Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i10.231
Peer-review started: July 17, 2020
First decision: September 21, 2020
Revised: September 27, 2020
Accepted: October 13, 2020
Article in press: October 13, 2020
Published online: October 28, 2020
Processing time: 103 Days and 11.6 Hours
7T cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) introduces several advantages, as well as some limitations, compared to lower-field imaging. The capabilities of ultra-high field (UHF) MRI have not been fully exploited in cardiac functional imaging.
To optimize 7T cardiac MRI functional imaging without the need for conducting B1 shimming or subject-specific tuning, which improves scan efficiency. In this study, we provide results from phantom and in vivo scans using a multi-channel transceiver modular coil.
We investigated the effects of adding a dielectric pad at different locations next to the imaged region of interest on improving image quality in subjects with different body habitus. We also investigated the effects of adjusting the imaging flip angle in cine and tagging sequences on improving image quality, B1 field homogeneity, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), blood-myocardium contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and tagging persistence throughout the cardiac cycle.
The results showed the capability of achieving improved image quality with high spatial resolution (0.75 mm × 0.75 mm × 2 mm), high temporal resolution (20 ms), and increased tagging persistence (for up to 1200 ms cardiac cycle duration) at 7T cardiac MRI after adjusting scan set-up and imaging parameters. Adjusting the imaging flip angle was essential for achieving optimal SNR and myocardium-to-blood CNR. Placing a dielectric pad at the anterior left position of the chest resulted in improved B1 homogeneity compared to other positions, especially in subjects with small chest size.
Improved regional and global cardiac functional imaging can be achieved at 7T MRI through simple scan set-up adjustment and imaging parameter optimization, which would allow for more streamlined and efficient UHF cardiac MRI.
Core Tip: The capabilities of ultra-high-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have not been fully exploited in cardiac functional imaging. In this study, we provide results from phantom and in vivo scans using a multi-channel transceiver modular coil to optimize 7T cardiac MRI functional imaging without the need for conducting B1 shimming or subject-specific system tuning. The results showed that improved regional and global cardiac functional imaging can be achieved at 7T MRI through simple scan set-up adjustment and imaging parameter optimization, which would allow for more streamlined and efficient ultra-high-field cardiac MRI with access to more information and details compared to lower-field imaging.
- Citation: Ibrahim EH, Arpinar VE, Muftuler LT, Stojanovska J, Nencka AS, Koch KM. Cardiac functional magnetic resonance imaging at 7T: Image quality optimization and ultra-high field capabilities. World J Radiol 2020; 12(10): 231-246
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v12/i10/231.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v12.i10.231
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for assessment of cardiac function due to its high resolution and tissue contrast. Cardiac MRI functional imaging can provide information not only about global heart function, e.g., ejection fraction (EF), but also about regional tissue contractility, e.g., myocardial strain using MRI tagging[1], where the latter has shown to reveal early manifestation of subclinical cardiac dysfunction that typically precedes EF reduction[2-6].
Cardiac function assessment using MRI has been established in clinical practice on 1.5T and 3T scanners, where it showed the capability for identification of different cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, and different valvular, vascular, and congenital heart diseases. Nevertheless, the capabilities of ultra-high field (UHF) MRI have not been fully exploited for cardiac functional imaging, which are expected to improve image quality and provide more information for better understanding of heart mechanics in both normal and pathophysiological conditions; thus, opening the door for new cardiac MRI applications[7-16].
With 7T MRI scanners from different vendors receiving clearance for clinical applications, it might be expected that 7T MRI will soon be adopted in clinical practice[7,8,17,18]. UHF MRI introduces several advantages, as well as some limitations, compared to lower-field imaging. As signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is proportional to magnetic field strength, 7T MRI provides more than double SNR compared to 3T imaging[19,20]. The enhanced SNR can be traded for improved image quality, higher spatial or temporal resolution, or shorter scan time. Furthermore, due to prolonged T1 relaxation times at 7T, improved tissue contrast can be achieved compared to lower magnetic fields[17]. The advantages of UHF imaging could lead to improved image quality, illustration of anatomical details, and shorter scan time, which are of particular importance in cardiac functional imaging.
Despite its advantages, high-field imaging at 7T is challenging due to a number of technical issues[9,11,21,22]. First, the applied radiofrequency (RF) field at such high frequency results in short wavelength (approximately 12 cm) and increased dielectric effect that can induce destructive and constructive wave interferences and results in distorted B1 field and non-uniform effective flip angle distribution with observed shading and signal drop-off effects[23,24]. Another challenge of UHF imaging is RF penetration to the posterior wall of the heart, where coils with dipole arrays provide superior penetration depth[25]. Imaging at UHF also results in increased B0 inhomogeneity[26,27] and specific absorption ratio (SAR) and noisy electrocardiogram (ECG) signal[22,28], although these effects are not prohibiting factors of conducting cardiac MRI at 7T. Besides technical challenges, UHF imaging could result in some undesirable effects on imaged subjects, where dizziness, nausea, metallic taste, light flashes, and peripheral nerve stimulations have been reported[7,10,29]. Nevertheless, there has been no significant clinical complications experienced at 7T MRI.
A promising technique for addressing B1 inhomogeneity in UHF imaging relies on parallel transmission methods[30,31] using multiple transmit RF channels[19,23,32]. Recent efforts have been made for developing multi-channel transceiver surface coil arrays tailored for UHF imaging[9,21,23,24,32-35]. The capability of independently modulating each coil element’s magnitude and phase allows for producing more uniform B1 field with less signal inhomogeneity across the imaged region while maintaining SAR within allowable limits. Furthermore, the modular design of such multi-channel coils allows for close fitting with the body, more patient’s comfort, and suitability for clinical applications[23,24]. The capabilities of combining multi-channel parallel imaging and simultaneous multi-slice acquisition for improving imaging efficiency have been recently investigated[36].
In this study, we provide preliminary results from phantom and in vivo scans using a multi-channel transceiver modular coil to optimize 7T cardiac MRI functional imaging without the need for conducting B1 shimming or subject-specific tuning, which improve scan efficiency. We investigate the effects of adding a dielectric pad at different locations next to the imaged region of interest on improving image quality in subjects with different body habitus. We also investigate the effects of adjusting the imaging flip angle in cine and tagging sequences on improving image quality, B1 field homogeneity, SNR, blood-myocardium contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and tagging persistence throughout the cardiac cycle.
This study was conducted with approval from our Institutional Review Board and informed consent was obtained from scanned human subjects. A static phantom and twelve healthy subjects were scanned on a GE MR950 7T whole-body scanner (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, United States) equipped with peak gradient amplitude and maximum slew rate of 50 mT/m and 200 T/m/s, respectively and using a 32-channel transceiver coil (MRI Tools, GmbH, Berlin, Germany). The modular coil array consists of 8 independent blocks: Four blocks located posteriorly in a planar fashion and four blocks located anteriorly in a bent fashion, which provide close fit to the chest with stable loading condition[9,37]. Each coil block contains 4 transceiver elements (2 × 2 array), whose phase settings were optimized based on simulations for a multi-oblique plane mimicking a standard cardiac view[37]. The coil elements are arranged in an interleaved fashion so that they are shifted from each other by a half-element size[9].
