Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Sep 28, 2014; 6(9): 726-729
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i9.726
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i9.726
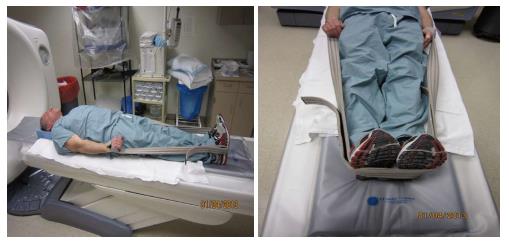
Figure 1 Position of patient for 4-dimensional computed tomography utilizing manufacture shoulder straps.
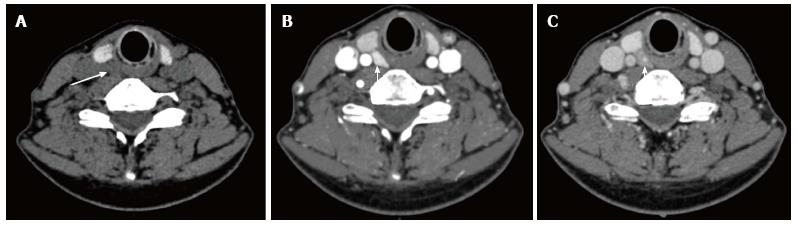
Figure 2 Four-dimensional computed tomography.
Axial noncontrast (A), axial arterial phase post contrast (B) and axial delayed phase post contrast (C) images show a hypodense nodule contiguous with the right thyroid gland, which demonstrates avid early contrast enhancement and rapid washout.
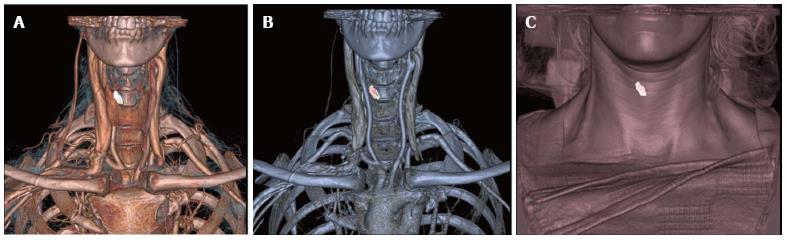
Figure 3 Three-dimensional volume rendering images in 3 different thresholds showing the presumed adenoma in relation to thyroid gland (A), bony landmarks (B) and skin (C).
- Citation: Platz TA, Kukar M, Elmarzouky R, Cance W, Abdelhalim A. Low dose four-dimensional computerized tomography with volume rendering reconstruction for primary hyperparathyroidism: How I do it? World J Radiol 2014; 6(9): 726-729
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i9/726.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i9.726