Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2017; 9(12): 454-458
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i12.454
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v9.i12.454
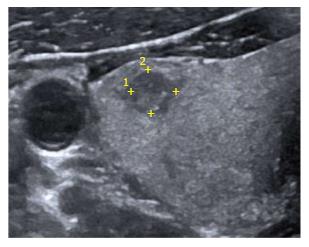
Figure 1 High resolution ultrasonography of the neck reveals a well-defined heteroechoic lesion in the right lobe of thyroid gland which appeared indeterminate on imaging (TIRADS 4B).
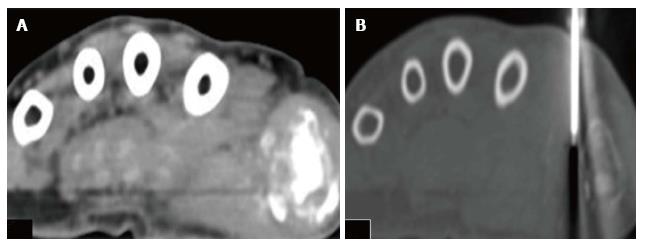
Figure 2 Axial computed tomography of the hand.
The patient is positioned in prone position. A: Axial CT scan image in soft tissue window; B: Axial CT scan image in bone window is showing Trucut biopsy needle taking tissue sample from the soft tissue component surrounding the area of lytic destructive lesion at the first metacarpo-phalangeal joint. CT: Computed tomography.
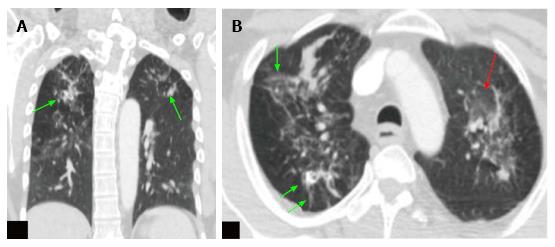
Figure 3 Computed tomography thorax images of the positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan.
A: Coronal CT scan image of the thorax in lung window; B: Axial CT scan image of the thorax in lung window at upper thorax. These images show ground glass opacities (red arrow) with multiple soft tissue density nodules (green arrow), fibrotic changes and calcified granulomas in both the lungs. Features are suggestive of active tuberculosis. CT: Computed tomography.
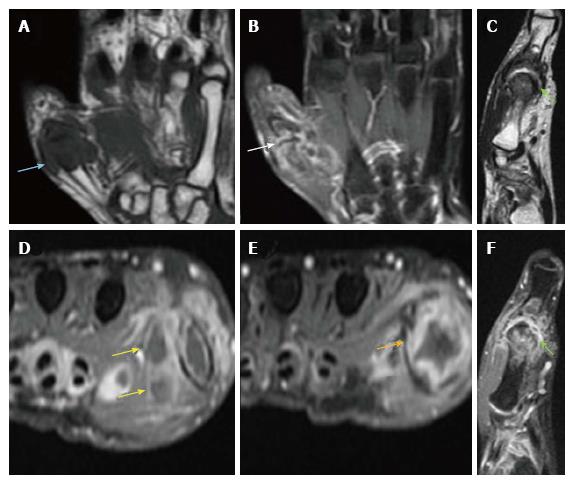
Figure 4 Plain and contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging images of proximal hand.
A: Coronal T1W. Hypointense soft-tissue is noted surrounding the first MCP joint with hypointense marrow changes; B: Coronal STIR. Irregular hyperintensities are seen surrounding the first MCP joint along with hyperintensity within the peri-articular bone marrow; C: Sagittal T2W. Mild joint effusion is seen with hypertrophied T2 hypointense synovium and pannus formation; D-F: Axial and sagittal post-contrast Fat Sat T1W. Arrows indicate peripherally enhancing abscesses adjacent to the first MCP joint. Also noted in the vicinity is enhancing proliferative pannus. MCP: Metacarpophalangeal.
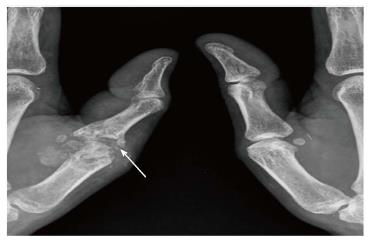
Figure 5 Radiograph of left thumb shows destruction of left first metacarpophalangeal joint with juxta-articular osteopenia and foci of calcification.
In view of this appearance gout was also considered in the differential. However in view of normal serum uric acid levels, infective arthropathy was the most likely diagnosis.
- Citation: Mahajan A, Santhoshkumar GV, Kawthalkar AS, Vaish R, Sable N, Arya S, Desai S. Case of victims of modern imaging technology: Increased information noise concealing the diagnosis. World J Radiol 2017; 9(12): 454-458
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v9/i12/454.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v9.i12.454