Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2014; 6(7): 515-518
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.515
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.515
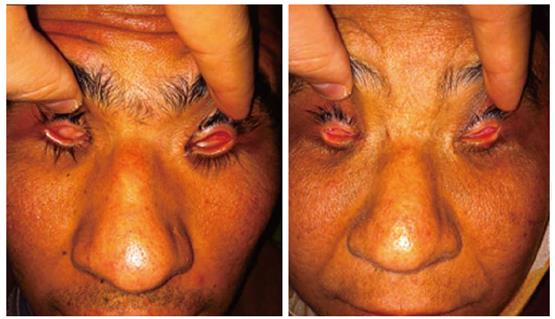
Figure 1 Clinical appearance of siblings.
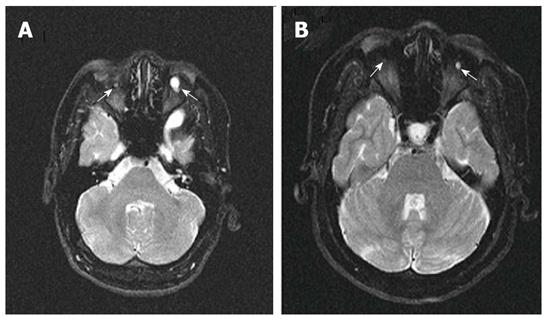
Figure 2 Axial fat-suppressed T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Axial fat-suppressed T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the male patient showed bilateral cystic structures that are synonymous with rudimentary eyeballs (white arrows); B: Axial fat-suppressed T2-weighted MRI of the female patient showed bilateral cystic structures that are synonymous with rudimentary eyeballs (white arrows).
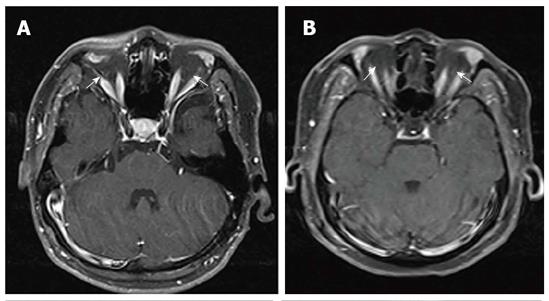
Figure 3 Post-contrast fat-suppressed T1-weighted axial magnetic resonance imaging of each patient show bilateral hypoplastic optic nerves between extraocular muscle groups (white arrows).
- Citation: Celebi ARC, Sasani H. Differentiation of true anophthalmia from clinical anophthalmia using neuroradiological imaging. World J Radiol 2014; 6(7): 515-518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i7/515.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.515