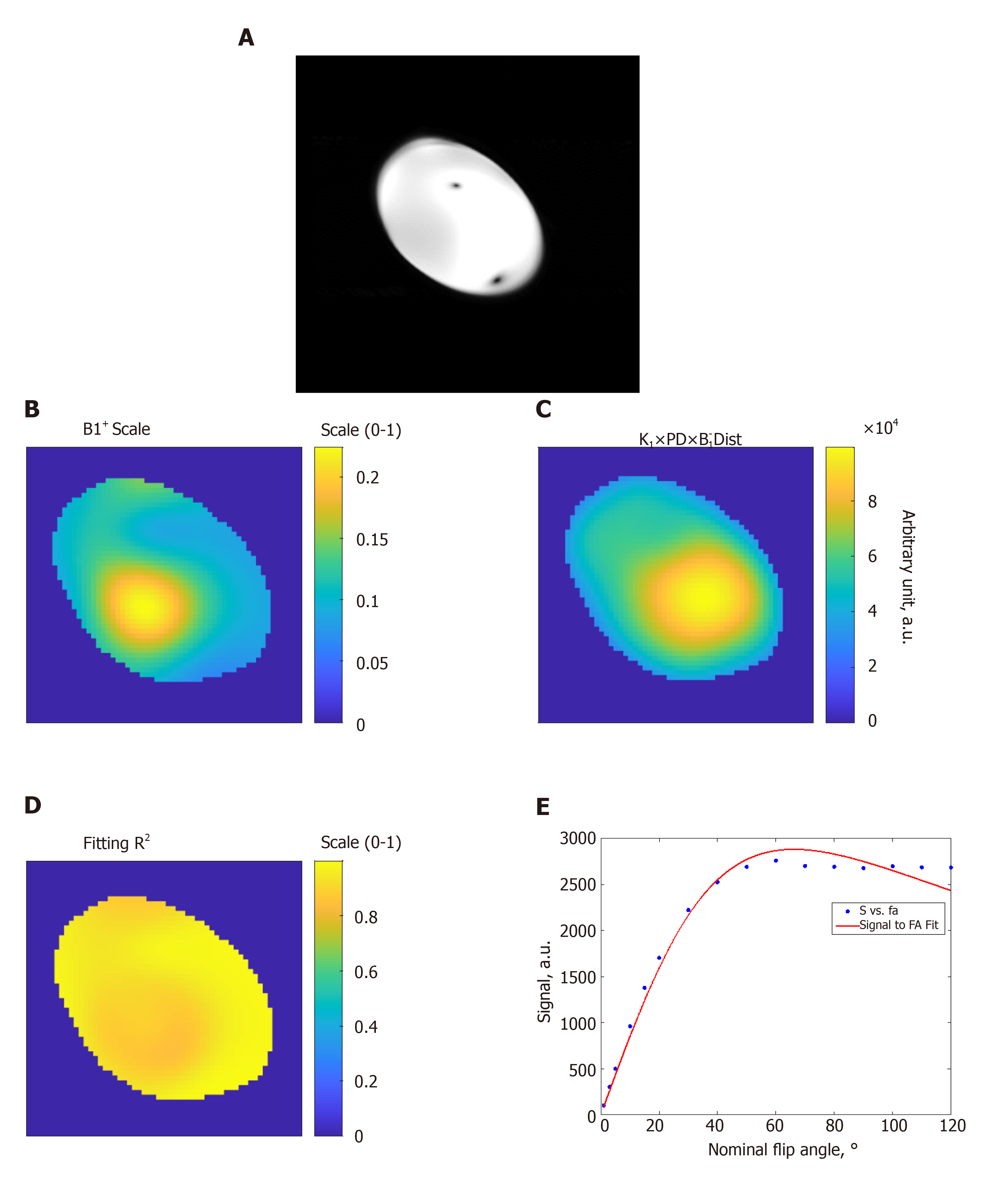
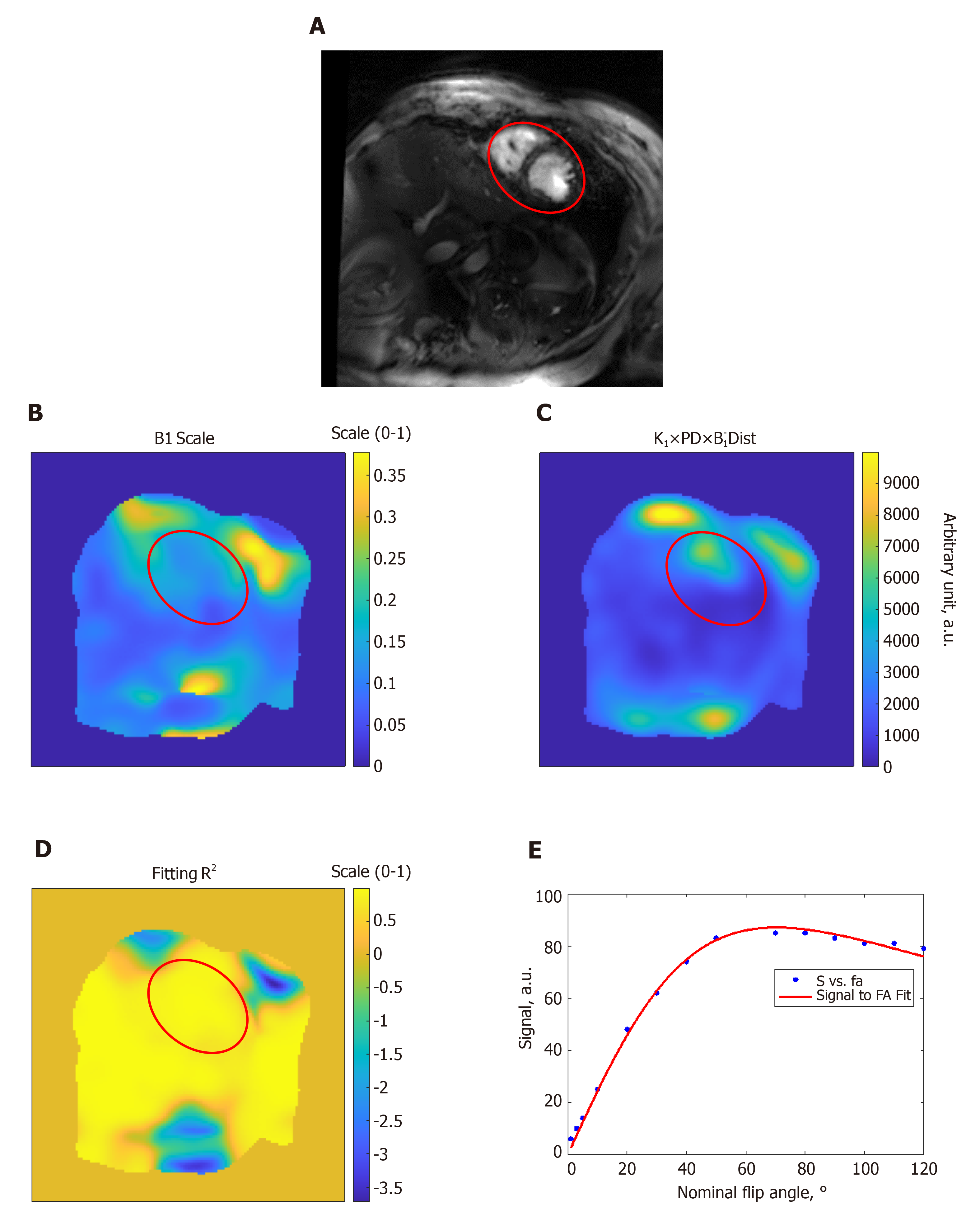
We conducted phantom and in vivo scans to generate an estimate of the B1 transmission frequency field in the imaged slice using the actual flip-angle imaging B1 mapping method[38,39]. A spoiled gradient echo cine sequence was used for repeated image acquisitions with nominal flip angles ranging from 1° to 120°, and forward simulation was conducted on the resulting images. To overcome the inherent motion problem in cardiac imaging, lowpass filtering was conducted to mitigate the motion problem and achieve better B1 estimates.
