Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Apr 28, 2016; 8(4): 355-369
Published online Apr 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i4.355
Published online Apr 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i4.355
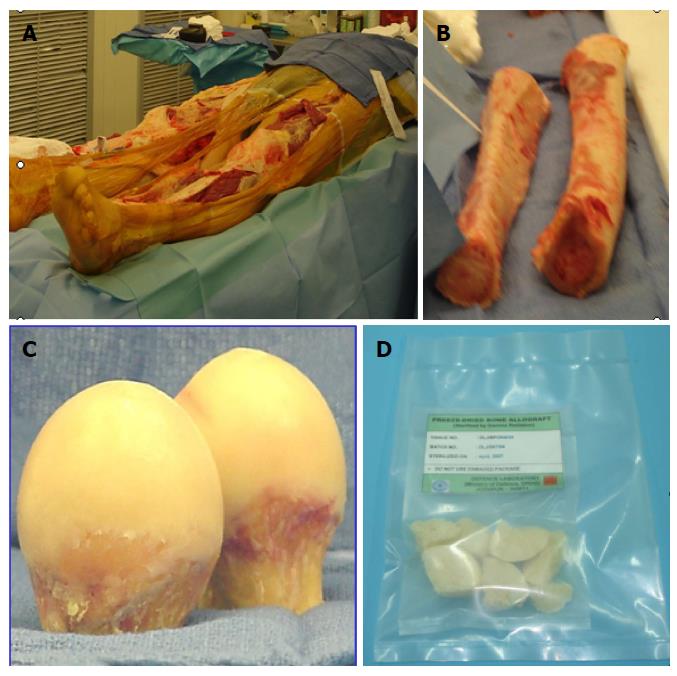
Figure 1 Bone allografts.
A: Bone collection from cadaveric donor; B: Cortical bone; C: Femoral heads excised during surgery; D: Processed bone allografts.
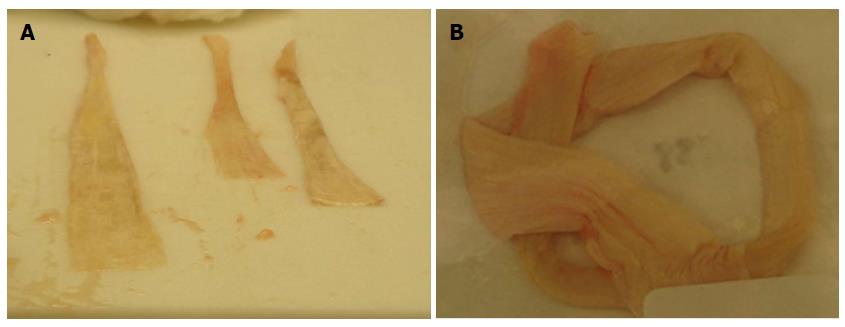
Figure 2 Soft tissue allografts.
A: Tendon allografts collected from cadaveric donor; B: Processed tendon allograft.
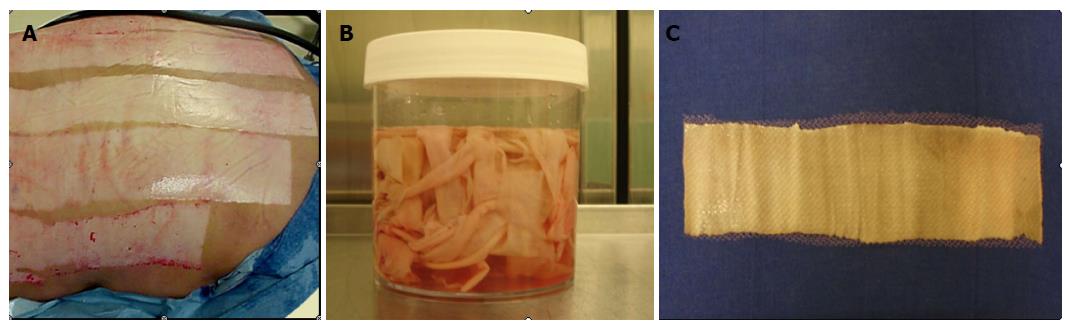
Figure 3 Allograft skin.
A: Cadaveric donor; B: Skin collected from cadaveric donor; C: Processed allograft skin.
Figure 4 Amniotic membrane.
A: Collection of amniotic tissue from placenta; B: Processed amniotic membrane dressing.
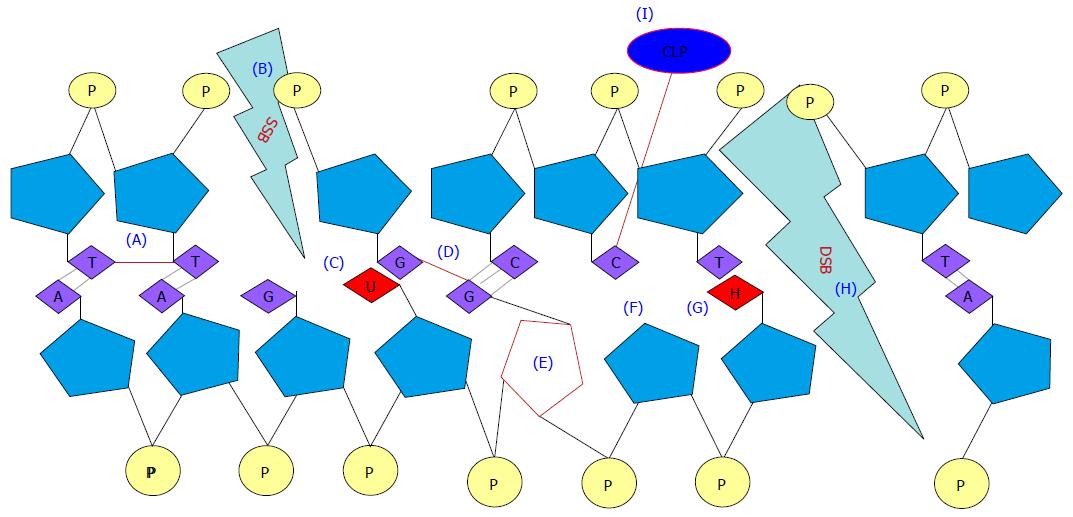
Figure 5 Types of DNA damage by ionizing radiation.
A: Intrastrand crosslink; B: SSB; C: Base deamination; D: Interstrand crosslink; E: Sugar residue alteration; F: Abasic site and hydrogen breakage; G: Base oxidation; H: DSB; I: CLP. SSB: Single strand break; DSB: Double strand break; CLP: Crosslinking protein.
- Citation: Singh R, Singh D, Singh A. Radiation sterilization of tissue allografts: A review. World J Radiol 2016; 8(4): 355-369
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i4/355.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i4.355