Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2015; 7(12): 438-447
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438
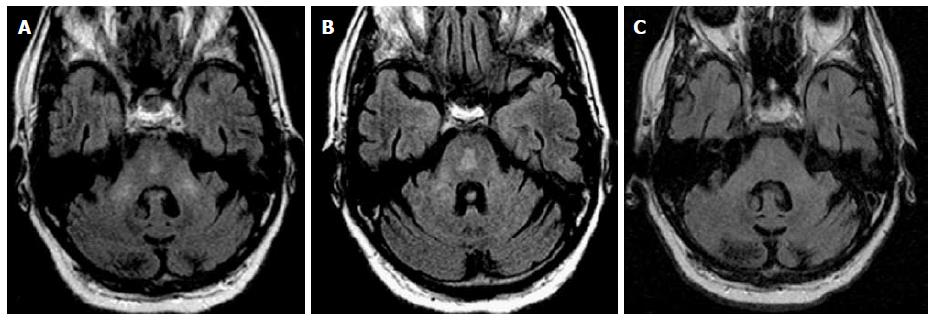
Figure 5 Osmotic demyelination syndrome.
History of ethanol abuse and rapid correction of hyponatremia. A and B: Axial FLAIR images at two different levels of the pons show abnormal signal in the bilateral MCP as well as abnormal signal in the central pons with subtle “trident” appearance; C: Three months f/u demonstrate resolution of abnormal signal in the MCP and pons. ODS characteristically involve the central pons with sparing of the corticospinal tract, peripheral pons and tegmentum. In some acute cases, restricted diffusion is possible, differing from ischemic insult, which extends to the periphery of the pons with sparing of the midline (see Figure 9B). ODS: Osmotic demyelination syndrome; MCP: Middle cerebellar peduncles.
- Citation: Morales H, Tomsick T. Middle cerebellar peduncles: Magnetic resonance imaging and pathophysiologic correlate. World J Radiol 2015; 7(12): 438-447
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i12/438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438