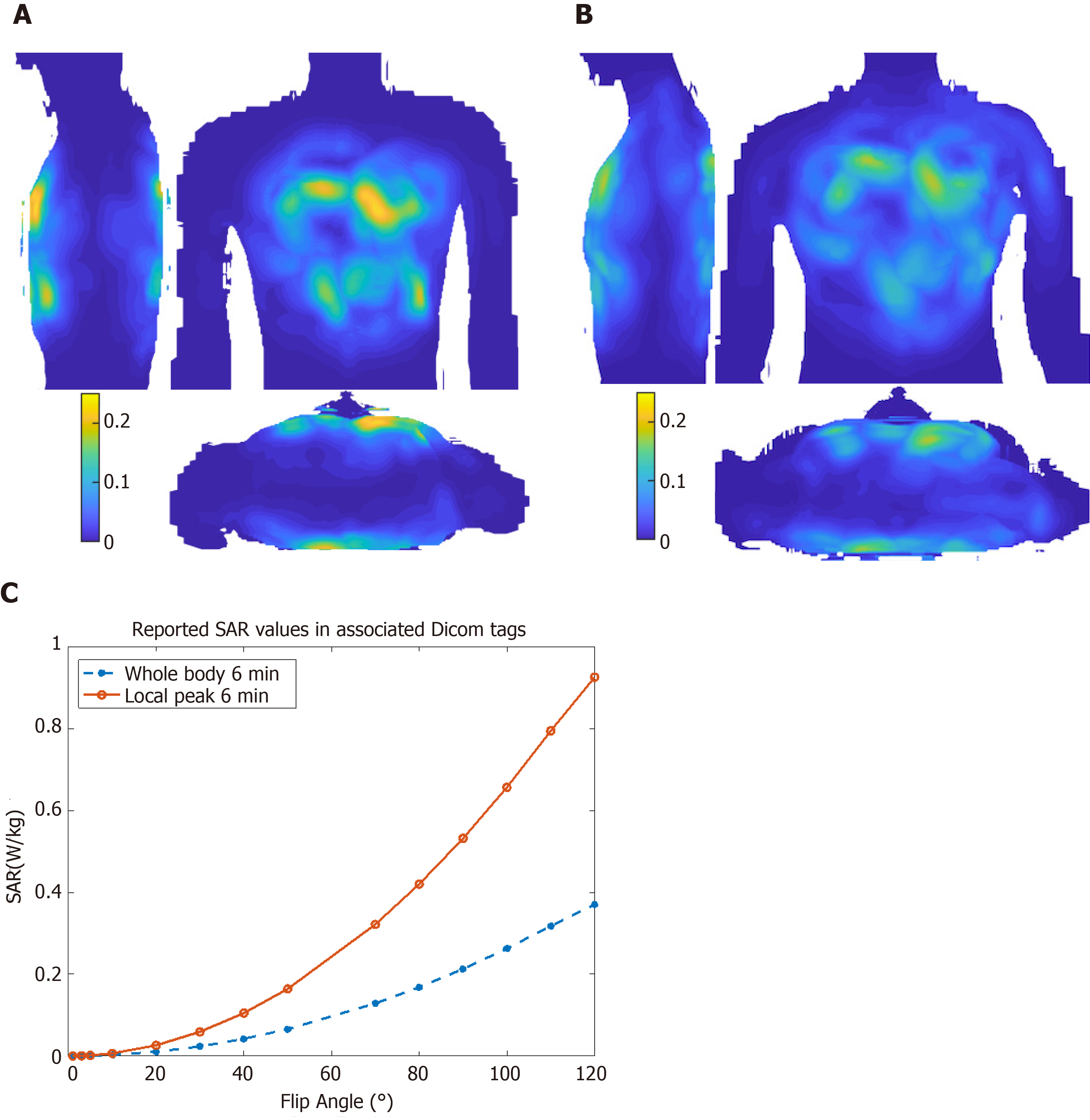
The MRI system first looks at the predicted global SAR, which is vendor-provided SAR tables specific to the coil used and its imaging mode (cardiac mode in this case). The 32 channels of the coil are grouped in blocks of four elements each with fixed inter-element phases for the transmission mode. The MRI system then calculates local SAR over a 10 g mass sample for the worst-case scenario using different virtual body models, as previously explained[40,41]. Upon comparing local and global SAR calculations, the more conservative one is taken into consideration and used for all scans.
Both cine and tagging images were acquired in the volunteers in standard cardiac short-axis and long-axis views, which are typically used for measuring cardiac functional parameters, e.g., EF. The coil placement and prescription flip angle were adjusted to improve image quality. Specifically, the effect of modifying the prescribed flip angle from 10° to 90° on myocardium SNR and myocardium-to-blood CNR was studied. Myocardial SNR was measured as the ratio between mean signal intensity in the myocardium divided by standard deviation (SD) of background noise. CNR was measured as the difference between mean signal intensities in blood and myocardium divided by SD of background noise.
The imaging parameters for cine imaging were as follows: Fast spoiled gradient echo sequence, repetition time (TR) = 8 ms, echo time (TE) = 4 ms, flip angle = 60°, matrix = 256 × 256, field-of-view (FOV) = 380 mm × 380 mm, slice thickness = 8 mm, acquisition bandwidth = 244 Hz/pixel, number of averages = 1, and number of cardiac phases = 25. The imaging parameters for the tagging sequence were as follows: Fast gradient echo sequence, TR = 4.9 ms, TE = 2 ms, flip angle = 15°, matrix = 256 × 256, FOV = 380 mm × 380 mm, slice thickness = 8 mm, acquisition bandwidth = 488 Hz/pixel, number of averages = 1, and number of cardiac phases = 25.
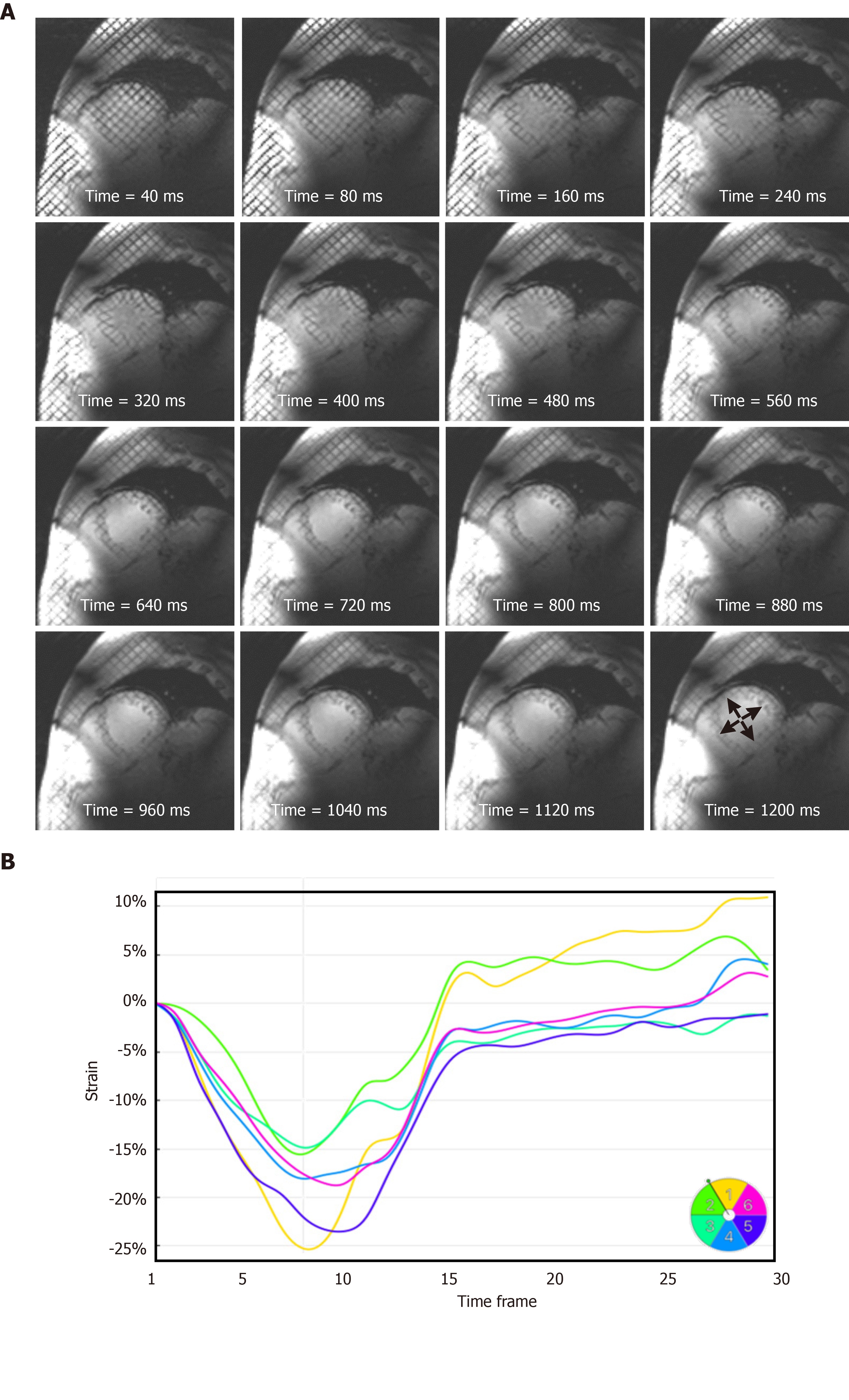
The elevated T1 value of normal myocardium at 7T (approximately 1900 ms at 7T compared to approximately 1150 ms and approximately 850 ms at 3T and 1.5T, respectively[9,42]) results in slower magnetization recovery towards equilibrium, and thus helps reduce taglines fading during later phases of the cardiac cycle. We conducted Bloch simulation to investigate the effect of elevated T1 value at 7T on improving tagging persistence compared to that at 1.5T. Furthermore, we used the sinusoidal modulation technique[43] to analyze the tagged images and measure myocardial strain in a subject with low heart rate of 50 beats per minute (bpm; cardiac cycle length = 1200 ms).
