Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Nov 5, 2024; 15(6): 98146
Published online Nov 5, 2024. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v15.i6.98146
Published online Nov 5, 2024. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v15.i6.98146
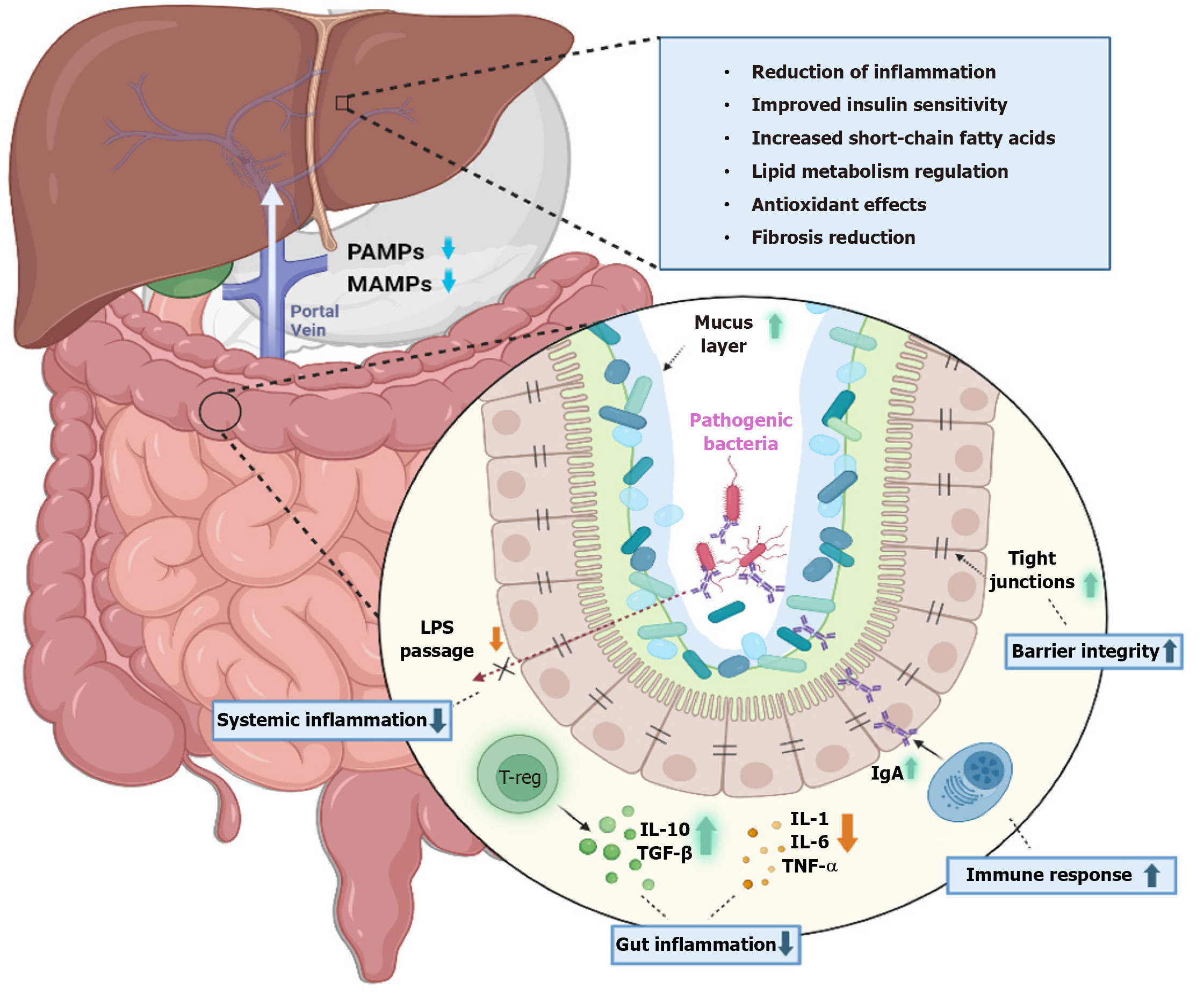
Figure 1 Role of gut microbiota in maintaining liver homeostasis.
