Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2022; 13(12): 943-956
Published online Dec 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i12.943
Published online Dec 24, 2022. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i12.943
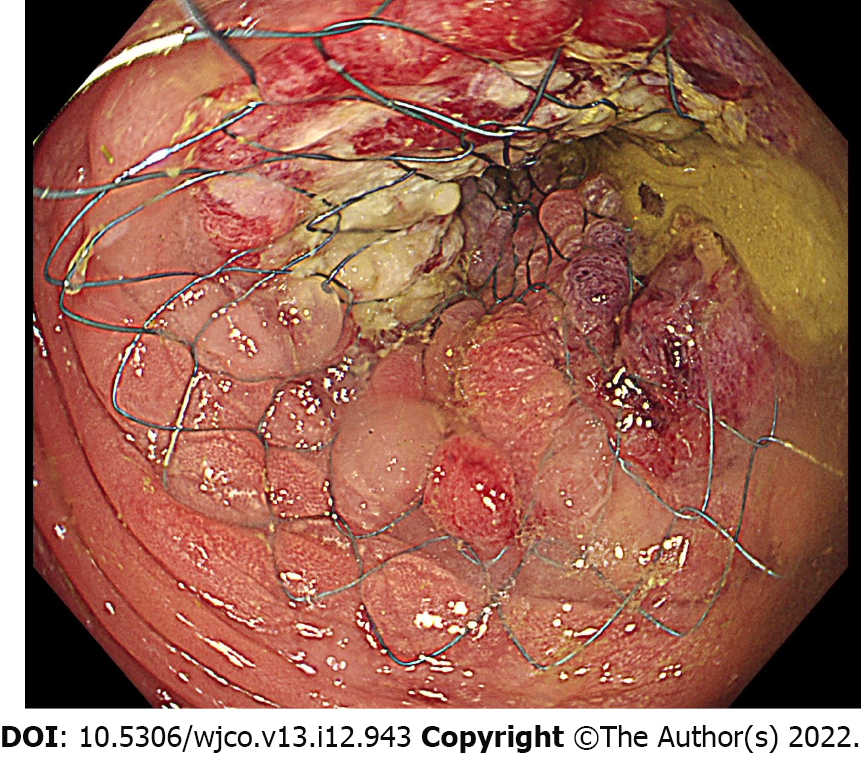
Figure 1 Endoscopic image of deployed stent.
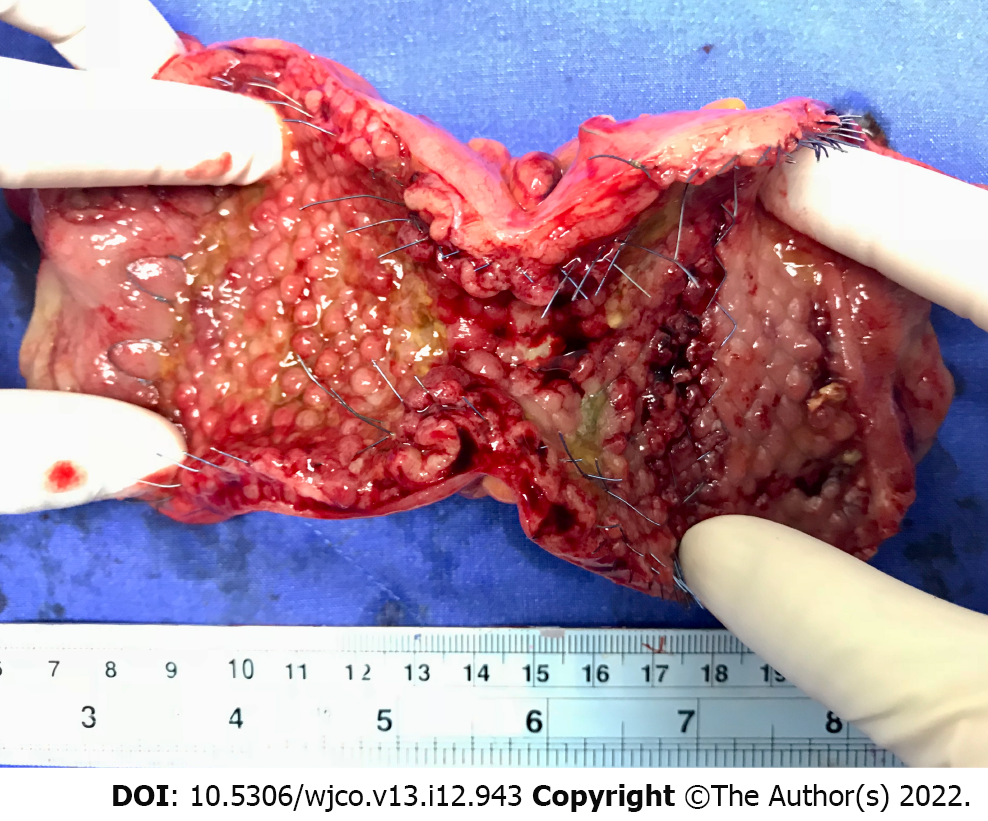
Figure 2 Surgical specimen after laparoscopic colectomy following colonic stenting as a bridge to surgery.
