Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Nov 15, 2014; 5(4): 487-495
Published online Nov 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.487
Published online Nov 15, 2014. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.487
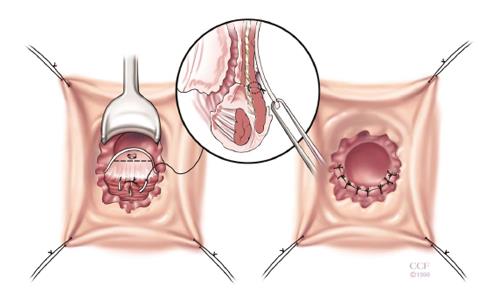
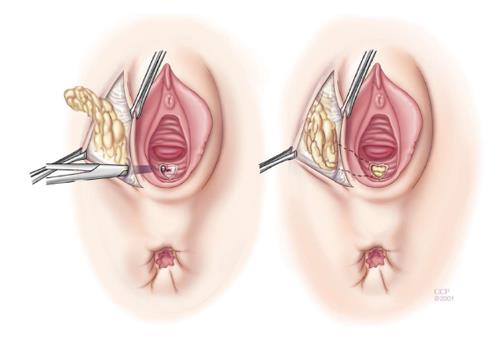
Figure 1 Rectal advancement flap.
The rectal advancement flap begins with a 180 degree curvilinear incision starting just distal to fistula opening and extends 4-5 cm cephalad, encompassing mucosa, submucosa and the rectal wall is dissected from the rectovaginal septum. After mobilization, the fistula tract is cored out and the opening is closed with absorbable sutures. The diseased distal portion of the flap is trimmed before and the flap is advanced distally and sutured to the cut edge with absorbable sutures. The vaginal or perineal external opening is left open for drainage. Reprinted with permission, Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art and Photography © 1999-2014. All Rights Reserved.
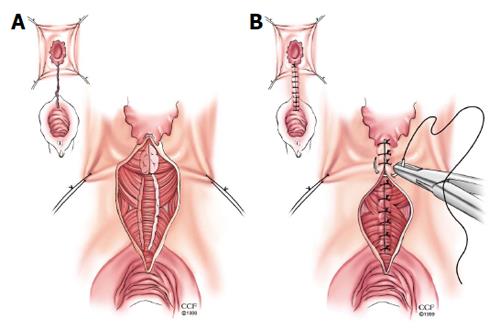
Figure 2 Rectal sleeve advancement flap.
A: Dissection begins at the dentate line with a 90%-100% circumferential mucosectomy of ulcerated mucosa and submucosa of the anal canal and is carried cephalad until the supralevator space is breeched. After sufficient rectal mobilization has been accomplished, the fistula tract is cored out and then closed with absorbable suture and the vaginal mucosa is left open; B: The diseased distal margin of tissue is trimmed and the cuff of rectum is advanced down and sutured to the ridge of anoderm using absorbable sutures. Reprinted with permission, Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art and Photography © 1999-2014. All Rights Reserved.
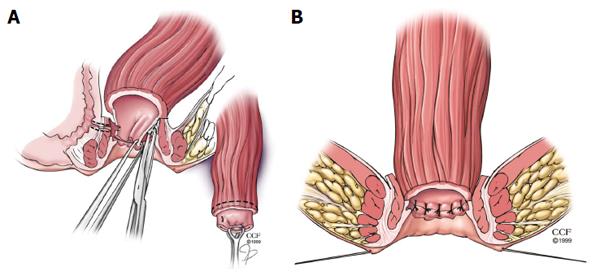
Figure 3 Episioproctotomy.
A: Episioproctotomy begins with fistulotomy and division of all tissue overlying the fistula, including sphincter muscles and rectal and vaginal walls. Complete debridement of the granulation tissue of the fistula tract is carried out along with the lateral identification and mobilization of the sphincter muscles; B: The rectal mucosa is repaired followed by an overlap repair of the sphincter muscles. The repair is completed by closing the vaginal mucosa. Reprinted with permission, Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art and Photography © 1999-2014. All Rights Reserved.
Figure 4 Turnbull-Cutait abdominalperineal pull-through procedure (A-D).
Reprinted with permission, Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art and Photography © 1999-2014. All Rights Reserved.
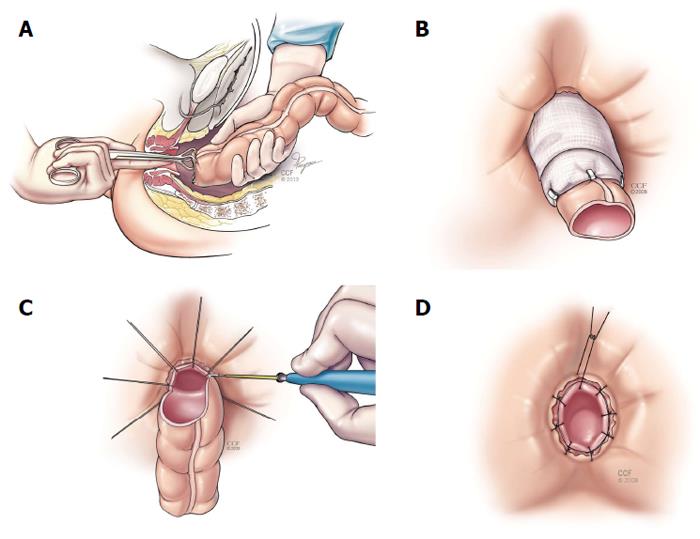
Figure 5 Martius graft.
The martius graft begins standard perineal dissection followed by longitudinal incision over the labia majora. Skin flaps are raised medially and laterally until entire fat pad with bulbocavernosus muscle is mobilized. A subcutaneous, subvaginal tunnel is made and the flap is pulled through the tunnel after the anterior end is divided and then sutured to the posterior vaginal wall. Reprinted with permission, Cleveland Clinic Center for Medical Art and Photography © 1999-2014. All Rights Reserved.
- Citation: Valente MA, Hull TL. Contemporary surgical management of rectovaginal fistula in Crohn's disease. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2014; 5(4): 487-495
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v5/i4/487.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.487