Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. May 12, 2020; 11(3): 64-77
Published online May 12, 2020. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v11.i3.64
Published online May 12, 2020. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v11.i3.64
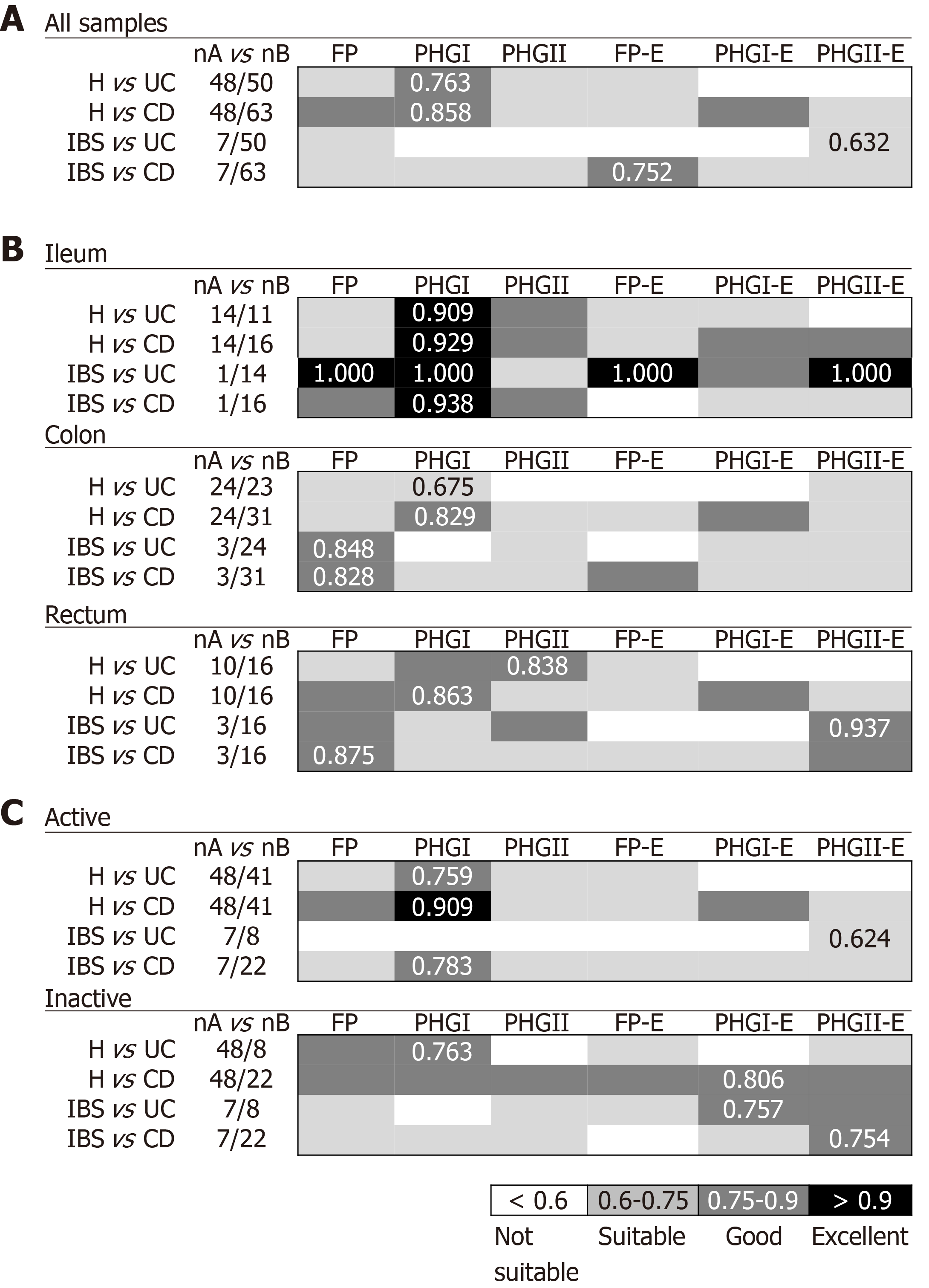
Figure 1 Usefulness of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, its phylogroups (PHGI and PHGII) and their index in conjunction to Escherichia coli to discriminate between milder gut conditions [Healthy controls (H) and irritable bowel syndrome] and inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease) by pooling all biopsy samples together (A), by location of sampling (B) and by activity status (C).
Best area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values for each comparison are shown. FP: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s disease; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome.