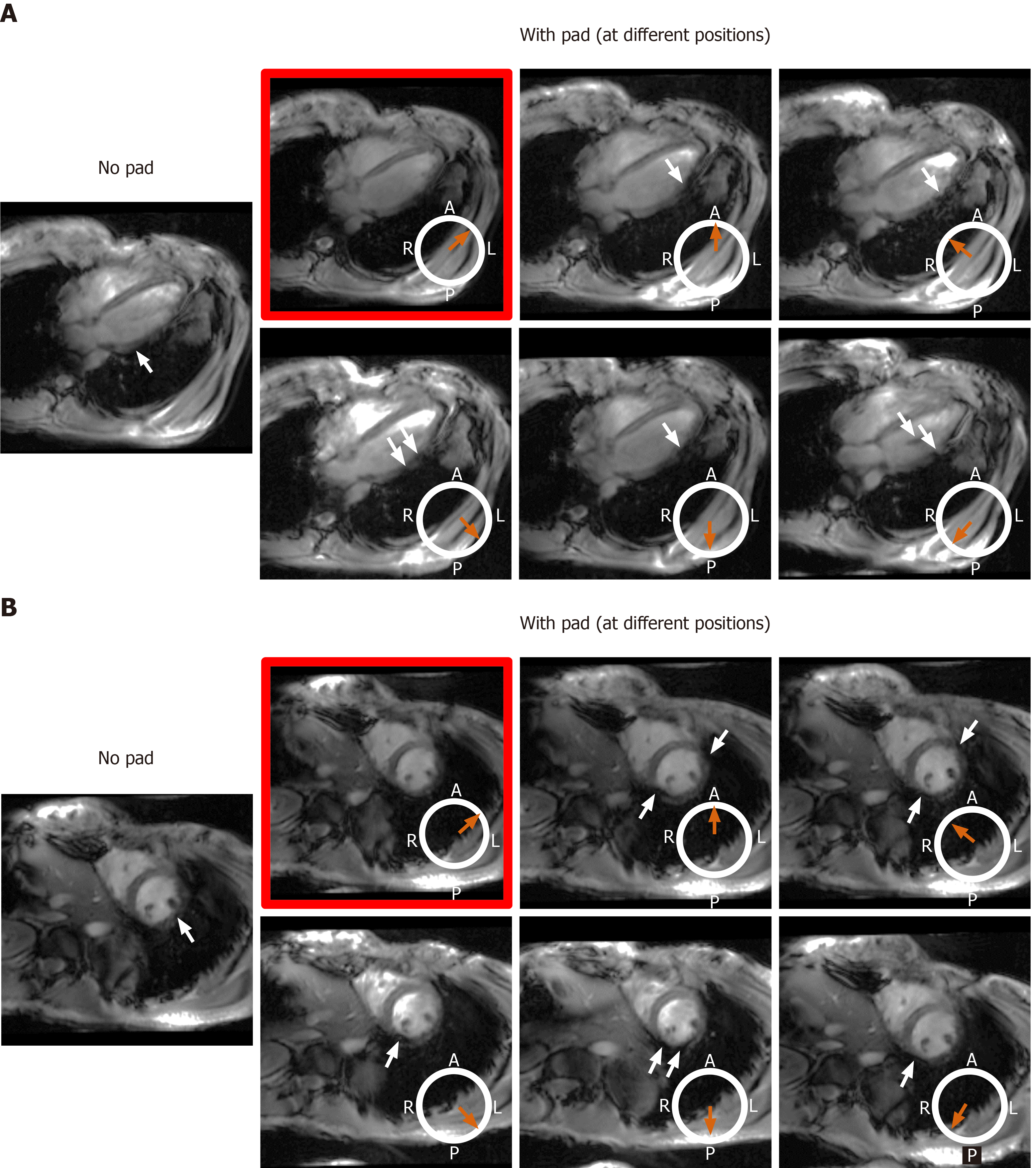
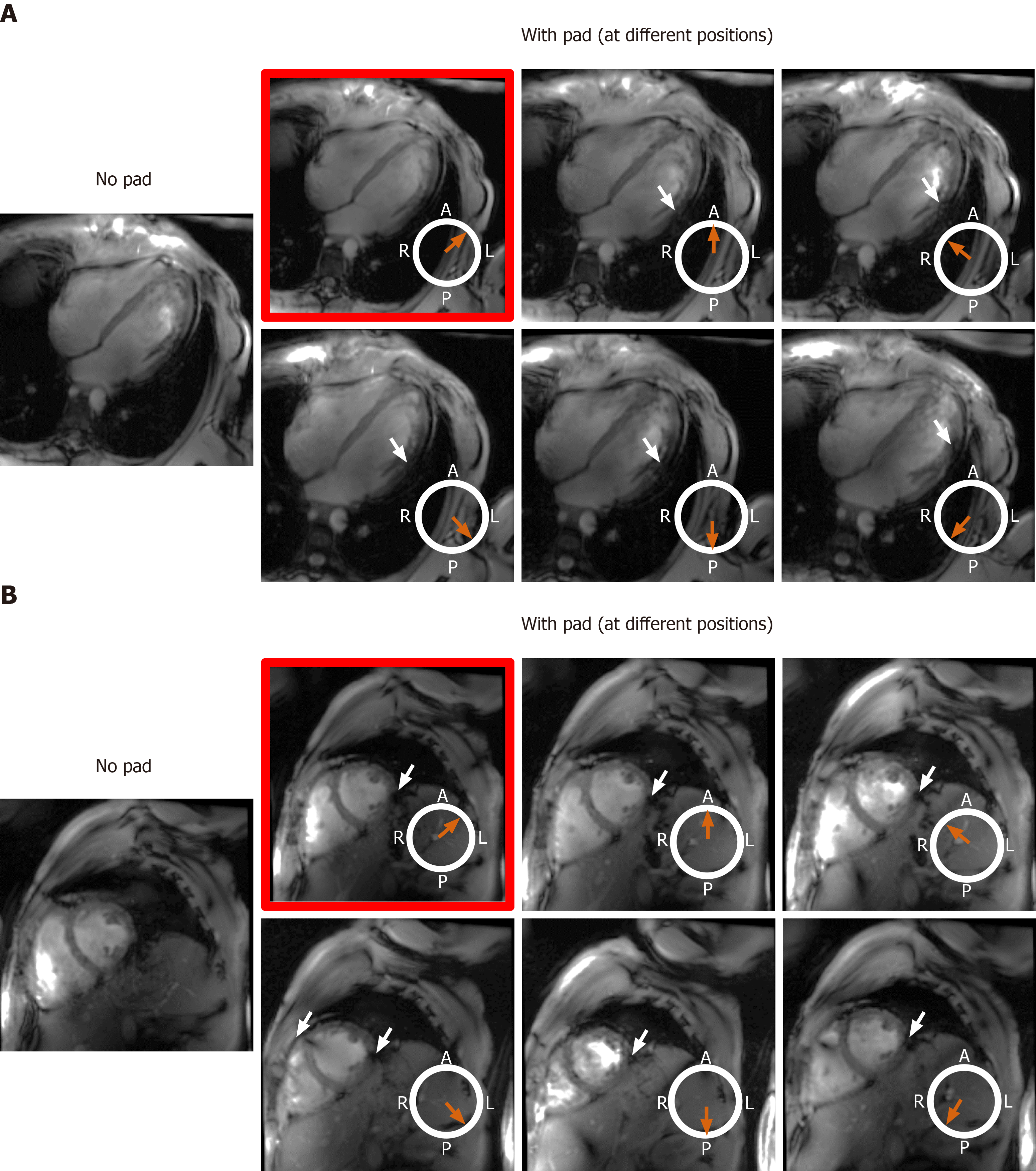
We investigated the effect of adding a dielectric pad (30 cm × 40 cm flexible pad from GE Healthcare, part number E8823JA) close to the imaged slice on improving B1 homogeneity. As moving the dielectric pad around the thorax area affects the presence and location of signal nulling regions, we studied the effect of changing the pad’s position in eight volunteers with different body habitus and chest size, which were divided into two groups. Group 1 consisted of four volunteers (2 males, 2 females) with small body habitus: Healthy-weight body mass index (BMI < 25 kg/m2) = 22.5 ± 2.5 kg/m2, chest expansion in the anterior-posterior and left-right directions = 24.8 ± 3.2 cm and 31.3 ± 2.2 cm, respectively. Group 2 consisted of four volunteers (2 males, 2 females) with larger body habitus: Overweight BMI (> 25 kg/m2) = 26.4 ± 1.1 kg/m2, chest expansion in the anterior-posterior and left-right directions = 28.8 ± 1.7 cm and 31.5 ± 2.4 cm, respectively.
With proper scan set-up and imaging parameter settings, all subjects were successfully scanned with good image quality. The ECG signal was reliable in all scans and image acquisition was correctly triggered at the R-wave, despite elevated T wave and noisier ECG signal compared to the case at lower magnetic fields.
Figures 1 and 2 show results from phantom and volunteer scans, respectively, to estimate the B1 field. The figures show signal intensity variation across the acquired slices, where the signal intensity profile changes with the prescribed flip angle. The estimated B1 map and proton density distribution reflect the observed signal intensity in the imaged slices, and the resulting R2 fitting maps show excellent data fitting.