IgA: Immunoglobulin A; IL: Interleukin; MAMP: Microbe-associated molecular patterns; PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
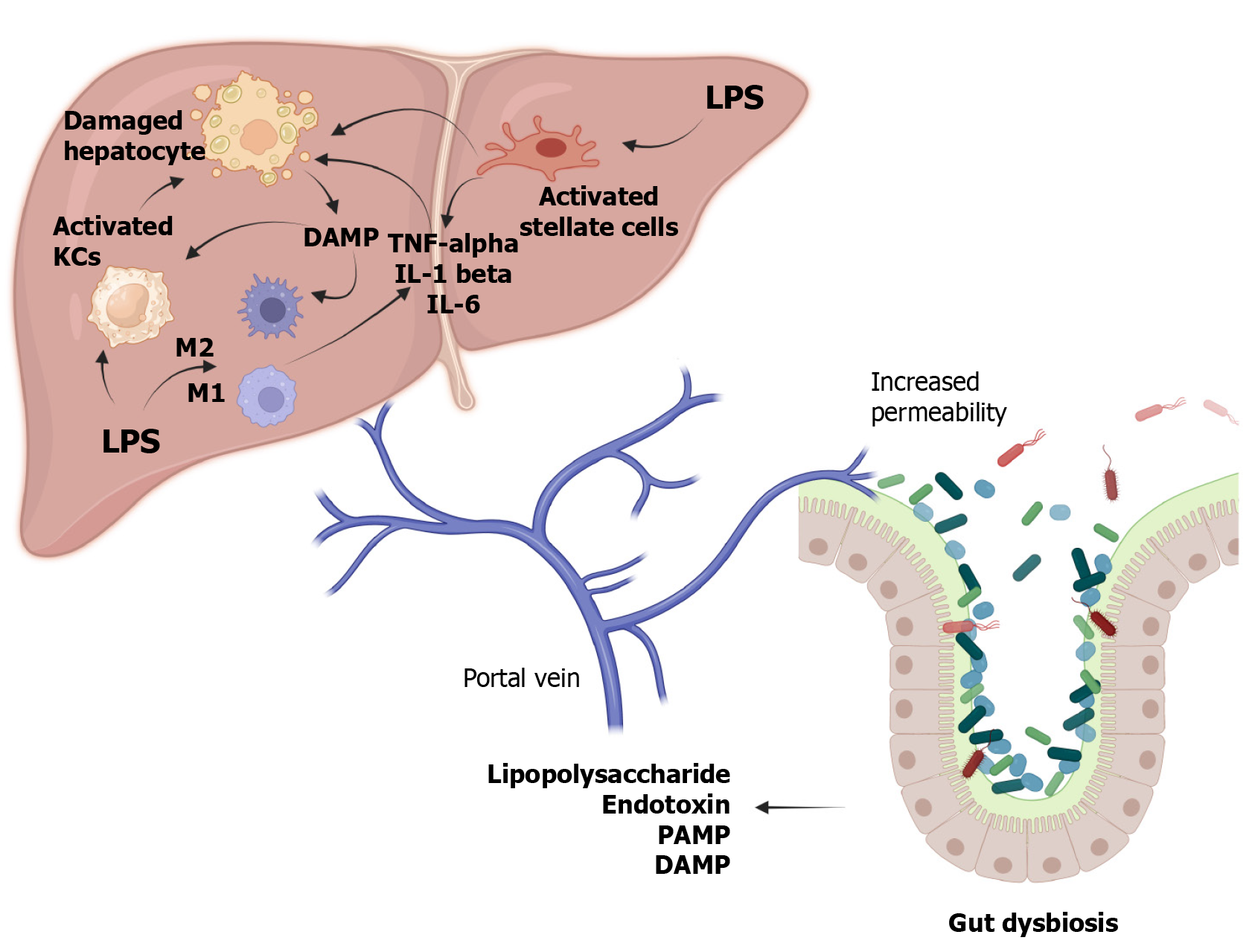
Figure 2 Dysbiotic gut-liver axis resulting in liver damage.