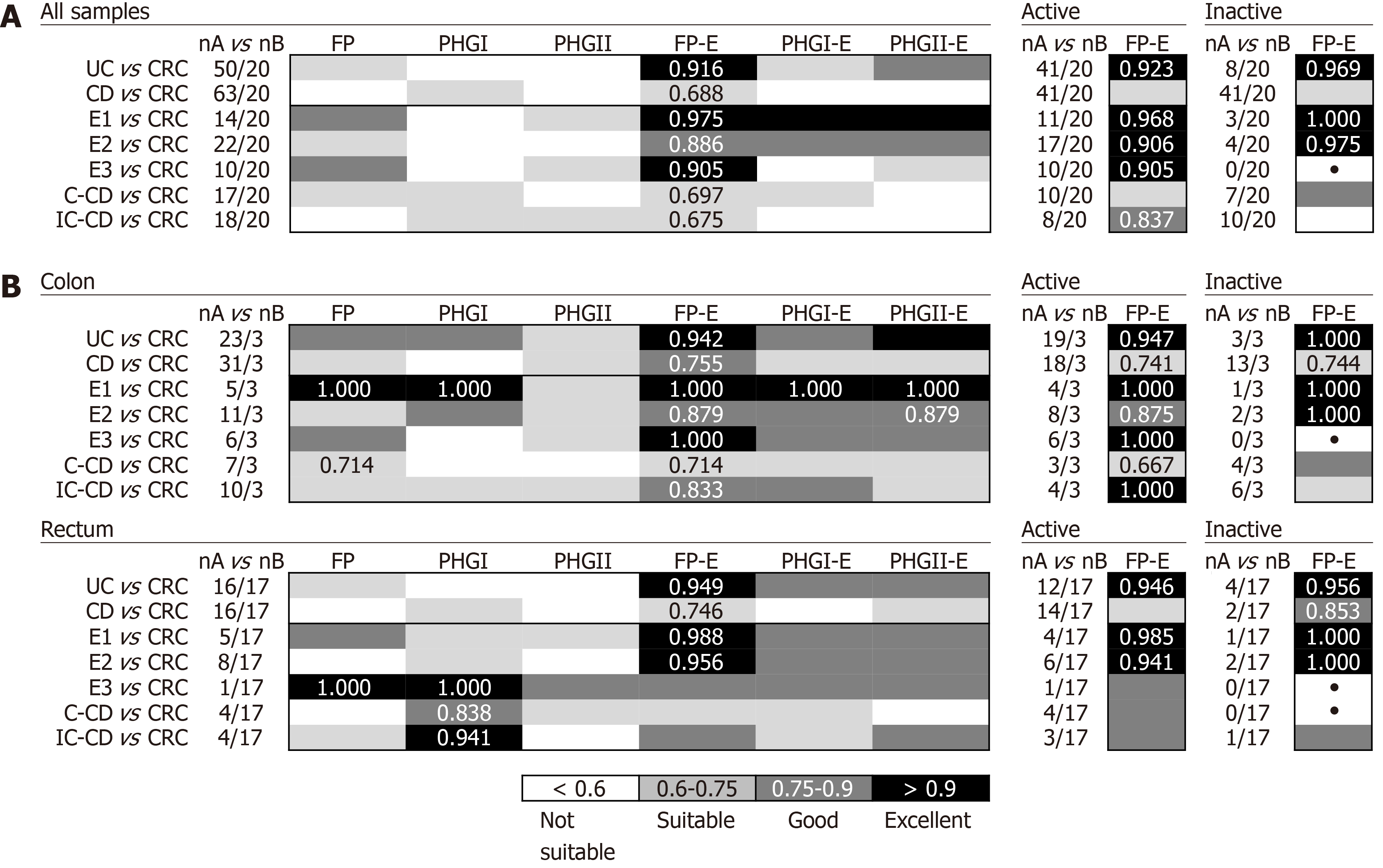
Figure 2 Usefulness of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, its phylogroups (PHGI and PHGII) and their index in conjunction to Escherichia coli to discriminate inflammatory bowel disease with colon inflammation and colorectal cancer by pooling all biopsy samples together (A) and by location of sampling (B).
For the best biomarker, results depicted by activity status of the patients are shown in the right panels. Best area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values for each comparison are shown. •: AUC not calculated (comparisons with one empty group of subjects). E1: Ulcerative proctitis; E2: Distal UC; E3: Extensive UC or ulcerative pancolitis; C-CD: Colonic-CD; IC-CD: Ileocolonic-CD; FP: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CRC: Colorectal cancer; CD: Crohn’s disease.
