Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2014; 6(8): 589-597
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.589
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.589
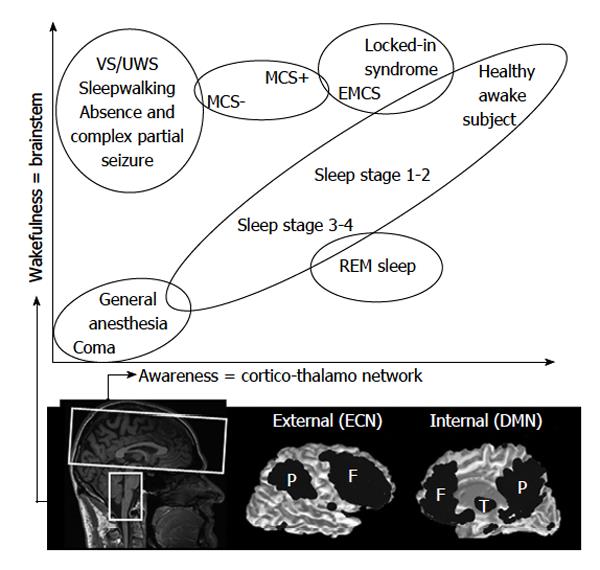
Figure 1 The two main components of consciousness: wakefulness and awareness.
Correlation between wakefulness, related to the brainstem, and awareness, related to the cortico-thalamic network. In most pathological and physiological states, the two components are linearly correlated along the spectrum of consciousness. However, they are dissociated in some cases. Vegetative state/unresponsive wakefulness syndrome (VS/UWS); minimally conscious state (MCS); emergence of MCS, EMCS. Adapted from ref. [3,4]. EMCS: Emerge from minimally conscious state; ECN: Executive control network; DMN: Default mode network; REM: Rapid eyes movement.
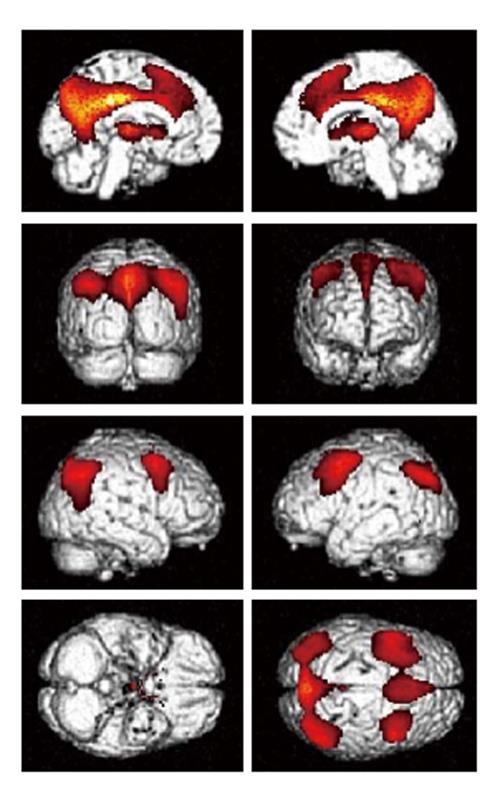
Figure 2 Brain areas where metabolism is impaired in vegetative state/unresponsive wakefulness syndrome patients compared to controls (areas in red), superimposed in a structural 3D image.
P < 0.05, family wise error corrected.
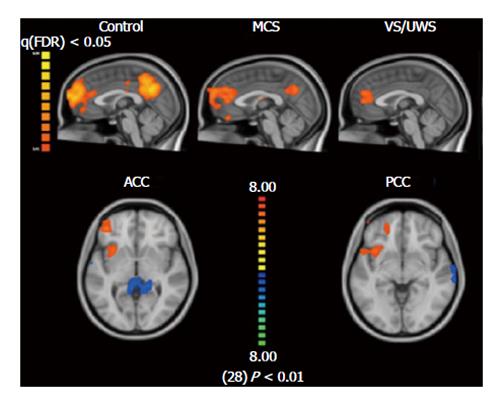
Figure 3 Default mode network in vegetative state/unresponsive wakefulness syndrome, minimally conscious state, healthy controls-sagittal view[68].
In vegetative state/unresponsive wakefulness syndrome (VS/UWS), the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) are hypoconnected to the default mode network (in blue) and hyperconnected to the fronto-insular cortex (in red), axial view. Correlation from random effect (P < 0.01) and clustered corrected (P < 0.05) results based on general linear model maps with seed region of interest comparing VS/UWS to healthy controls[60]. MCS: Minimally conscious state.
- Citation: Di Perri C, Thibaut A, Heine L, Soddu A, Demertzi A, Laureys S. Measuring consciousness in coma and related states. World J Radiol 2014; 6(8): 589-597
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i8/589.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.589