Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Oncol. Oct 24, 2020; 11(10): 809-835
Published online Oct 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i10.809
Published online Oct 24, 2020. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i10.809
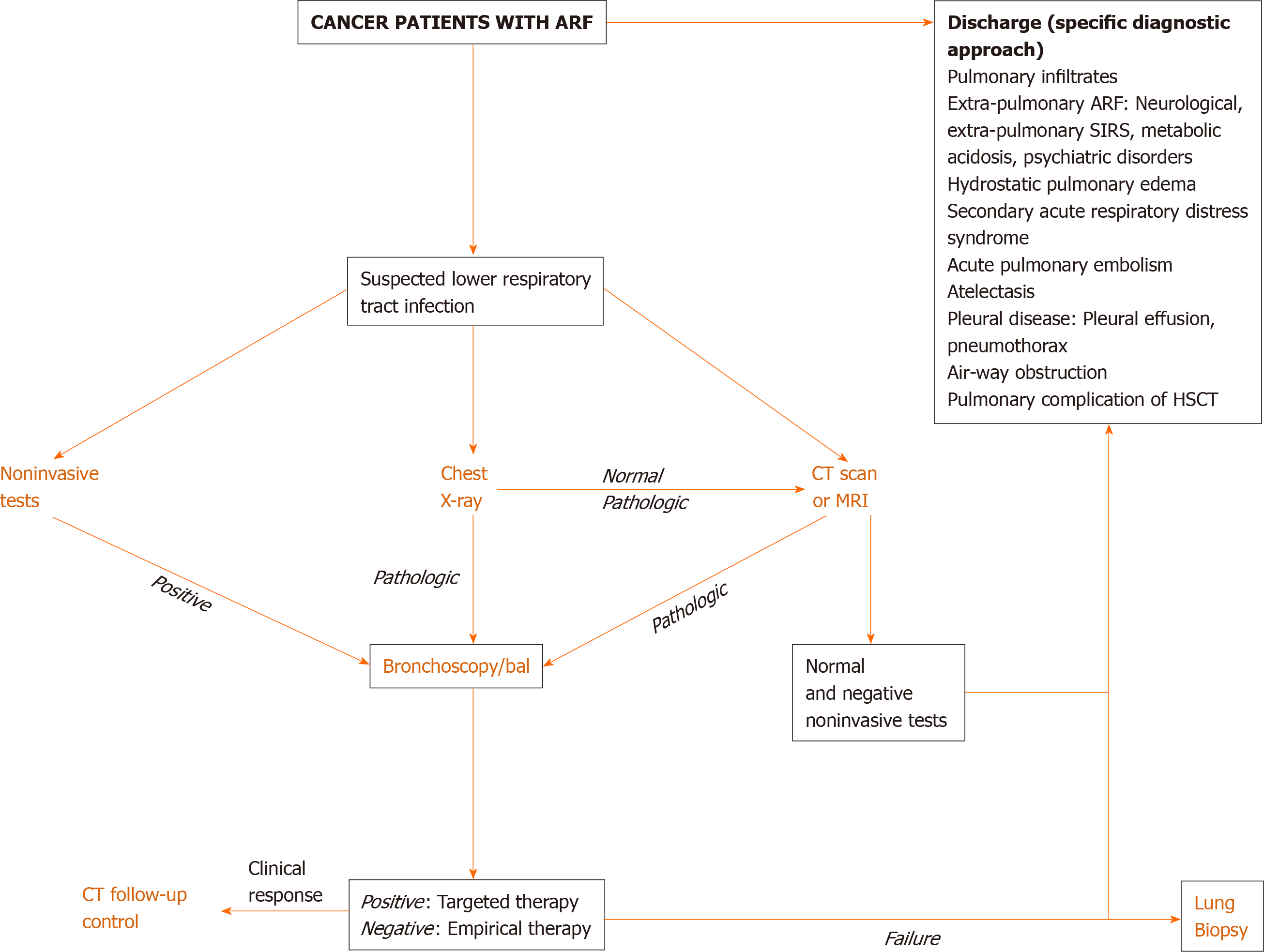
Figure 1 Diagnostic approach for cancer patients with suspected pulmonary infection.
