Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2015; 6(4): 219-227
Published online Nov 15, 2015. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.219
Published online Nov 15, 2015. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.219
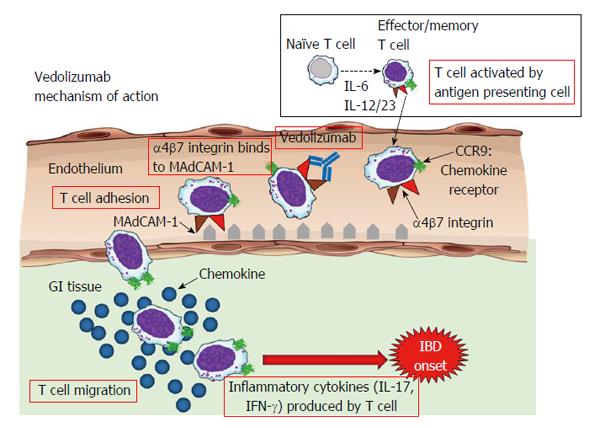
Figure 1 A mechanism of action that works to reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract (Reprinted with permission from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co.
). Vedolizumab selectively inhibits the movement of a discrete subset of T lymphocytes that preferentially migrate into inflamed GI tissue. Vedolizumab specifically binds to the α4β7 integrin, blocking its interaction with MAdCAM-1, which is mainly expressed on gut endothelial cells. This interaction facilitates lymphocyte homing to the gut and is an important contributor to inflammation that is a hallmark of ulcerative colitis. GI: Gastrointestinal; MAdCAM-1: Mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; CCR: Chemokine receptor; IL: Interleukine; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ.
- Citation: Akiho H, Yokoyama A, Abe S, Nakazono Y, Murakami M, Otsuka Y, Fukawa K, Esaki M, Niina Y, Ogino H. Promising biological therapies for ulcerative colitis: A review of the literature. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2015; 6(4): 219-227
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v6/i4/219.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.219