Figure 3 shows maximum intensity projections of 10 g-averaged SAR normalized to 1W forward power at the coil plug using male and female virtual body models for a cardiac imaging[40]. Differences between male and female body habitus were taken into consideration for the virtual model simulation. For example, a breast mass of 490 g was used for female body simulation to account for the effects of the mammary glands on resulting calculations and their effect on image characteristics, e.g., signal nulling or contrast variation[40]. During volunteer scans, SAR is limited based on the chosen excitation mode[41], where worst-case scenario among different body models is taken into consideration and used for all cases. Figure 3 also shows local and global SAR values as reported by the Dicom tags for in vivo cine imaging with different flip angles, where local SAR is the limiting factor for SAR calculations.
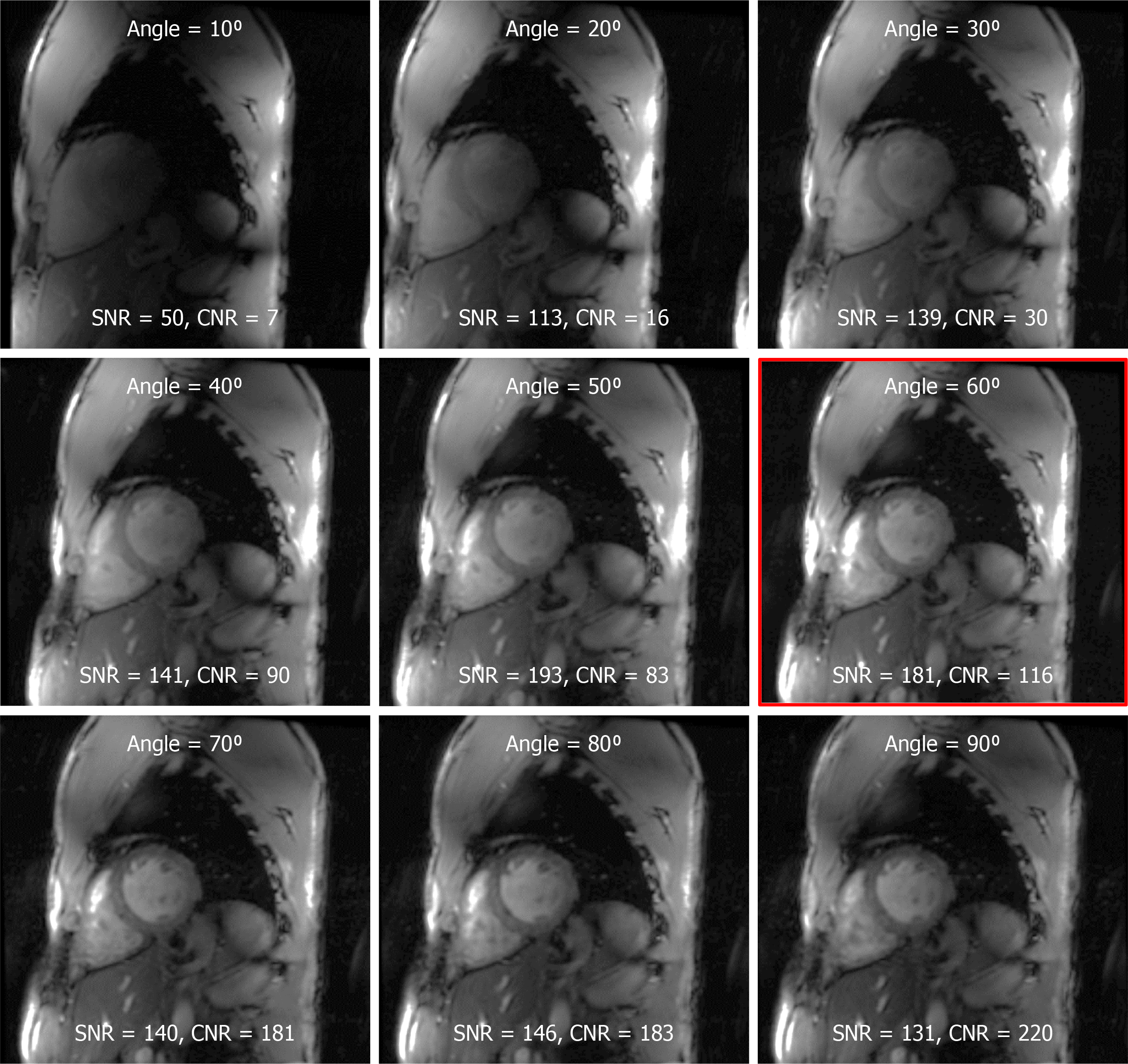
We found that moving the coil up towards the chin of the imaged subject (average of 5 cm offset shift of the coil center from heart center) resulted in improved signal intensity, especially at the basal and lateral regions of the heart, compared to when the coil was centered around the heart. The prescribed imaging flip angle played a key role in determining SNR and CNR (Figure 4). Due to the difference between nominal and actual flip angles at 7T imaging, as shown in Figures 1 and 2, the prescribed flip angle for gradient echo cine imaging at 7T needed to be much higher than that used at 1.5T and 3T fields (approximately 10°-20°). Based on results from this study, a prescribed flip angle of approximately 60° resulted in sufficient RF penetration and improved image quality. In the example shown in Figure 4, a 60° flip angle resulted in optimal SNR/CNR of 181/116, which is much higher than those reported at lower magnetic fields, for example SNR/CNR of 79/43 at 1.5T[44].
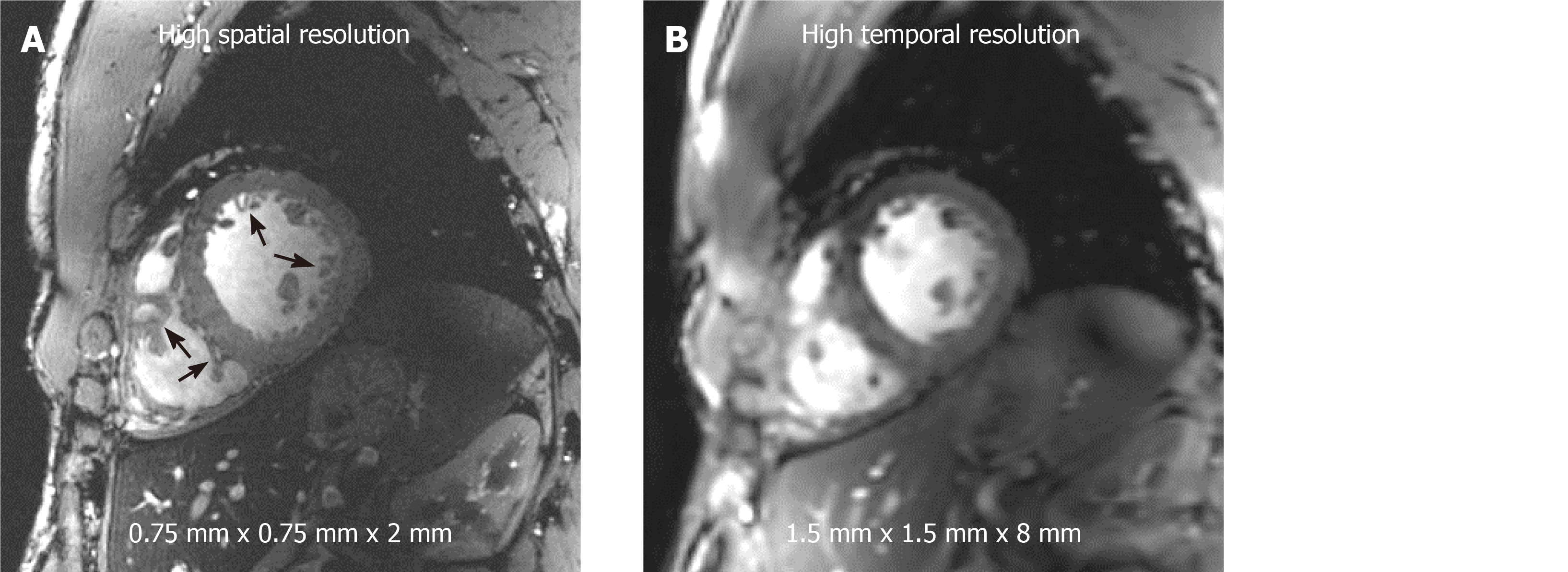
With high SNR at 7T, high spatial resolution can be achieved compared to that available at lower field strength. Figure 5 shows a high-resolution cine image with voxel size of 0.75 mm × 0.75 mm × 2 mm and the same slice acquired with conventional resolution of 1.5 mm × 1.5 mm × 8 mm that is typically used in clinical practice on 1.5T and 3T scanners. The high-resolution image shows fine anatomical details of the trabecula, papillary muscles, and right ventricle that appear blurry at conventional resolution. Otherwise, high SNR can be traded for improved temporal resolution, where we were able to achieve cine imaging with 20 ms temporal resolution (50 frames for a heart rate of 60 bpm) at conventional spatial resolution reported above.