ARF: Acute respiratory failure; BAL: Bronchoalveolar lavage; CT: Computed tomography; HSCT: Hematopoietic stem cell transplant; MRI: Magnetic resonance image; SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
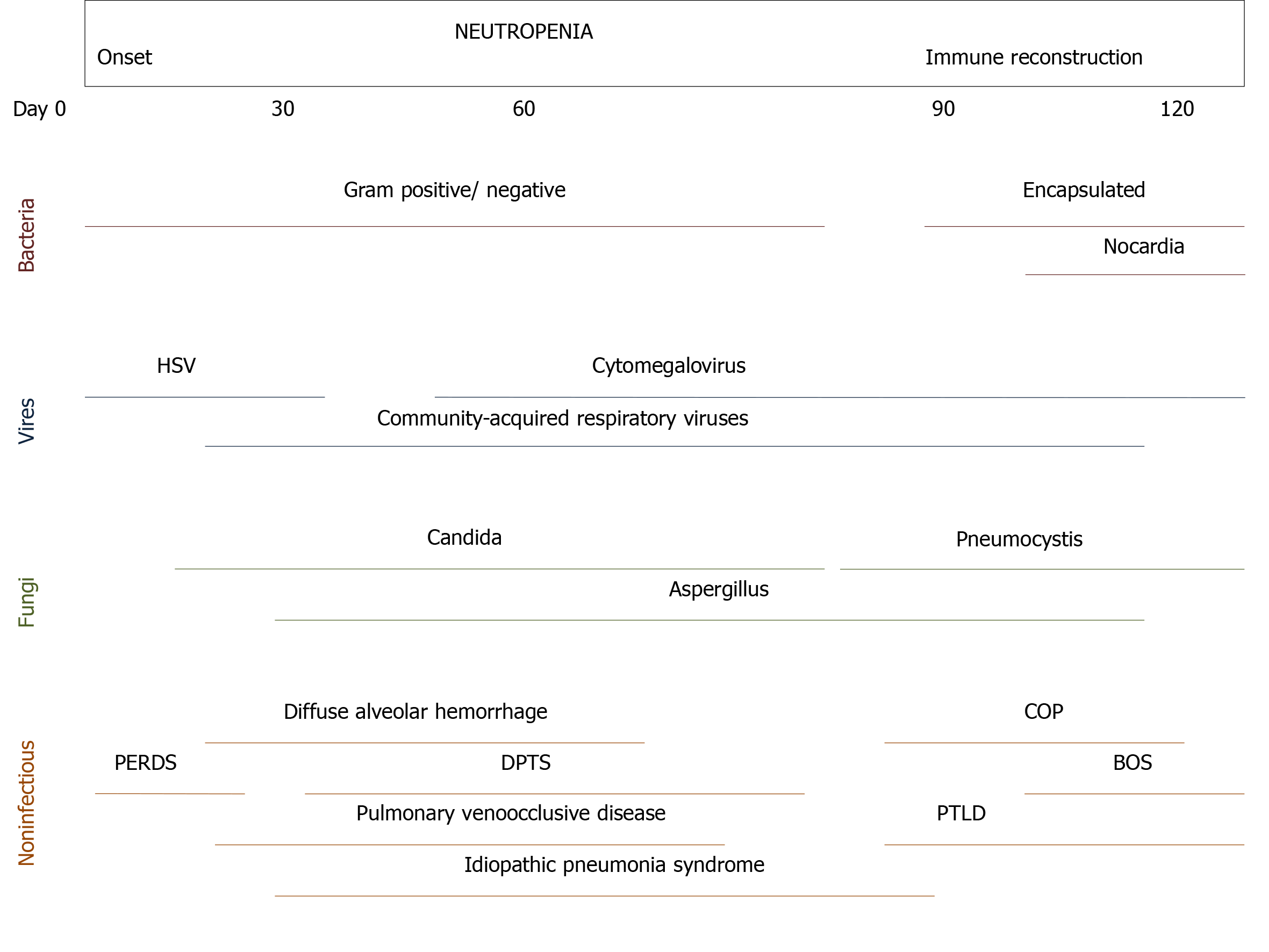
Figure 2 Pulmonary complications in patients with hematopoietic stem cell transplant[41].
BOS: Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome; COP: Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; DPTS: Delayed pulmonary toxicity syndrome; HSV: Herpes simplex virus; PERDS: Peri-engraftment respiratory distress syndrome; PTLD: Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder.
