Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Dec 15, 2011; 2(6): 93-99
Published online Dec 15, 2011. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v2.i6.93
Published online Dec 15, 2011. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v2.i6.93
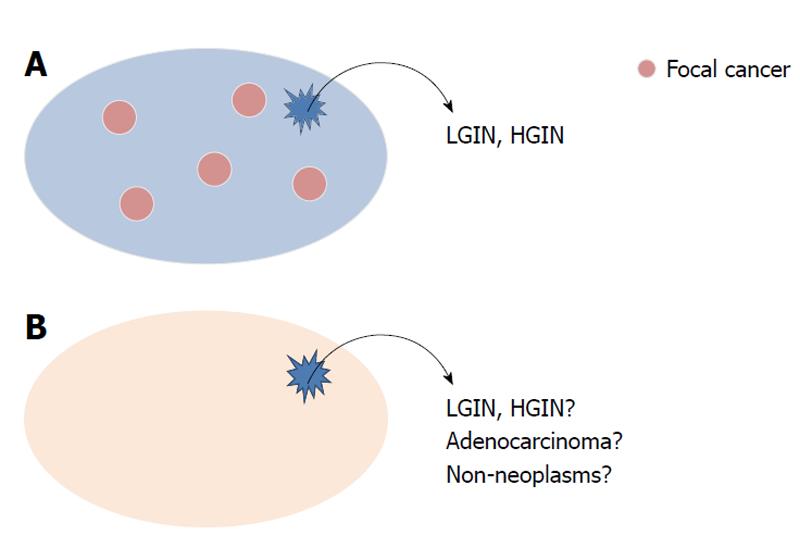
Figure 1 Reasons for the difficulty in making an accurate diagnosis based on a biopsy specimen.
Cancer sometimes exists focally in the lesion and sampling error might occur (A); the structural atypia of both adenoma and well-differentiated adenocarcinoma is too subtle for small biopsy specimen. Moreover, regeneration of atypia induced by gastritis induces histological modification (B). LGIN: Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia.
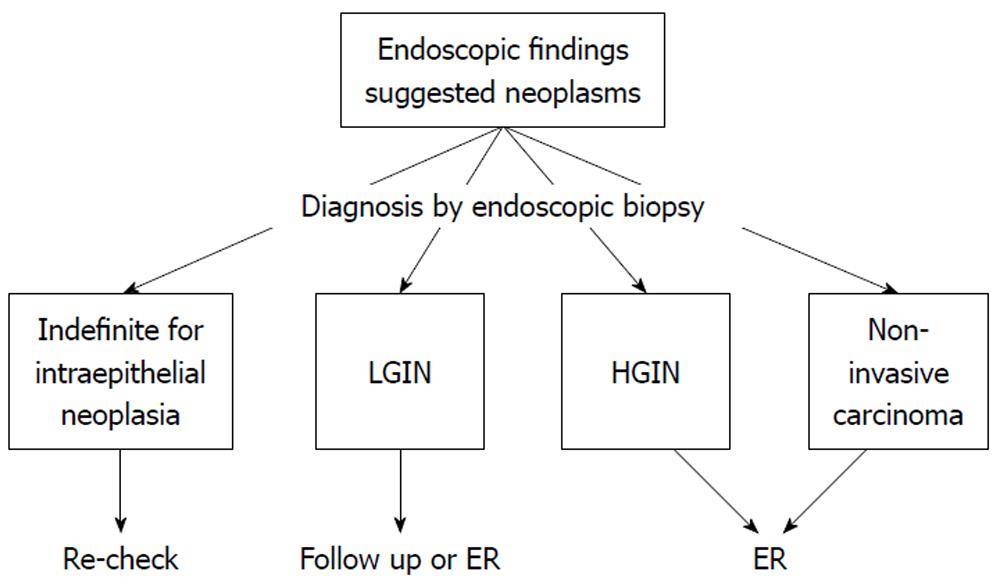
Figure 2 Treatment strategy for gastric non-invasive intraepithelial neoplasia diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy as a treatment flowchart (our opinion).
LGIN: Low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; ER: Endoscopic resection.
- Citation: Nishida T, Tsutsui S, Kato M, Inoue T, Yamamoto S, Hayashi Y, Akasaka T, Yamada T, Shinzaki S, Iijima H, Tsujii M, Takehara T. Treatment strategy for gastric non-invasive intraepithelial neoplasia diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2011; 2(6): 93-99
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v2/i6/93.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v2.i6.93