Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Nov 6, 2016; 7(4): 524-530
Published online Nov 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i4.524
Published online Nov 6, 2016. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i4.524
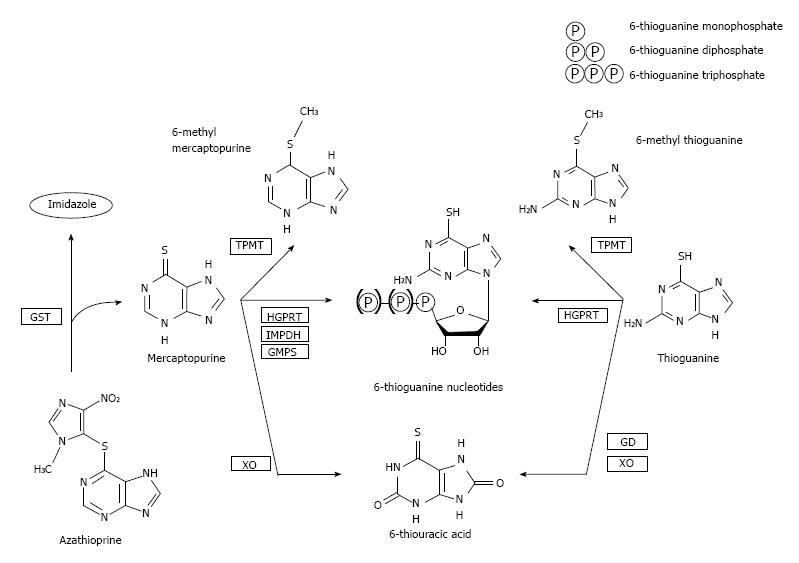
Figure 1 Simplified scheme of thiopurine metabolism.
Azathioprine is converted to mercaptopurine by the enzyme glutathione S-transferase (GST), by separating the imidazole-group. 6-Mercaptopurine is enzymatically converted into 6-methylmercaptopurine (6-MMP) by thiopurine-S-methyltransferase (TPMT) and into 6-thiouracic acid (6-TUA) by xanthine oxidase (XO). The remaining portion of mercaptopurine is converted into the biochemically active end-metabolites 6-thioguaninenucleotides (6-TGN, consisting of 6-thioguanine monophosphate, 6-thioguanine diphosphate and 6-thioguanine triphosphate) by a pathway of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT), inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) and guanosine monophosphate synthetase (GMPS). Thioguanine is metabolized by TPMT into 6-methylthioguanine (6-MTG) and into 6-TUA by guanine deaminase (GD) and XO. The remaining portion of thioguanine is directly converted into 6-TGN by HGPRT. Squared abbreviations display enzymatic conversions. Adapted from van Asseldonk et al[5].
- Citation: Meijer B, Mulder CJ, van Bodegraven AA, de Boer NKH. How I treat my inflammatory bowel disease-patients with thiopurines? World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2016; 7(4): 524-530
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v7/i4/524.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i4.524