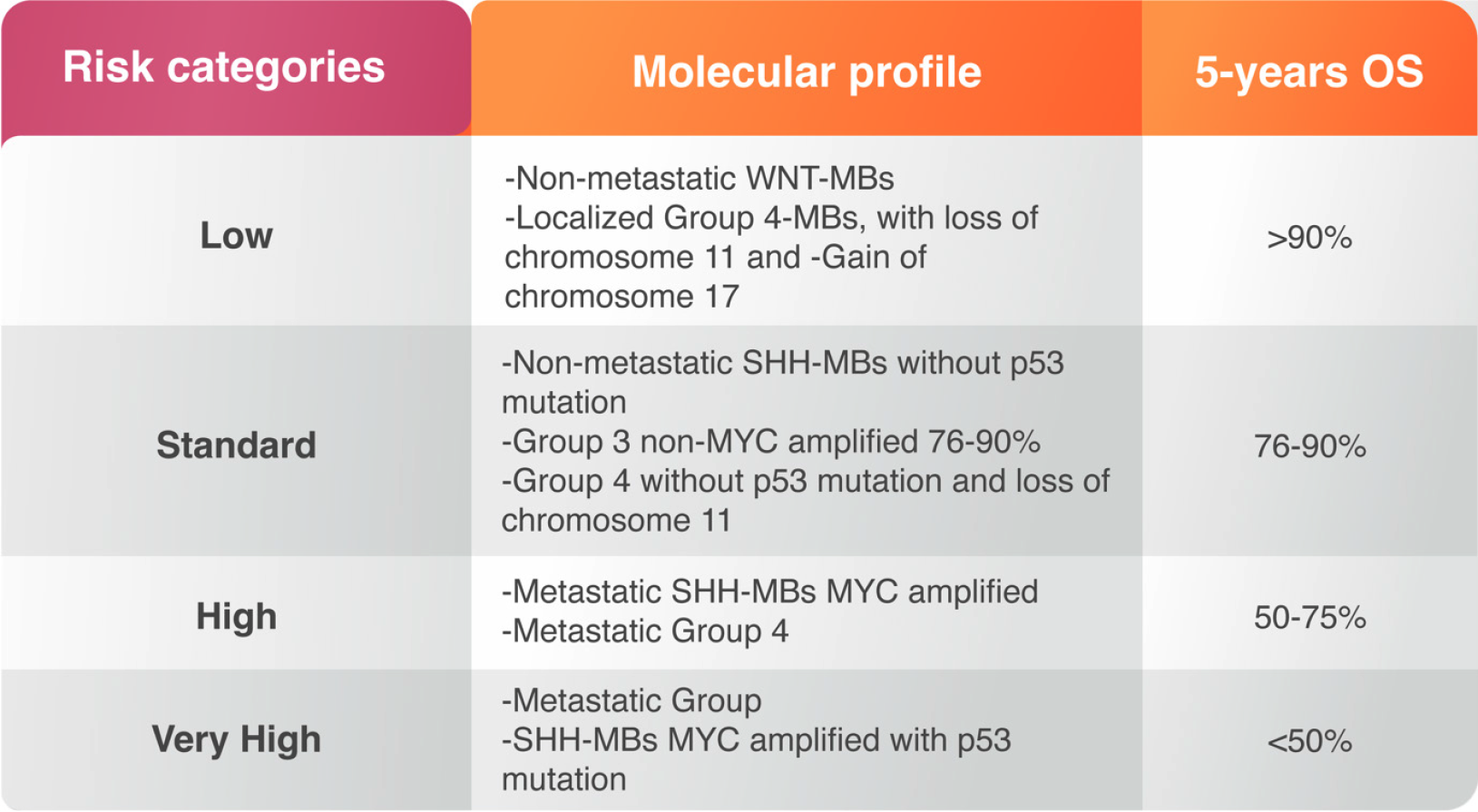
Figure 2 Risk groups and categories of medulloblastoma with their molecular profiles and the 5-years survival associated with each group.
The information presented in this figure were taken with permission from the reference: Luzzi et al[91], 2020. SHH: Sonic-hedgehog; MB: Medulloblastoma; MYC: Myelocytomatosis oncogene; OS: Overall survival; WNT: Wingless.