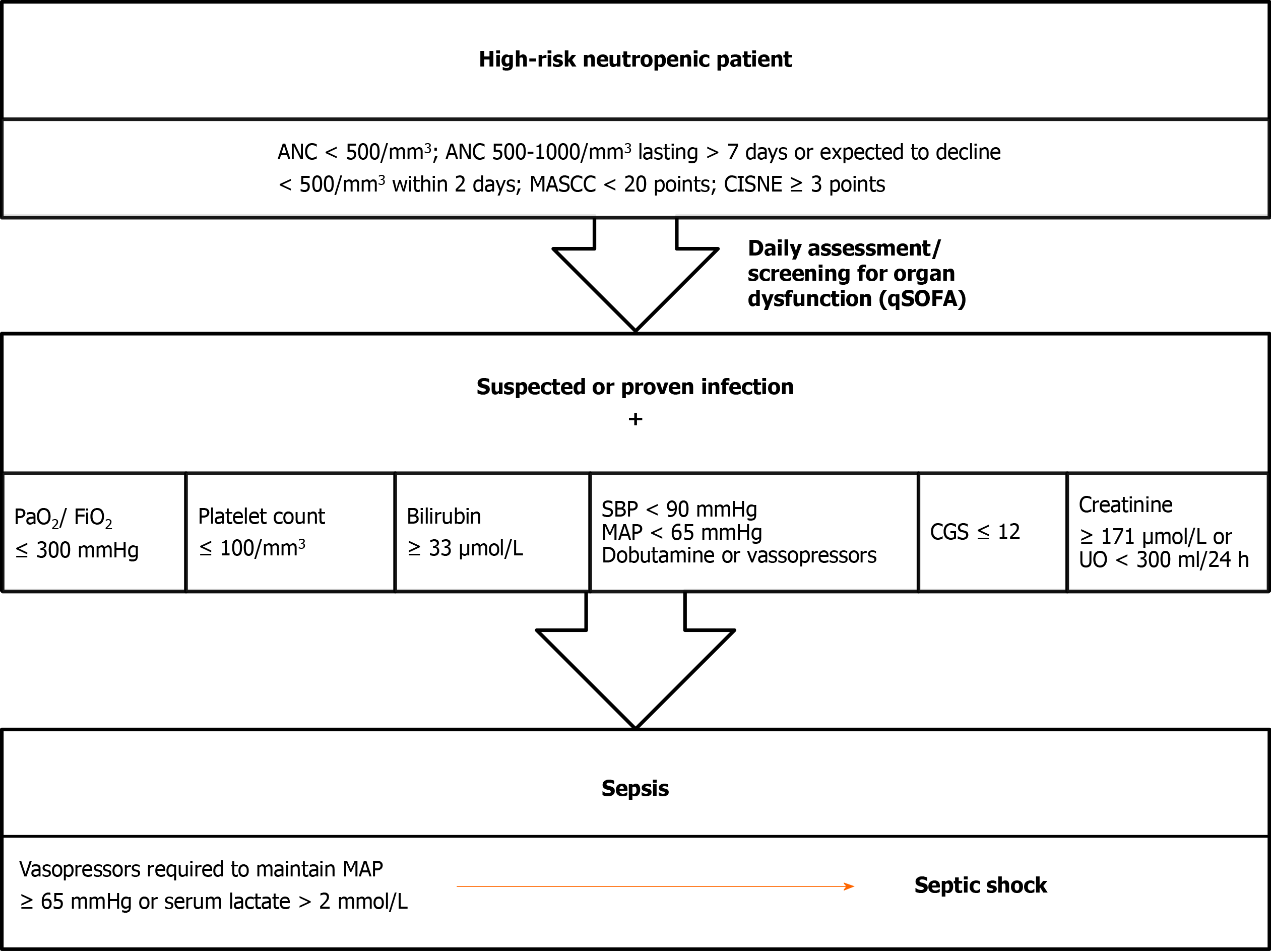
Figure 3 Sepsis diagnosis and treatment in neutropenic patients.
ANC: Absolute neutrophil count; CISNE: Clinical Index of Stable Febrile Neutropenia score; CGS: Coma Glasgow Scale; MAP: Mean arterial pressure; MASCC: Multinational association of supportive care of cancer risk-index; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; UO: Urine output.