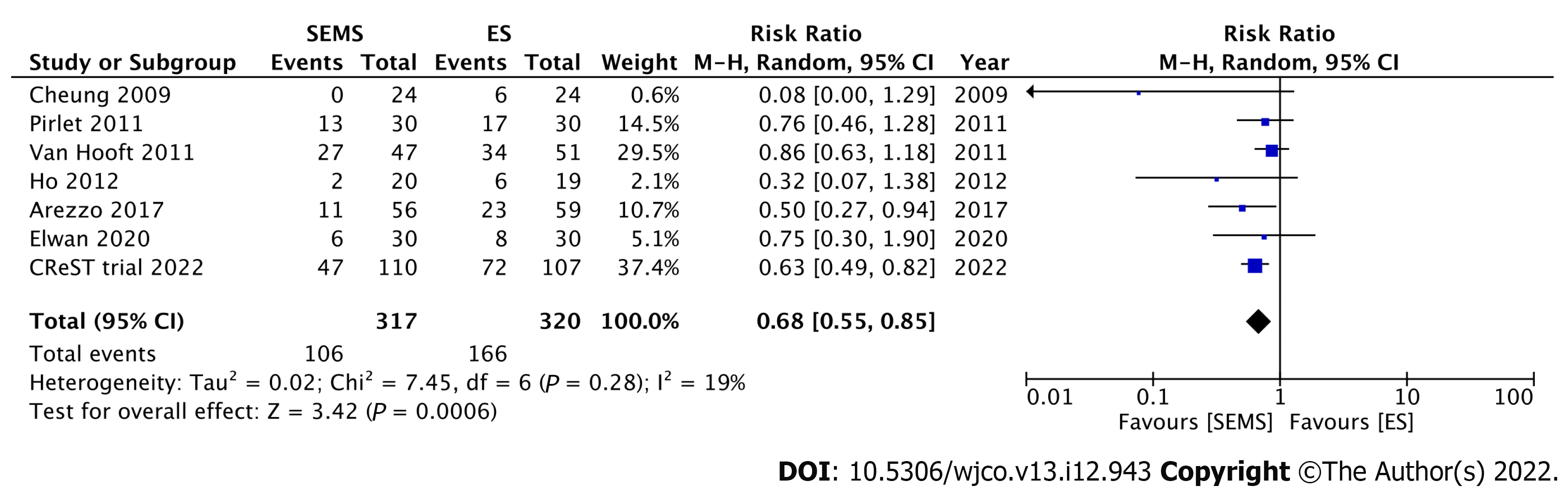
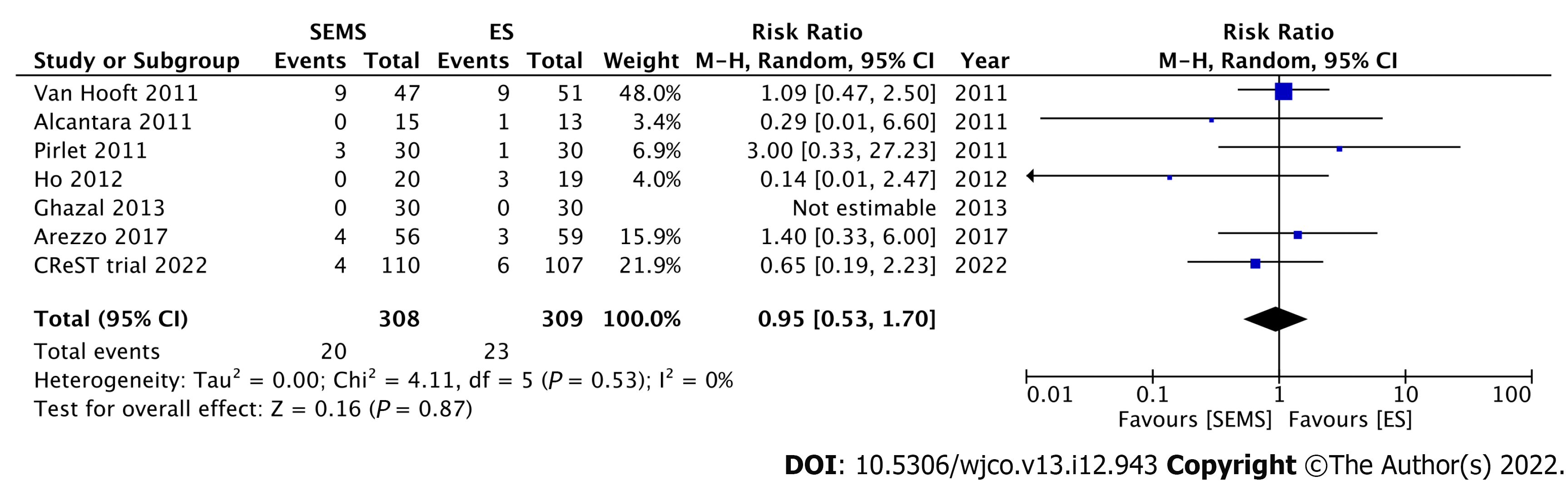
Figure 3 Forest plot showing the stoma rate.
