Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Radiol. Mar 28, 2016; 8(3): 281-287
Published online Mar 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.281
Published online Mar 28, 2016. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.281
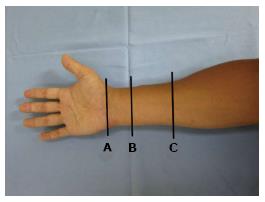
Figure 1 Demonstration of probe location at the forearm.
The cross sectional area of the median nerve was measured (A) level with the pisiform bone (B) level with the proximal third of the pronator quadratus and (C) level with a point 12 cm proximal to the pisiform bone.
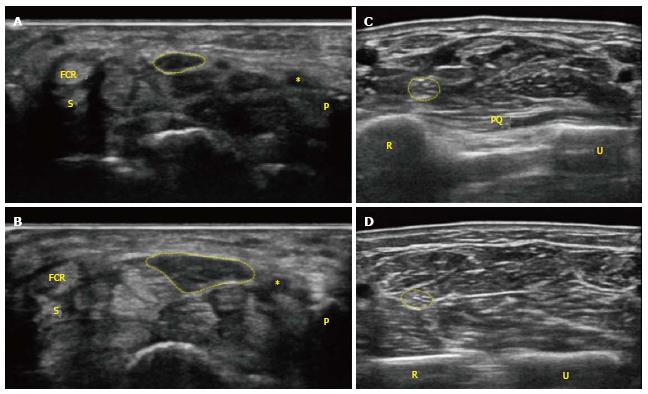
Figure 2 Transverse images in a 79-year-old female with carpal tunnel syndrome.
A: A conventional grey scale sonographic image shows the cross-sectional area of the median nerve (CSA) corresponding to the circle in the normal side with an area of 8 mm2 at the level of the pisiform bone; B: CSA in the carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) side shows 21 mm2 at pisiform bone level; C: CSA in the CTS side shows 7 mm2 at the proximal third of the pronator quadratus level; D: CSA in the CTS side shows 6 mm2 at a point 12 cm proximal to the pisiform bone. In this case, the calculated “delta CSA” and “CSA ratio” were 14 mm2 and 3.5, respectively. *: Ulnar artery. FCR: Flexor carpi radialis; P: Pisiform bone; S: Scaphoid bone; PQ: Pronator quadratus muscle; R: Radius; U: Ulnar.
- Citation: Miyamoto H, Morizaki Y, Kashiyama T, Tanaka S. Grey-scale sonography and sonoelastography for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. World J Radiol 2016; 8(3): 281-287
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v8/i3/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v8.i3.281