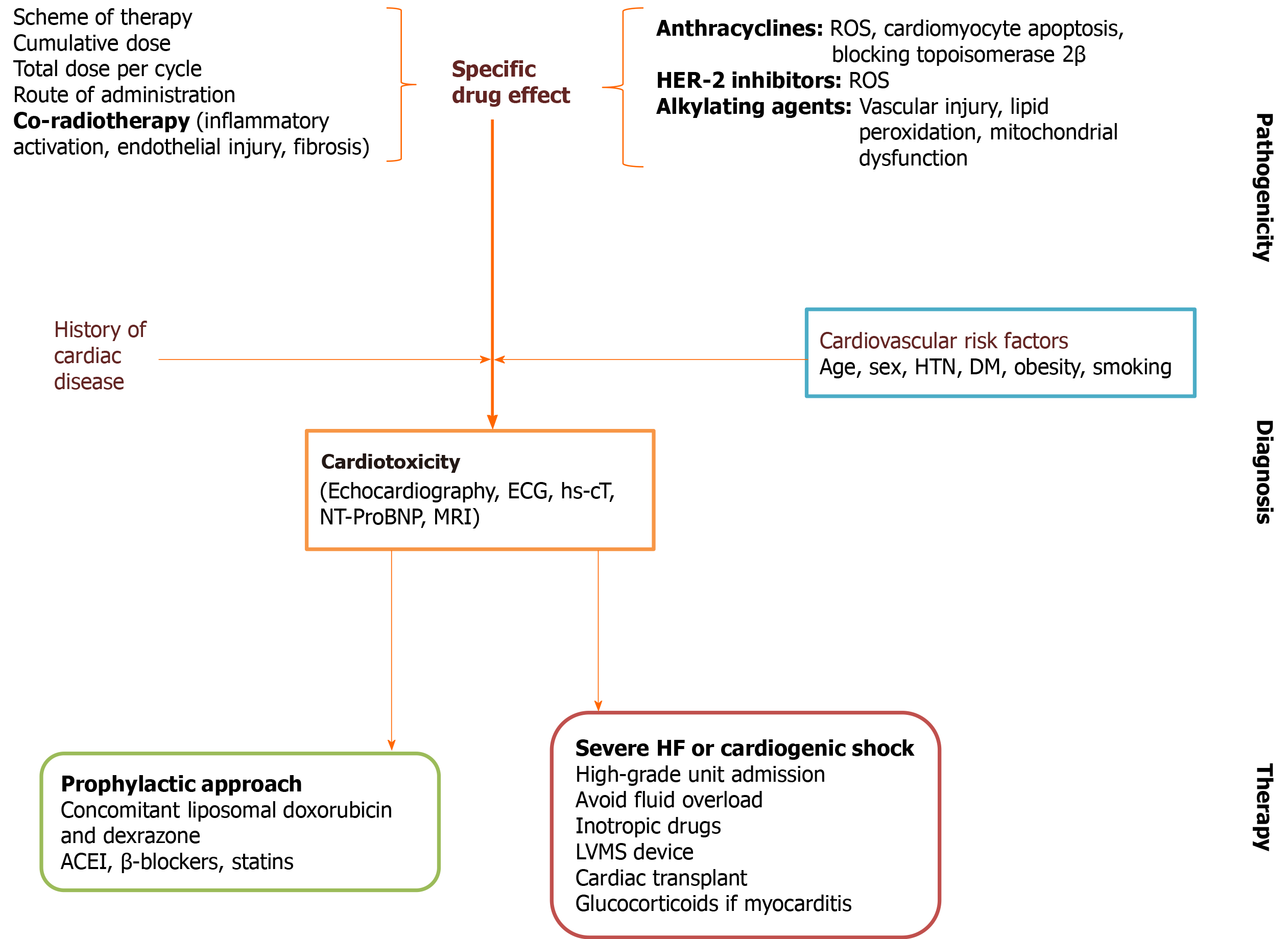
Figure 4 Pathogenic, diagnostic and therapeutic approach of chemotherapy-associated cardiac dysfunction[92,102,103].
ACEI: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ECG: Electrocardiography; DM: Diabetes mellitus; hs-cT: High-sensitive cardiac troponins; HTN: Arterial hypertension; LVMS: Left ventricular mechanical support; MRI: Magnetic resonance image; NT-ProBNP: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Martos-Benítez FD, Soler-Morejón CD, Lara-Ponce KX, Orama-Requejo V, Burgos-Aragüez D, Larrondo-Muguercia H, Lespoir RW. Critically ill patients with cancer: A clinical perspective. World J Clin Oncol 2020; 11(10): 809-835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v11/i10/809.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v11.i10.809