Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Feb 15, 2016; 7(1): 97-107
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.97
Published online Feb 15, 2016. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.97
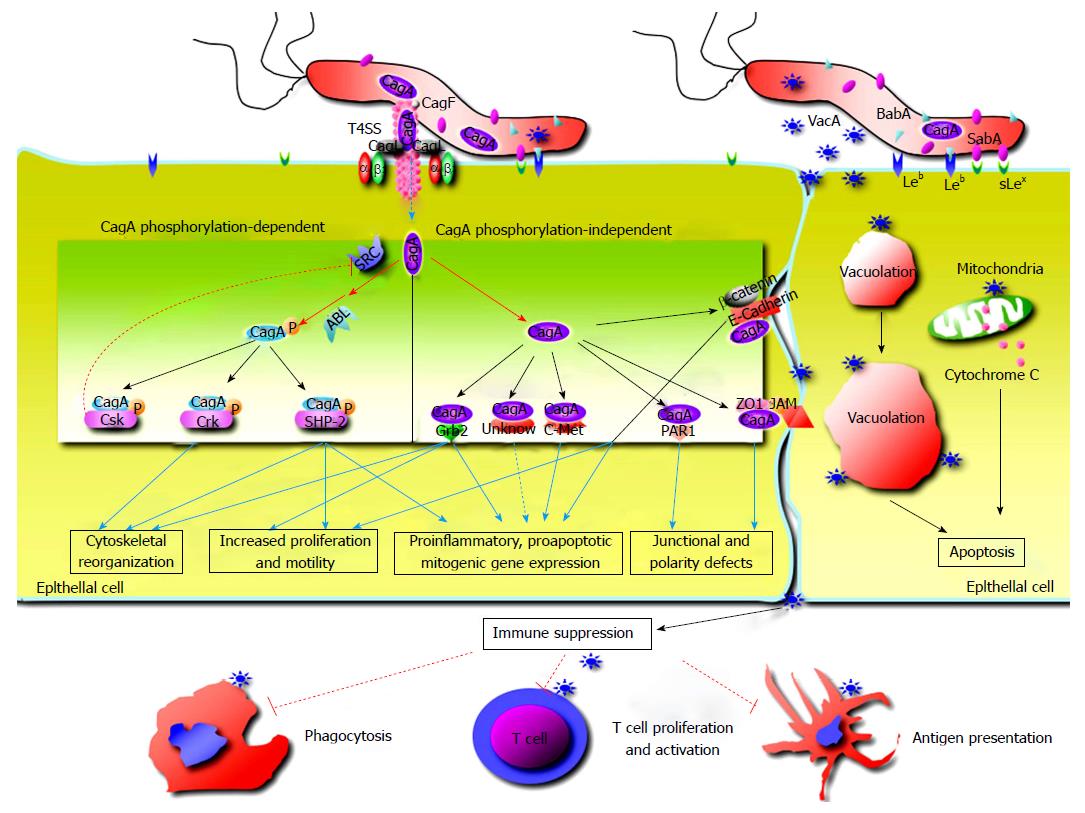
Figure 1 The roles of the main virulence factors in pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection[6].
Adherence of Helicobacter pylori to gastric epithelial cells is mediated by BabA and SabA binding Leb and Lewis x/a respectively. CagA is translocated into epithelial cells through T4SS, and then tyrosine phosphorylated at EPIYA sites by Src and Abl kinases. CagA contributes to alteration of myriad signaling transduction, which affects host cell physiology with disruption of intercellular junctions, loss of cell polarity, promotion of inflammation, dysregulation of cellular apoptosis and proliferation. VacA inducts cytoplasmic vacuolation, apoptosis and immune suppression[6].
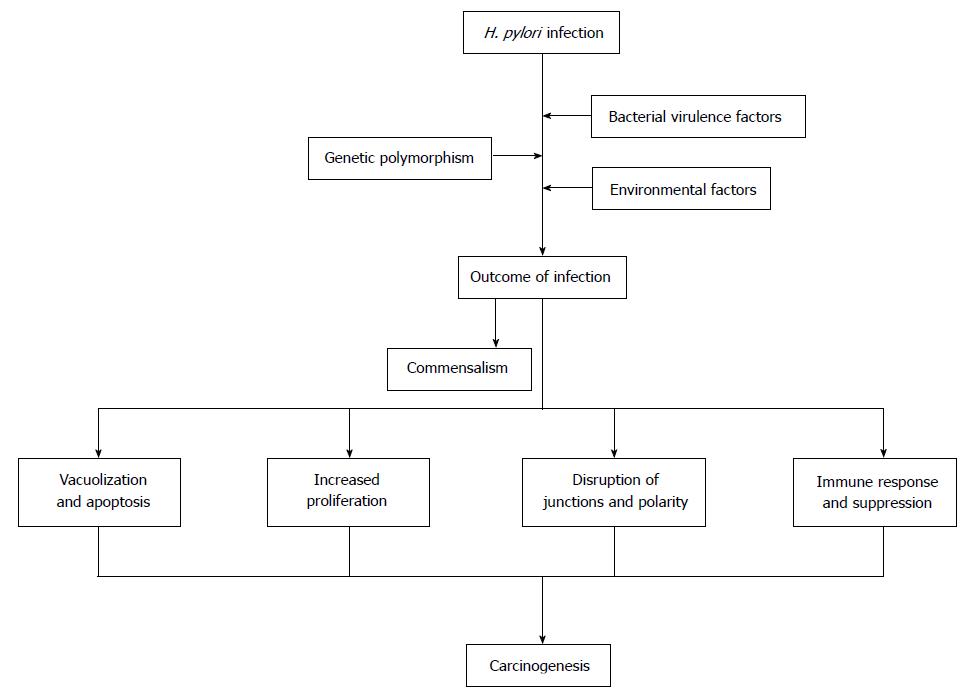
Figure 2 The pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer.
The pathogenesis of H. pylori-associated GC is a multi-factorial process, its development depends on a combination of host, bacterial and environmental factors, and the pathological changes might progress in steps. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; GC: Gastric cancer.
- Citation: Zhang RG, Duan GC, Fan QT, Chen SY. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in pathogenesis of gastric carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2016; 7(1): 97-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v7/i1/97.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v7.i1.97