Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Oncol. Aug 24, 2021; 12(8): 609-622
Published online Aug 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.609
Published online Aug 24, 2021. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.609
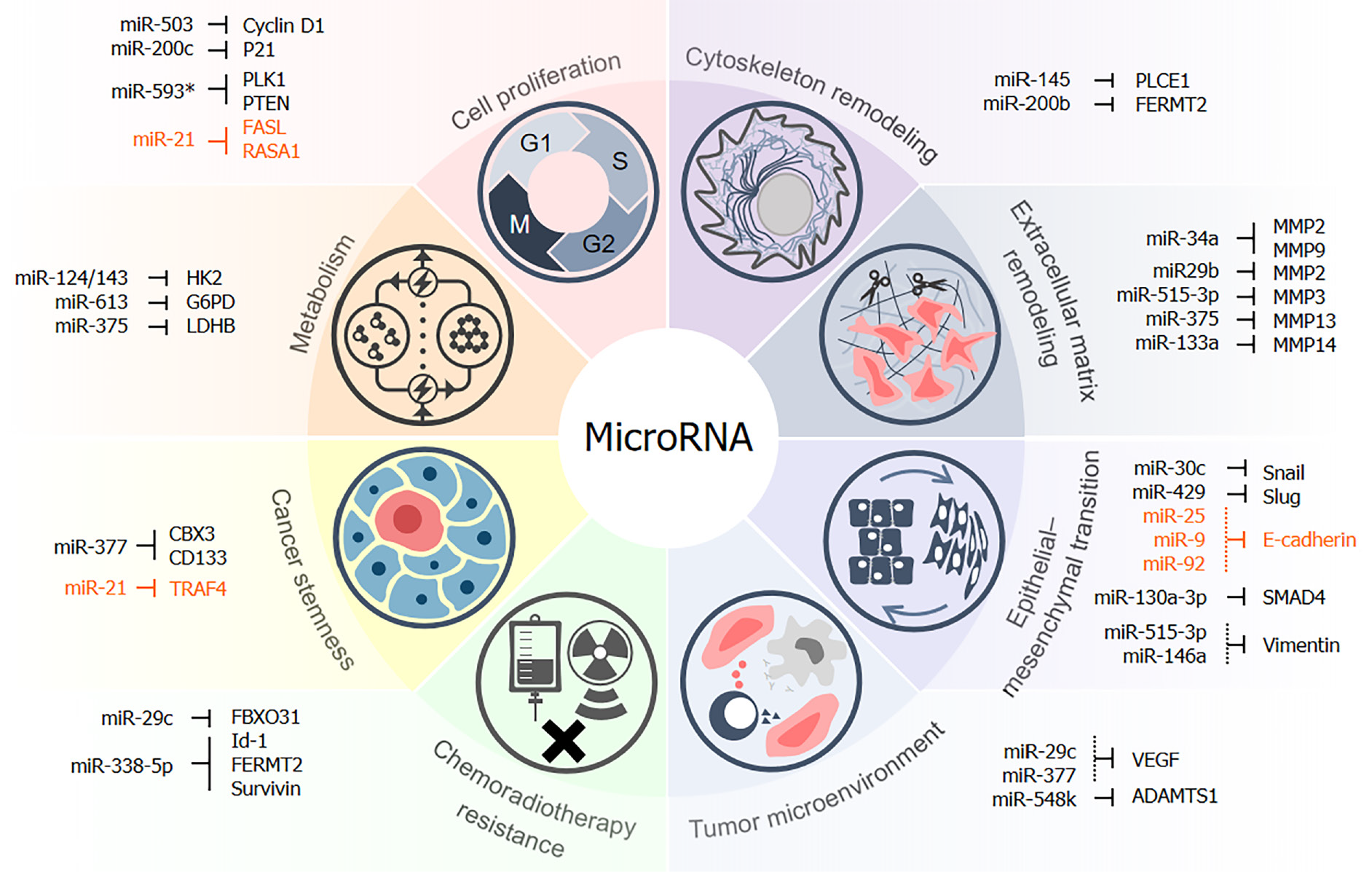
Figure 1 Multiple roles of miRNAs during development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
This figure summarizes the targets and regulatory functions of miRNAs in multiple biological processes during esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) development. MicroRNAs inhibit or promote tumorigenesis and recurrence of ESCC by modulating cell proliferation, metabolism, cancer stemness, and resistance to chemo- or radiotherapy. They also regulate metastasis by targeting functional molecules involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation, remodeling of the cytoskeleton, extracellular matrix, and tumor microenvironment. Oncogenic miRNAs and target genes are marked in orange. PLCE1: Phospholipase C epsilon 1; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Cui D, Cheung AL. Roles of microRNAs in tumorigenesis and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2021; 12(8): 609-622
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v12/i8/609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v12.i8.609