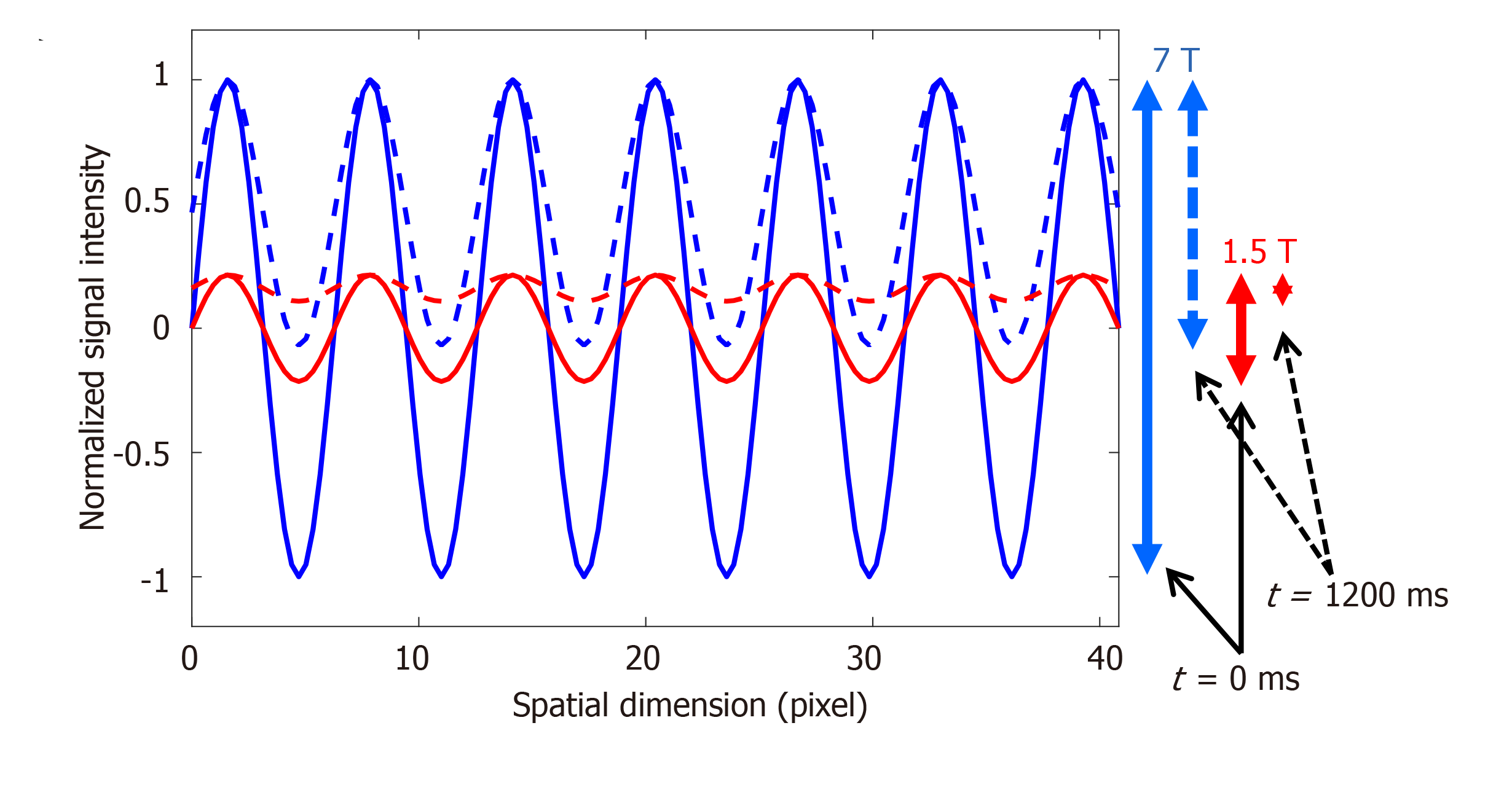
Figures 6 and 7 show the effect of elevated myocardial T1 value and large field strength at 7T on improving tagging persistence. Figure 6 shows the results of Bloch simulation of the tagging pattern evolution during a 1200 ms cardiac cycle (50 bpm heart rate) for both 7T and 1.5T field strengths. The slow magnetization recovery at 7T resulted in maintaining more than half (53%) of the original tagging contrast (measured as the peak-to-peak difference in signal intensity of the tagging pattern) by the end of the 1200 ms cardiac cycle at 7T, compared to only 24% of the original tagging contrast at 1.5T. When taking the field strength effect into consideration, then there is a reduction of 90% in tagging contrast when switching from 7T to 1.5T by the end the 1200 ms cardiac cycle. Therefore, it is typically difficult to measure myocardial strain at later diastolic cardiac phases for low-field imaging due to fading of the tagging pattern, which is not the case at 7T, as shown by the in vivo results in Figure 7 of a subject with heart rate of 50 bpm, where the tagging pattern was visible throughout the whole cardiac cycle and allowed for measuring strain throughout end-diastole. It should be noted that optimal prescribed flip angle for tagging MRI was 15°, as larger flip angles resulted in faster fading of the taglines. On the other hand, lower flip angles resulted in poor tissue contrast.
The effect of the dielectric pad’s position on improving B1 uniformity was impacted by the imaged subject’s body habitus (Figures 8 and 9). For volunteers with small-to-medium weight (BMI < 25 kg/m2), placing the pad at the anterior left position of the chest (the volunteers were scanned in the supine position) resulted in improved B1 uniformity compared to other anterior and posterior positions, as shown in Figure 8. This behavior was consistent in all scanned volunteer with small-to-medium body habitus. On the other hand, in volunteers with larger body habitus (BMI > 25 kg/m2), B1 uniformity was acceptable even without using the dielectric pad, and it was similar to the case when the pad was positioned in the anterior left position of the chest, as shown in Figure 9. Moving the pad to other positions resulted in less B1 uniformity and appearance of regions with signal nulling. This behavior was consistent in all scanned volunteers with large body habitus.
While the majority of UHF studies have focused on brain and orthopedic applications, recent improvements in multi-channel coil development opened the door for cardiac imaging to benefit from UHF MRI capabilities[9-11]. The results from this study show that high-quality global (cine) and regional (tagging) cardiac functional imaging can be obtained at 7T by simple optimization of the scan set-up and imaging parameters, especially to mitigate B1-related signal inhomogeneity effects.
Adjusting the prescription flip angle and adding a dielectric pad next to the imaged region-of-interest helped improve B1 homogeneity and reduce signal nulling artifacts. The actual flip angle across the heart can vary by as much as 50% from the nominal flip angle, even at 3T[45], which is imperative in certain applications that use 180° RF pulses as in fast spin-echo imaging and inversion-recovery-based T1 mapping[42]. Nevertheless, these constraints can be loosened in gradient-echo-based cardiac functional imaging by increasing the prescription flip angle to ensure sufficient RF penetration to the whole heart and generation of images with good SNR and tissue contrast.
It should be noted that shallow flip angle (15°) was used in acquisition of the tagged images, compared to 60° in the case of cine images, in order to maintain the tagging pattern throughout the whole cardiac cycle. Although larger flip angle results in better myocardium-to-blood contrast, it results in more tipping of the magnetization vector into the transverse plane, and therefore the magnetization pattern fades quickly due to short T2 relaxation time of the myocardium (approximately 50 ms). On the contrary, using a shallow flip angle allows for maintaining the tagging pattern for a long time due to slow longitudinal magnetization recovery with long myocardial T1 relaxation time (approximately 1900 ms). It should be noted that the shallow flip angle does not affect the tagging-to-myocardium contrast as the tag lines appear dark due to magnetization saturation during the tagging preparation step. Furthermore, because the tagging pattern is maintained in the myocardium and destroyed in the blood pool, due to blood motion, there is still good contrast between myocardium and blood in the tagged images.
Adding a dielectric pad next to the imaged region of interest and properly adjusting its location based on body habitus resulted in generating a more homogeneous B1 field around the heart, rendering patient-specific tuning and matching of individual coil elements unnecessary in this study, which helps streamline UHF cardiac imaging. Specifically, the results showed that: (1) Adding a dielectric pad had more effect on improving B1 homogeneity in subjects with small body habitus compared to subjects with large body habitus; and (2) Placing the dielectric pad in the anterior left position of the chest resulted in improved B1 homogeneity compared to other anterior and posterior positions. These results can be understood in light of the dielectric pad’s effect on changing B1 distribution in its vicinity, which is affected by the coil loading as a result of specific body habitus. Generally, the dielectric pad helps improve impedance matching for B1 field propagation[46]. Furthermore, the secondary local RF field in the pad enhances the original B1 field. The more effect noticed in subjects with small body habitus could be understood, in part, by the more pronounced standing wave effect in subjects with small chest area compared to those with larger chest area. The more effect of the dielectric pad when placed in the anterior left position could be understood because the pad is closest to the heart in this position, and thus has more effect on changing the B1 field around the heart.