IL: Interleukin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; M: Macrophage; KCs: Kupffer cells; DAMP: Damage-associated molecular patterns; PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
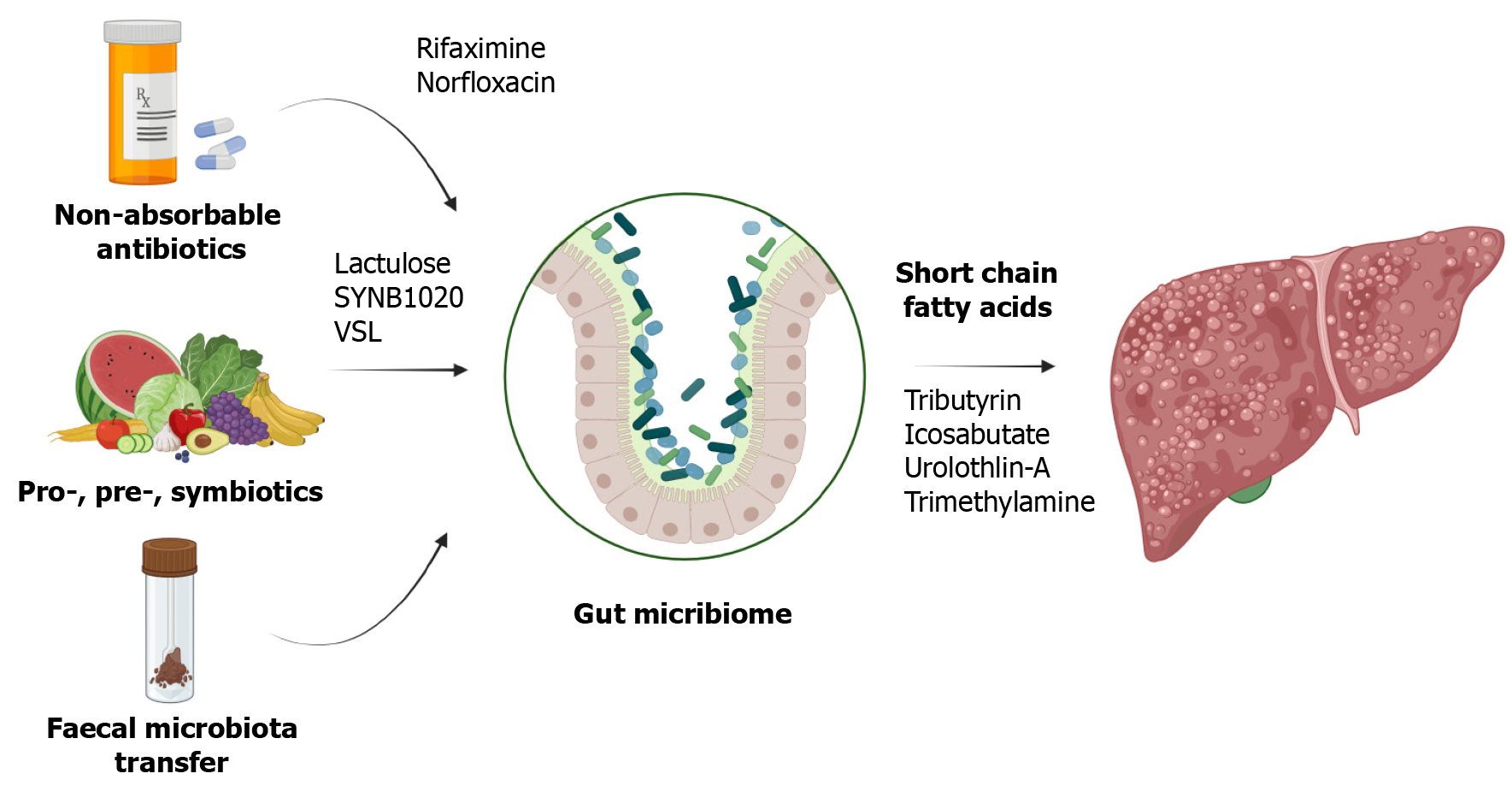
Figure 3
Therapeutic potential of intestinal microbiome in liver disease management.
- Citation: Jeyaraman N, Jeyaraman M, Mariappan T, Muthu S, Ramasubramanian S, Sharma S, Santos GS, da Fonseca LF, Lana JF. Insights of gut-liver axis in hepatic diseases: Mechanisms, clinical implications, and therapeutic potentials. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2024; 15(6): 98146
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v15/i6/98146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v15.i6.98146