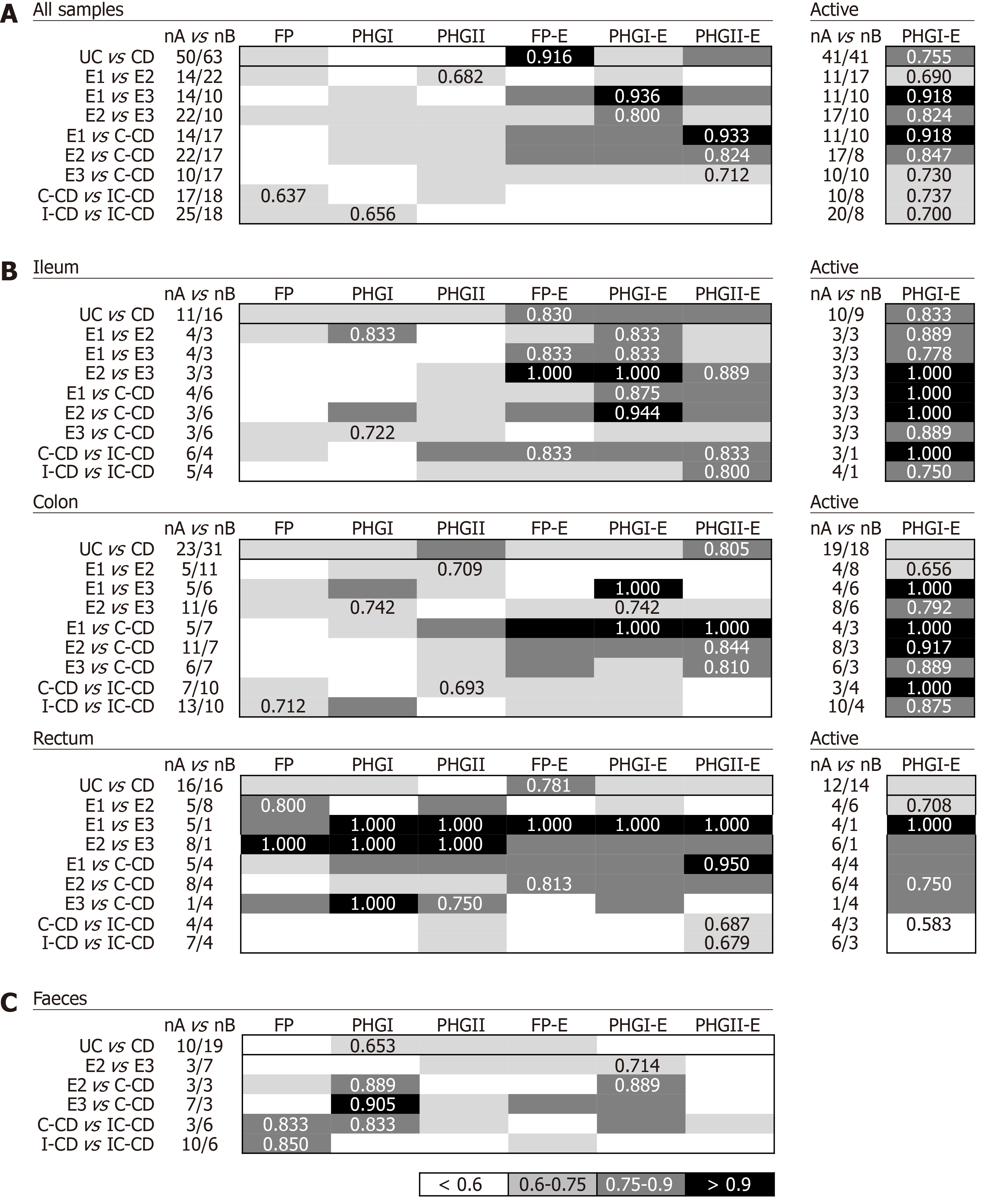
Figure 3 Usefulness of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, its phylogroups (PHGI and PHGII) and their index in conjunction to Escherichia coli to discriminate within inflammatory bowel disease with colon inflammation taking into account all biopsy samples together (A), by location of sampling (B) and faeces (C).
For tissue samples, selected results for PHGI- Escherichia coli of active patients are shown in the right panels. Data for inactive patients is not included because of the small cohort engaged. Best area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values for each comparison are shown. UC: Ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn’s disease; E1: Ulcerative proctitis; E2: Distal UC; E3: Extensive UC or ulcerative pancolitis; C-CD: Colonic-CD; IC-CD: Ileocolonic-CD; FP: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CRC: Colorectal cancer; CD: Crohn’s disease.
- Citation: Lopez-Siles M, Aldeguer X, Sabat-Mir M, Serra-Pagès M, Duncan SH, Flint HJ, Garcia-Gil LJ, Martinez-Medina M. Evaluation of bacterial biomarkers to aid in challenging inflammatory bowel diseases diagnostics and subtype classification. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2020; 11(3): 64-77
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v11/i3/64.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v11.i3.64