Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Oct 6, 2011; 2(5): 36-41
Published online Oct 6, 2011. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v2.i5.36
Published online Oct 6, 2011. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v2.i5.36
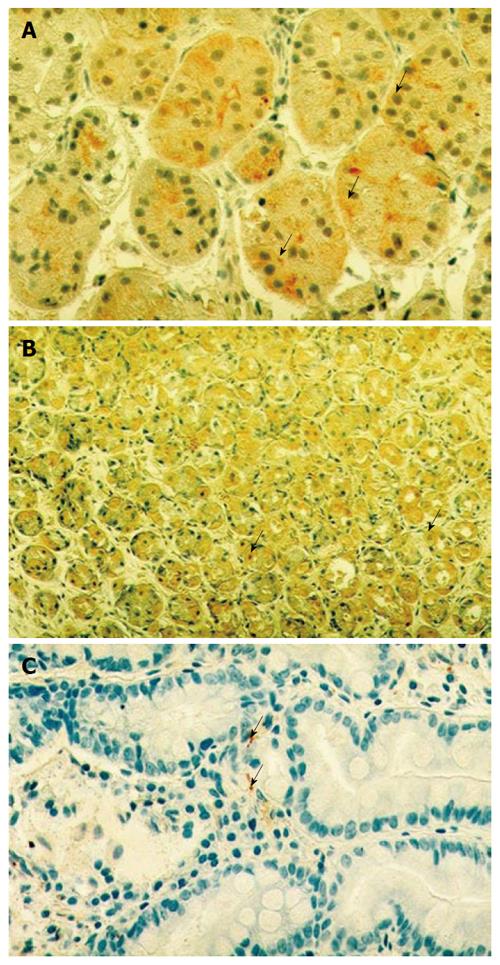
Figure 1 Immune-staining for transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (A), calcitonin gene-related peptide (B) and substance P (C) in the gastric mucosa of patients with Helicobacter pylori positive chronic gastritis (× 100).
A: The arrows show the cytoplasmic immunosignals; B: The arrows show the immunosignals of calcitonin gene-related peptide; C: The granular small spot-like signals of substance P along the mucosal blood vessels are indicated by arrows.
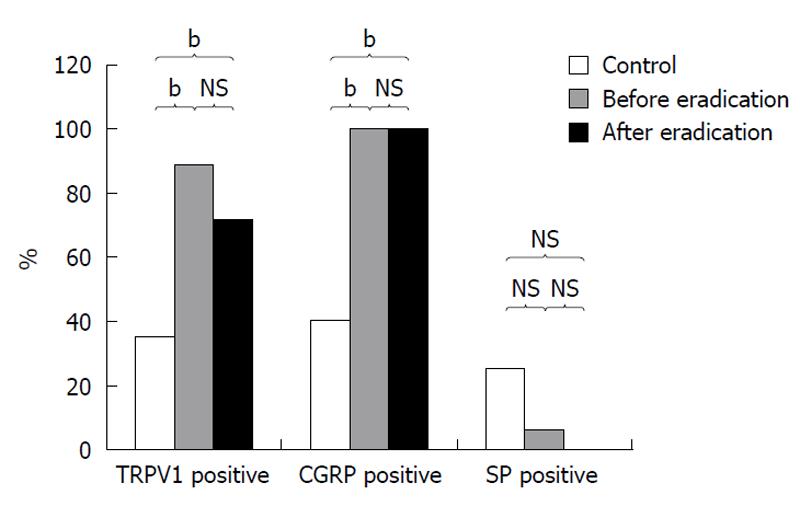
Figure 2 Changes in the presence of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in the gastric mucosa of patients with Helicobacter pylori positive chronic gastritis before and after eradication therapy obtained by immnohistochemistry.
TRVP1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; SP: Substance P; NS: Not significant. bP < 0.01.
-
Citation: Lakner L, Dömötör A, Tóth C, Szabó IL, Meczker &, Hajós R, Kereskai L, Szekeres G, Döbrönte Z, Mózsik G. Capsaicin-sensitive afferentation represents an indifferent defensive pathway from eradication in patients with
H. pylori gastritis. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2011; 2(5): 36-41 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v2/i5/36.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v2.i5.36