Intrinsic characteristics of UHF imaging, e.g., prolonged myocardium T1 values, can be a key advantage for cardiac MRI tagging. As shown in this study, the prolonged myocardium T1 value resulted in improved tagging persistence throughout the whole cardiac cycle even at slow heart rates, which allowed for analyzing the myocardial contractility pattern until end-diastole, an appreciated feature considering the rapid taglines fading during late cardiac phases in conventional low-field imaging.
In this study, we showed the capability of 7T cardiac MRI for generating high-resolution cardiac cine images with voxel size that is 16 times smaller than that in clinical standards. Such high spatial resolution allows for visualizing detailed anatomical features without sacrificing SNR as one would expect in lower field MRI. This feature is appreciated in applications when high-fidelity anatomical details need to be imaged, e.g., in pediatric imaging, congenital heart diseases, diffusion tensor imaging of myofiber tractography, right ventricle imaging[44], and for patient triaging in certain cardiomyopathies[47]. Alternatively, the extra SNR in 7T MRI can be traded for high temporal resolution in applications where accurate measurements require high temporal resolution, e.g., flow imaging[13] and time-resolved cine imaging of patients with fast heart rate.
The transceiver modular coil used in this study allowed for obtaining high-quality in vivo images with high resolution and adequate myocardium-to-blood contrast. Future coil developments with increased number of RF transceiver elements would allow for even more improvement in scan performance and parallel imaging capability. Other advancements in developing shorter, actively shielded, and wider bore 7T magnets would allow for more adoption of UHF cardiac MRI in clinical practice.
One limitation of the current study is the limited number of studied subjects, which does not allow for conducting a thorough statistical analysis. Nevertheless, our goal in this study was to provide a proof-of-concept of improved quality 7T cardiac MRI cine and tagging imaging and illustrate achieved advantages compared to low-field imaging capabilities. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to focus on this important application, especially the effect of adding a dielectric pad on improving signal homogeneity and the capability of improving tagging imaging and strain analysis at 7T. Nevertheless, more studies on a larger cohort are warranted to confirm the results from this study and to investigate more details, e.g., the effect of the dielectric pad size or material on the results.
In conclusions, improved cardiac functional imaging can be achieved at 7T through simple scan set-up and imaging parameter adjustments, which would allow for more streamlined and efficient UHF cardiac imaging with more adoption in clinical practice and access to more information and details compared to lower-field imaging.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for assessment of cardiac function, which can provide information not only about global heart function, but also about regional tissue contractility patterns. With 7T MRI scanners from different vendors receiving clearance for clinical applications, it might be expected that 7T cardiac MRI will soon be adopted in clinical practice to get benefit from ultra-high field (UHF) capabilities.
The capabilities of UHF cardiac MRI have not been fully exploited in cardiac functional imaging, which are expected to improve image quality and provide more information compared to imaging capabilities at current clinical magnetic field strengths.
To optimize 7T cardiac MRI functional imaging without the need for conducting B1 shimming or subject-specific system tuning, which improves scan efficiency.
We conducted both phantom and in vivo scans using a multi-channel transceiver modular coil. We investigated the effects of adding a dielectric pad at different locations next to the imaged region of interest on improving image quality in subjects with different body habitus. We also investigated the effects of adjusting the imaging flip angle in cine and tagging sequences on improving image quality, B1 field homogeneity, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), blood-myocardium contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and tagging persistence throughout the cardiac cycle.
The results showed the capability of achieving improved image quality with high spatial resolution, high temporal resolution, and increased tagging persistence at 7T cardiac MRI after adjusting scan set-up and imaging parameters. Adjusting the imaging flip angle was essential for achieving optimal SNR and myocardium-to-blood CNR. Placing a dielectric pad at the anterior left position of the chest resulted in improved B1 homogeneity compared to other positions, especially in subjects with small chest size.
Improved regional and global cardiac functional imaging can be achieved at 7T MRI through simple scan set-up adjustment and imaging parameter optimization, which allows for access to more information and details compared to lower-field MRI.
The developed optimized MRI exam would allow for more streamlined and efficient UHF cardiac functional imaging. Future studies should investigate the clinical usefulness of the developed technique by implementing it on large number of patients with different cardiovascular diseases.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Corresponding Author's Membership in Professional Societies: International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine; Society of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance; Radiological Society of North America; Institute for Electric and Electronic Engineers; International Society of Cardio Oncology; and American Heart Association.
Specialty type: Radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging
Country/Territory of origin: United States
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Li M, Nassar G S-Editor: Huang P L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wu YXJ
| 1. | Manning WJ, Pennell DJ. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance: A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease. 3rd ed. Elsevier, 2018. |
| 2. | Ibrahim EH. Heart Mechanics: Magnetic Resonance Imaging―The Complete Guide. 1st ed. CRC Press, 2017. |
| 3. | Kongbundansuk S, Hundley WG. Noninvasive imaging of cardiovascular injury related to the treatment of cancer. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7:824-838. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Choi EY, Rosen BD, Fernandes VR, Yan RT, Yoneyama K, Donekal S, Opdahl A, Almeida AL, Wu CO, Gomes AS, Bluemke DA, Lima JA. Prognostic value of myocardial circumferential strain for incident heart failure and cardiovascular events in asymptomatic individuals: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2354-2361. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 116] [Cited by in RCA: 120] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Wong DT, Leong DP, Weightman MJ, Richardson JD, Dundon BK, Psaltis PJ, Leung MC, Meredith IT, Worthley MI, Worthley SG. Magnetic resonance-derived circumferential strain provides a superior and incremental assessment of improvement in contractile function in patients early after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Radiol. 2014;24:1219-1228. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Toro-Salazar OH, Gillan E, O'Loughlin MT, Burke GS, Ferranti J, Stainsby J, Liang B, Mazur W, Raman SV, Hor KN. Occult cardiotoxicity in childhood cancer survivors exposed to anthracycline therapy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:873-880. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 84] [Cited by in RCA: 88] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Niendorf T, Paul K, Oezerdem C, Graessl A, Klix S, Huelnhagen T, Hezel F, Rieger J, Waiczies H, Frahm J, Nagel AM, Oberacker E, Winter L. W(h)ither human cardiac and body magnetic resonance at ultrahigh fields? NMR Biomed. 2016;29:1173-1197. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Snyder CJ, DelaBarre L, Metzger GJ, van de Moortele PF, Akgun C, Ugurbil K, Vaughan JT. Initial results of cardiac imaging at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61:517-524. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 112] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Niendorf T, Graessl A, Thalhammer C, Dieringer MA, Kraus O, Santoro D, Fuchs K, Hezel F, Waiczies S, Ittermann B, Winter L. Progress and promises of human cardiac magnetic resonance at ultrahigh fields: a physics perspective. J Magn Reson. 2013;229:208-222. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Niendorf T, Sodickson DK, Krombach GA, Schulz-Menger J. Toward cardiovascular MRI at 7 T: clinical needs, technical solutions and research promises. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:2806-2816. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Frauenrath T, Prothmann M, Dieringer MA, Hezel F, Renz W, Kretschel K, Niendorf T, Schulz-Menger J. Cardiac chamber quantification using magnetic resonance imaging at 7 Tesla--a pilot study. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:2844-2852. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Brandts A, Westenberg JJ, Versluis MJ, Kroft LJ, Smith NB, Webb AG, de Roos A. Quantitative assessment of left ventricular function in humans at 7 T. Magn Reson Med. 2010;64:1471-1477. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Hess AT, Bissell MM, Ntusi NA, Lewis AJ, Tunnicliffe EM, Greiser A, Stalder AF, Francis JM, Myerson SG, Neubauer S, Robson MD. Aortic 4D flow: quantification of signal-to-noise ratio as a function of field strength and contrast enhancement for 1.5T, 3T, and 7T. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73:1864-1871. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Huelnhagen T, Hezel F, Serradas Duarte T, Pohlmann A, Oezerdem C, Flemming B, Seeliger E, Prothmann M, Schulz-Menger J, Niendorf T. Myocardial effective transverse relaxation time T2* Correlates with left ventricular wall thickness: A 7.0 T MRI study. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77:2381-2389. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Tao Y, Hess AT, Keith GA, Rodgers CT, Liu A, Francis JM, Neubauer S, Robson MD. Optimized saturation pulse train for human first-pass myocardial perfusion imaging at 7T. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73:1450-1456. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Harteveld AA, van der Kolk AG, Zwanenburg JJ, Luijten PR, Hendrikse J. 7-T MRI in Cerebrovascular Diseases: Challenges to Overcome and Initial Results. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;25:89-100. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Stäb D, Al Najjar A, O'Brien K, Strugnell W, Richer J, Rieger J, Niendorf T, Barth M. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7 Tesla. J Vis Exp. 2019;:. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Hoff MN, McKinney A 4th, Shellock FG, Rassner U, Gilk T, Watson RE Jr, Greenberg TD, Froelich J, Kanal E. Safety Considerations of 7-T MRI in Clinical Practice. Radiology. 2019;292:509-518. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Pohmann R, Speck O, Scheffler K. Signal-to-noise ratio and MR tissue parameters in human brain imaging at 3, 7, and 9.4 tesla using current receive coil arrays. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75:801-809. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 206] [Cited by in RCA: 270] [Article Influence: 27.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Erturk MA, Li X, Van de Moortele PF, Ugurbil K, Metzger GJ. Evolution of UHF Body Imaging in the Human Torso at 7T: Technology, Applications, and Future Directions. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;28:101-124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Steensma BR, Voogt IJ, Leiner T, Luijten PR, Habets J, Klomp DWJ, van den Berg CAT, Raaijmakers AJE. An 8-channel Tx/Rx dipole array combined with 16 Rx loops for high-resolution functional cardiac imaging at 7 T. MAGMA. 2018;31:7-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | van Elderen SG, Versluis MJ, Webb AG, Westenberg JJ, Doornbos J, Smith NB, de Roos A, Stuber M. Initial results on in vivo human coronary MR angiography at 7 T. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62:1379-1384. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Gräßl A, Winter L, Thalhammer C, Renz W, Kellman P, Martin C, von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Tkachenko V, Schulz-Menger J, Niendorf T. Design, evaluation and application of an eight channel transmit/receive coil array for cardiac MRI at 7.0 T. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:752-759. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Thalhammer C, Renz W, Winter L, Hezel F, Rieger J, Pfeiffer H, Graessl A, Seifert F, Hoffmann W, von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Tkachenko V, Schulz-Menger J, Kellman P, Niendorf T. Two-dimensional sixteen channel transmit/receive coil array for cardiac MRI at 7.0 T: design, evaluation, and application. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36:847-857. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Ertürk MA, Raaijmakers AJ, Adriany G, Uğurbil K, Metzger GJ. A 16-channel combined loop-dipole transceiver array for 7 Tesla body MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77:884-894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 120] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Spincemaille P, Anderson J, Wu G, Yang B, Fung M, Li K, Li S, Kovanlikaya I, Gupta A, Kelley D, Benhamo N, Wang Y. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: MRI at 7T versus 3T. J Neuroimaging. 2020;30:65-75. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Stockmann JP, Wald LL. In vivo B0 field shimming methods for MRI at 7T. Neuroimage. 2018;168:71-87. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 13.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Frauenrath T, Hezel F, Heinrichs U, Kozerke S, Utting JF, Kob M, Butenweg C, Boesiger P, Niendorf T. Feasibility of cardiac gating free of interference with electro-magnetic fields at 1.5 Tesla, 3.0 Tesla and 7.0 Tesla using an MR-stethoscope. Invest Radiol. 2009;44:539-547. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Klix S, Els A, Paul K, Graessl A, Oezerdem C, Weinberger O, Winter L, Thalhammer C, Huelnhagen T, Rieger J, Mehling H, Schulz-Menger J, Niendorf T. On the subjective acceptance during cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging at 7.0 Tesla. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0117095. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Orzada S, Solbach K, Gratz M, Brunheim S, Fiedler TM, Johst S, Bitz AK, Shooshtary S, Abuelhaija A, Voelker MN, Rietsch SHG, Kraff O, Maderwald S, Flöser M, Oehmigen M, Quick HH, Ladd ME. A 32-channel parallel transmit system add-on for 7T MRI. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0222452. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Rietsch SHG, Orzada S, Bitz AK, Gratz M, Ladd ME, Quick HH. Parallel transmit capability of various RF transmit elements and arrays at 7T MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2018;79:1116-1126. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Schmitter S, Wu X, Uğurbil K, Van de Moortele PF. Design of parallel transmission radiofrequency pulses robust against respiration in cardiac MRI at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2015;74:1291-1305. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Winter L, Kellman P, Renz W, Gräßl A, Hezel F, Thalhammer C, von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Tkachenko V, Schulz-Menger J, Niendorf T. Comparison of three multichannel transmit/receive radiofrequency coil configurations for anatomic and functional cardiac MRI at 7.0T: implications for clinical imaging. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:2211-2220. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Ruytenberg T, Webb A, Zivkovic I. Shielded-coaxial-cable coils as receive and transceive array elements for 7T human MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2020;83:1135-1146. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 8.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Yan X, Zhang X, Gore JC, Grissom WA. Improved traveling-wave efficiency in 7T human MRI using passive local loop and dipole arrays. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;39:103-109. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Schmitter S, Moeller S, Wu X, Auerbach EJ, Metzger GJ, Van de Moortele PF, Uğurbil K. Simultaneous multislice imaging in dynamic cardiac MRI at 7T using parallel transmission. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77:1010-1020. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Graessl A, Renz W, Hezel F, Dieringer MA, Winter L, Oezerdem C, Rieger J, Kellman P, Santoro D, Lindel TD, Frauenrath T, Pfeiffer H, Niendorf T. Modular 32-channel transceiver coil array for cardiac MRI at 7.0T. Magn Reson Med. 2014;72:276-290. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Yarnykh VL. Actual flip-angle imaging in the pulsed steady state: a method for rapid three-dimensional mapping of the transmitted radiofrequency field. Magn Reson Med. 2007;57:192-200. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 743] [Cited by in RCA: 812] [Article Influence: 45.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Schmitter S, DelaBarre L, Wu X, Greiser A, Wang D, Auerbach EJ, Vaughan JT, Uğurbil K, Van de Moortele PF. Cardiac imaging at 7 Tesla: Single- and two-spoke radiofrequency pulse design with 16-channel parallel excitation. Magn Reson Med. 2013;70:1210-1219. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Christ A, Kainz W, Hahn EG, Honegger K, Zefferer M, Neufeld E, Rascher W, Janka R, Bautz W, Chen J, Kiefer B, Schmitt P, Hollenbach HP, Shen J, Oberle M, Szczerba D, Kam A, Guag JW, Kuster N. The Virtual Family--development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:N23-N38. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1016] [Cited by in RCA: 706] [Article Influence: 44.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Eichfelder G, Gebhardt M. Local specific absorption rate control for parallel transmission by virtual observation points. Magn Reson Med. 2011;66:1468-1476. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in RCA: 196] [Article Influence: 14.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Rodgers CT, Piechnik SK, Delabarre LJ, Van de Moortele PF, Snyder CJ, Neubauer S, Robson MD, Vaughan JT. Inversion recovery at 7 T in the human myocardium: measurement of T(1), inversion efficiency and B(1) (+). Magn Reson Med. 2013;70:1038-1046. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Arts T, Prinzen FW, Delhaas T, Milles JR, Rossi AC, Clarysse P. Mapping displacement and deformation of the heart with local sine-wave modeling. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29:1114-1123. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Tkachenko V, Winter L, Rieger J, Thalhammer C, Hezel F, Graessl A, Dieringer MA, Niendorf T, Schulz-Menger J. Assessment of the right ventricle with cardiovascular magnetic resonance at 7 Tesla. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013;15:23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Suttie JJ, Delabarre L, Pitcher A, van de Moortele PF, Dass S, Snyder CJ, Francis JM, Metzger GJ, Weale P, Ugurbil K, Neubauer S, Robson M, Vaughan T. 7 Tesla (T) human cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging using FLASH and SSFP to assess cardiac function: validation against 1.5 T and 3 T. NMR Biomed. 2012;25:27-34. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Yang QX, Mao W, Wang J, Smith MB, Lei H, Zhang X, Ugurbil K, Chen W. Manipulation of image intensity distribution at 7.0 T: passive RF shimming and focusing with dielectric materials. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:197-202. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 101] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Prothmann M, von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff F, Töpper A, Dieringer MA, Shahid E, Graessl A, Rieger J, Lysiak D, Thalhammer C, Huelnhagen T, Kellman P, Niendorf T, Schulz-Menger J. High Spatial Resolution Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance at 7.0 Tesla in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy - First Experiences: Lesson Learned from 7.0 Tesla. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0148066. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |