Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2015; 6(4): 243-248
Published online Nov 15, 2015. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.243
Published online Nov 15, 2015. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.243
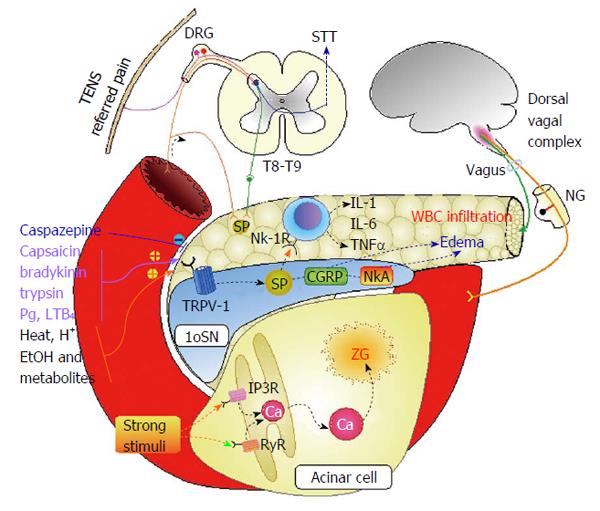
Figure 1 Schematic model illustrating possible mechanisms of neurogenic pancreatitis.
AP: Acute pancreatitis; STT: Spinothalamic tract; TENS: Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation; DRG: Dorsal root ganglion; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NK-1R: Neurokinin receptor 1; 1oSN: Primary sensory neuron; NG: Nodose ganglion; Pg: Prostaglandins; SP: Substance P; TRPV-1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; CGRP: Calcitonin gene related protein; NkA: Neurokinin A; IP3R: Inositol-3-phosphate receptor; RyR: Ryanodine receptor.
- Citation: Shmelev A, Abdo A, Sachdev S, Shah U, Kowdley GC, Cunningham SC. Energetic etiologies of acute pancreatitis: A report of five cases. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2015; 6(4): 243-248
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v6/i4/243.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.243