Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2018; 10(7): 65-77
Published online Jul 28, 2018. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v10.i7.65
Published online Jul 28, 2018. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v10.i7.65
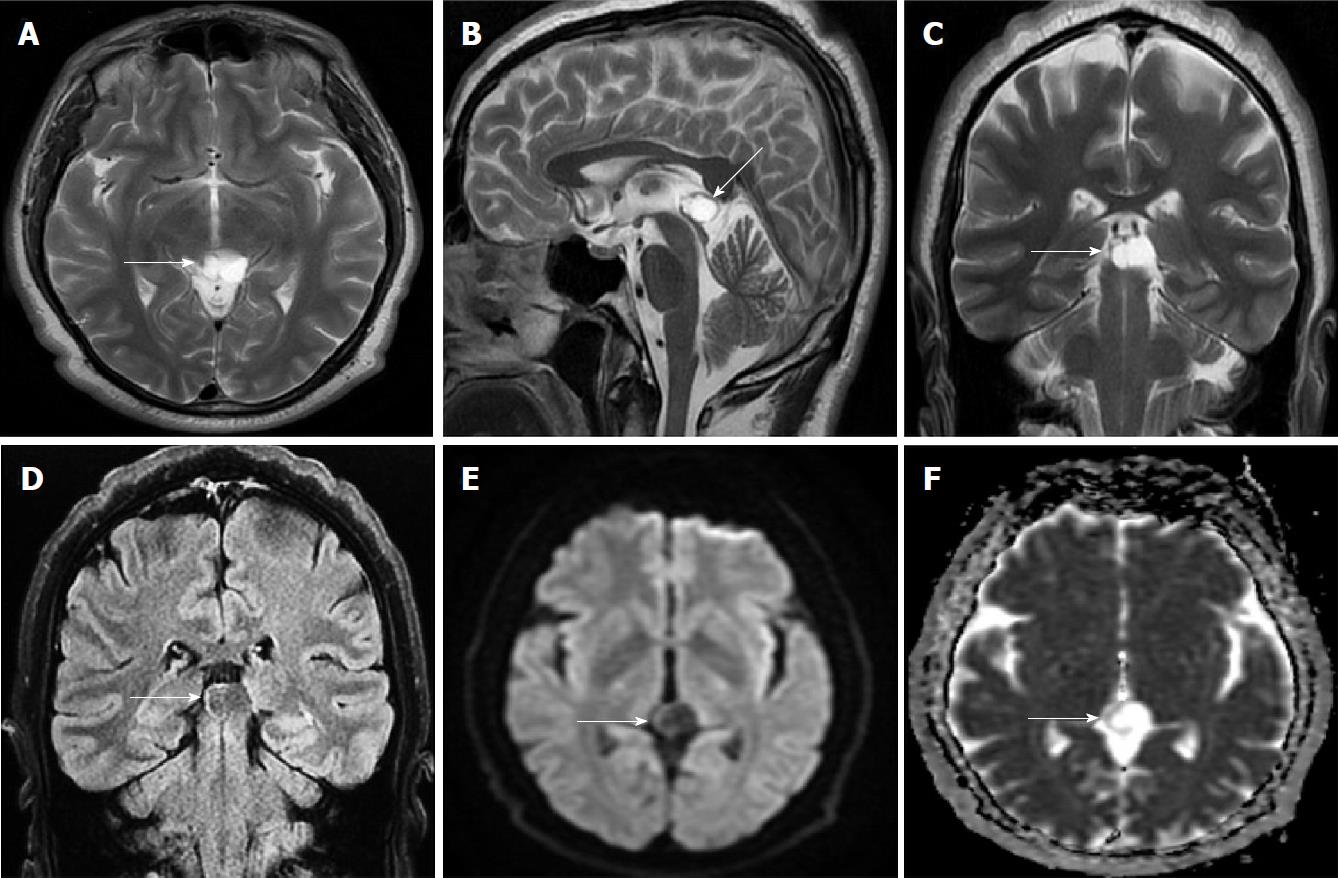
Figure 4 Fifty years old male patient with atypical pineal cyst (patient No.
40). Axial plane (A) sagittal plane magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (B) coronal plane T2 weighted (C) and coronal plane FLAIR magnetic resonance imaging (D) axial plane diffusion weighted imaging (E) axial plane apparent diffusion coefficient map (F). A, B, C, D, E and F: Bilocular, lobule contoured atypical pineal cyst is shown in pineal area (white arrows); D: The slightly hyperintense pineal cyst compared to CSF is shown on FLAIR sequence; E and F: No diffusion restriction. CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; FLAIR: Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery.
- Citation: Gokce E, Beyhan M. Evaluation of pineal cysts with magnetic resonance imaging. World J Radiol 2018; 10(7): 65-77
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v10/i7/65.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v10.i7.65