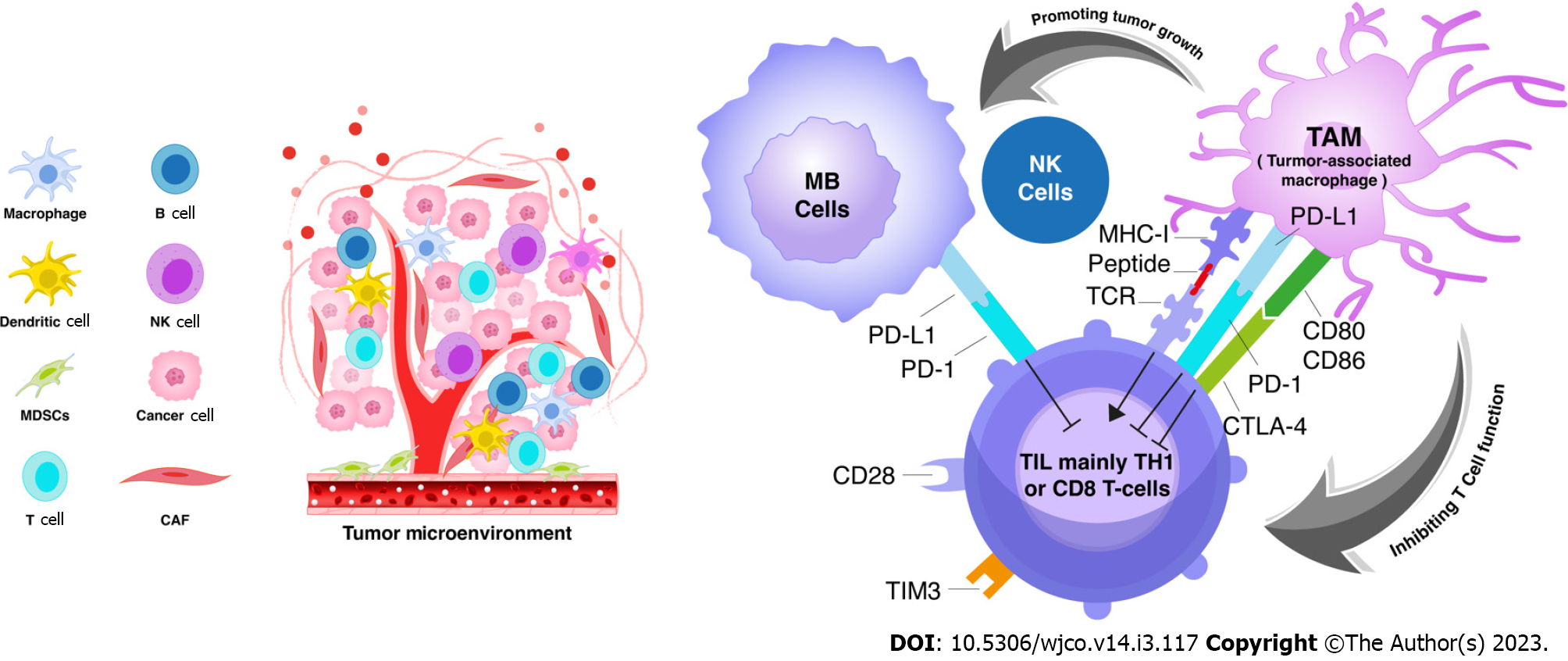
Figure 3 The signaling interaction between tumour cells, tumor-associated macrophages, and tumour infiltrating lymphocytes in medulloblastoma microenvironment.
Tumour microenvironment represents diverse cellular heterogeneities including immune and none-immune cells. The targeted receptors linked between immune cells represent a potential targeted therapy. CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; MB: Medulloblastoma; NK: Natural killer; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage; TIL: Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes.
- Citation: Kurdi M, Mulla N, Malibary H, Bamaga AK, Fadul MM, Faizo E, Hakamy S, Baeesa S. Immune microenvironment of medulloblastoma: The association between its molecular subgroups and potential targeted immunotherapeutic receptors. World J Clin Oncol 2023; 14(3): 117-130
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v14/i3/117.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v14.i3.117