SEMS: Self-expandable metal stent; ES: Emergency surgery.
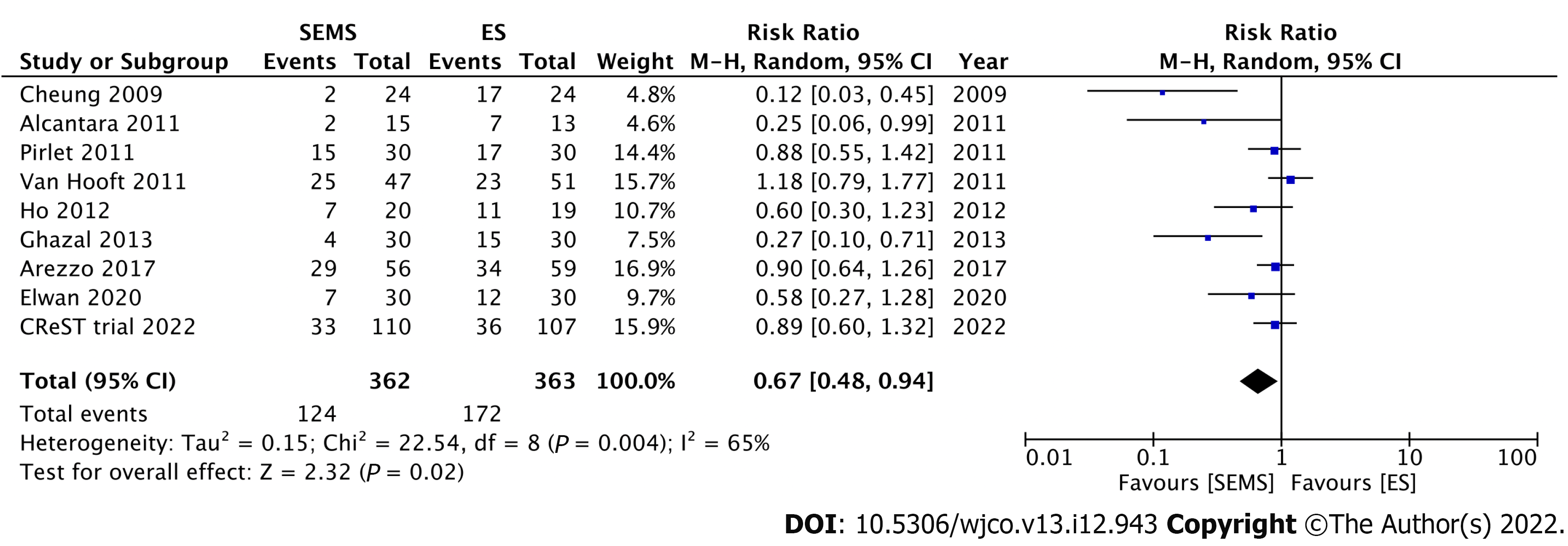
Figure 4 Forest plot showing the postoperative morbidity rate.
SEMS: Self-expandable metal stent; ES: Emergency surgery.
Figure 5 Forest plot showing the overall mortality rate.
SEMS: Self-expandable metal stent; ES: Emergency surgery.
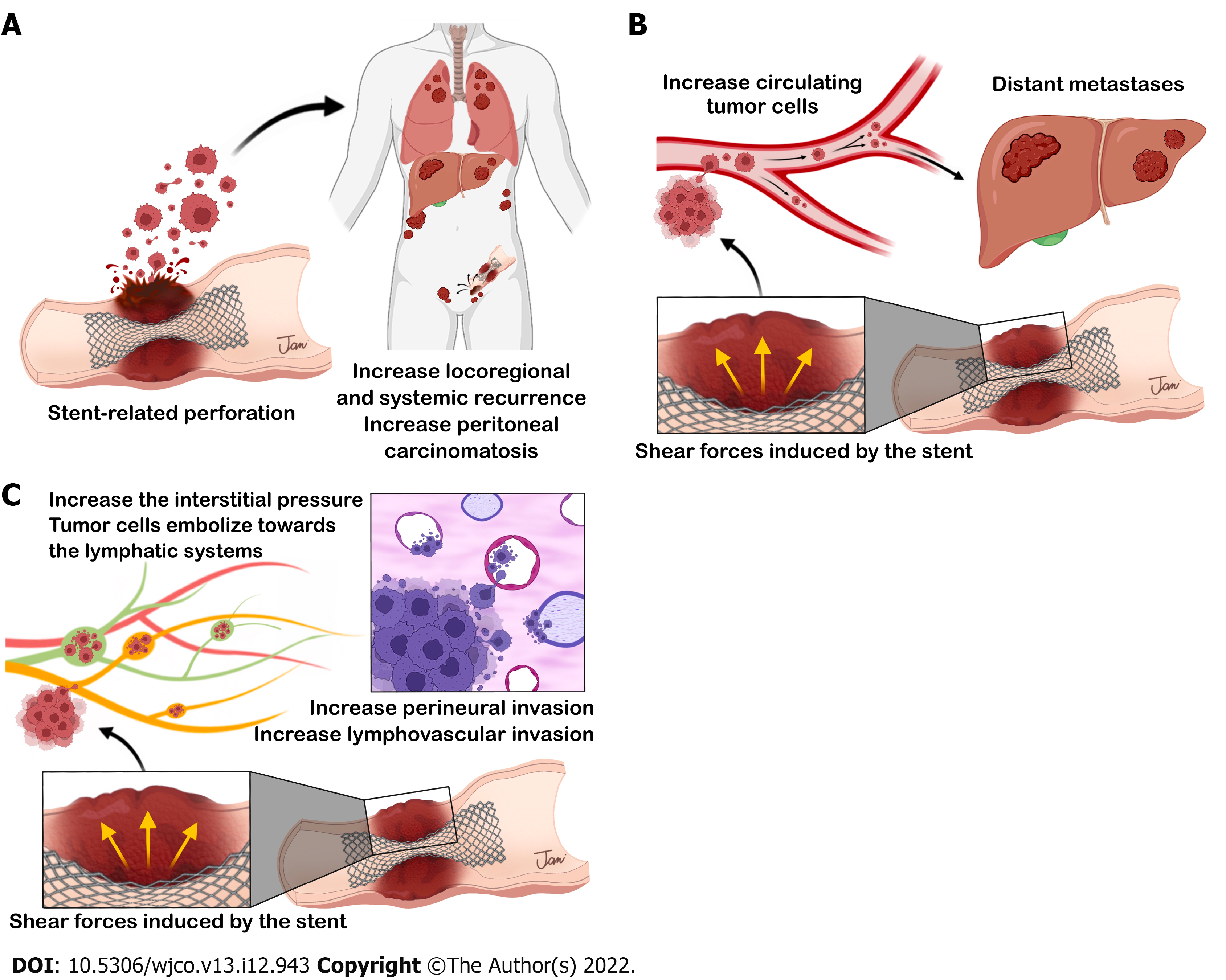
Figure 6 Three possible mechanisms of tumor dissemination after self-expandable metal stent placement.
A: self-expandable metal stent (SEMS)-related perforation; B: Increased circulating tumor cells; C: Aggressive pathological features after SEMS placement.
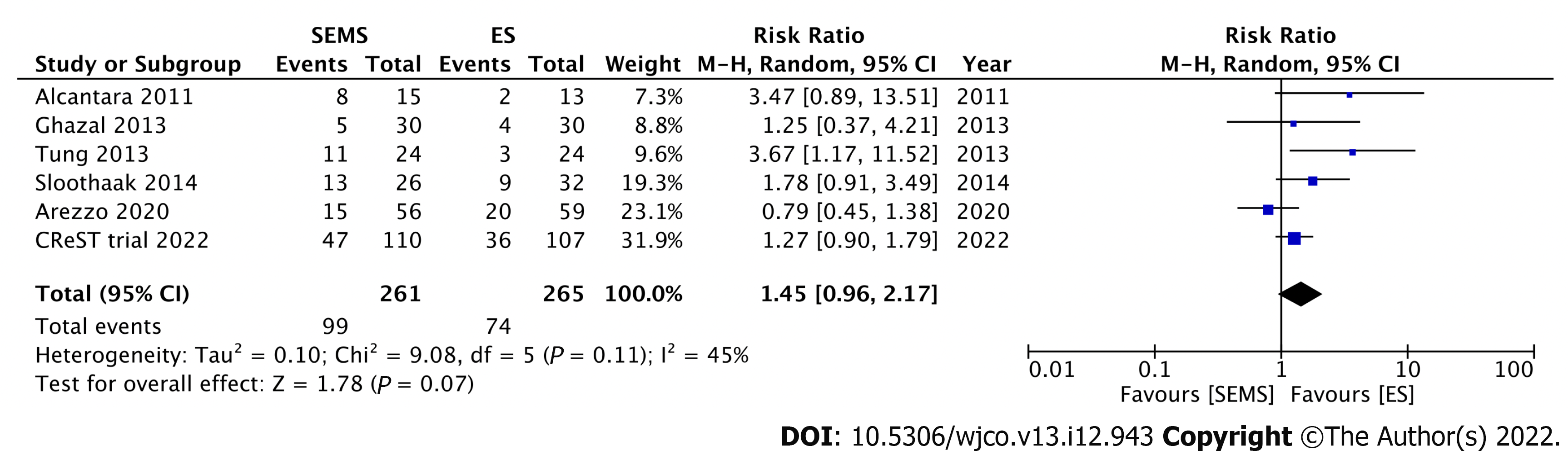
Figure 7 Forest plot showing the overall recurrence rate.
SEMS: Self-expandable metal stent; ES: Emergency surgery.
- Citation: Pattarajierapan S, Sukphol N, Junmitsakul K, Khomvilai S. Oncologic safety of colonic stenting as a bridge to surgery in left-sided malignant colonic obstruction: Current evidence and prospects. World J Clin Oncol 2022; 13(12): 943-956
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v13/i12/943.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i12.943