Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2014; 6(7): 493-501
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.493
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.493
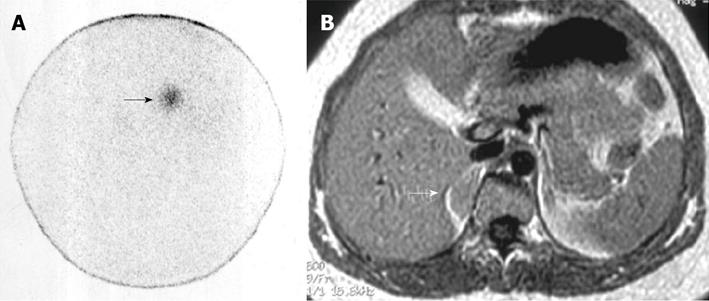
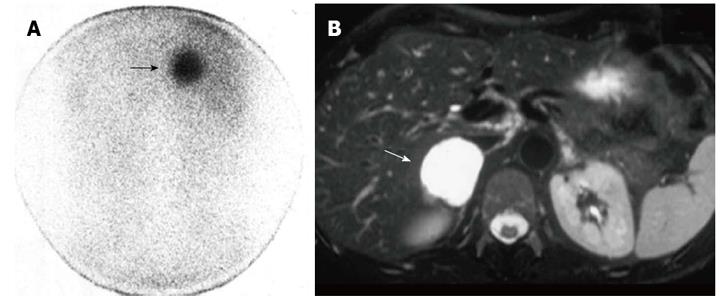
Figure 1 Right non-hypersecreting adrenal adenoma.
A: Abdominal posterior scan of I-131 nor-cholesterol scintigraphy demonstrates abnormal (faint) focal uptake in the right adrenal (black arrow) where a mass was detected by magnetic resonance (MR); no detectable tracer uptake in the left adrenal bed; B: T1-weighted axial MR detects a small lesion in the right adrenal bed (white arrow) isointense compared to liver signal intensity.
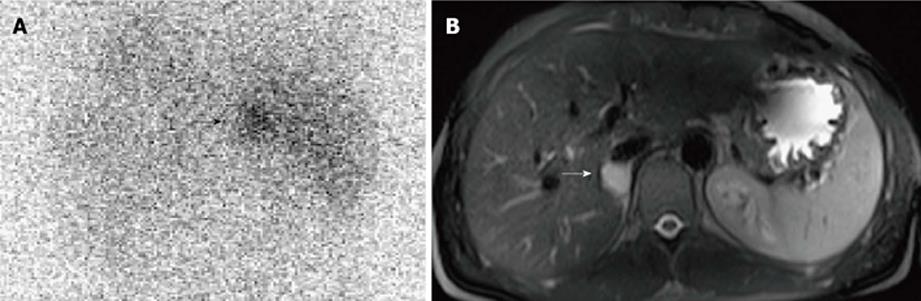
Figure 2 Right benign non-hypersecreting pheochromocytoma.
A: Abdominal posterior scan of I-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy demonstrates abnormal (faint) focal uptake in the right adrenal (black arrow) where a small mass was detected by magnetic resonance (MR); no detectable tracer uptake in the left adrenal bed; B: T2-weighted axial MR with fat-suppression detects a small right adrenal lesion hyperintense compared to liver signal intensity (white arrow).
Figure 3 Right adrenal metastasis by melanoma.
A: Axial fluorine-18 fludeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scan detects abnormal focal uptake in the right adrenal region (black arrow) where a large adrenal metastasis was detected by magnetic resonance (MR); diffuse normal liver tracer activity is detectable; physiologic tracer activity is also detectable in kidneys; B: T1-weighted axial MR detects a right adrenal tumor hypointense compared to liver signal intensity (white arrow).
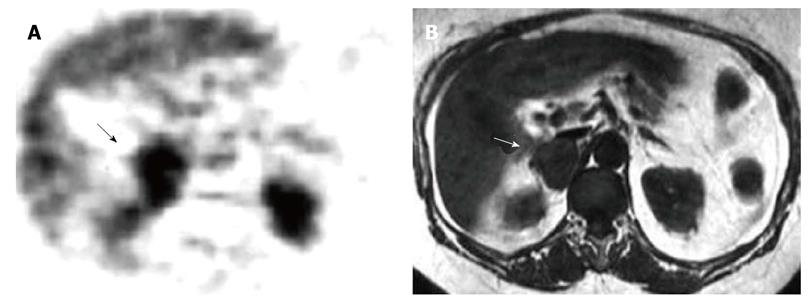
Figure 4 Right hypersecreting adenoma of the adrenal gland.
A: Abdominal posterior scan of I-131 nor-cholesterol scintigraphy demonstrates abnormal (intense) focal uptake in the right adrenal (black arrow) where a mass was detected by magnetic resonance (MR); no uptake is detected on the contralateral side; normal bowel uptake is detectable on the left; B: T1-weighted axial MR detects a right adrenal lesion isointense compared to liver signal intensity (white arrow).
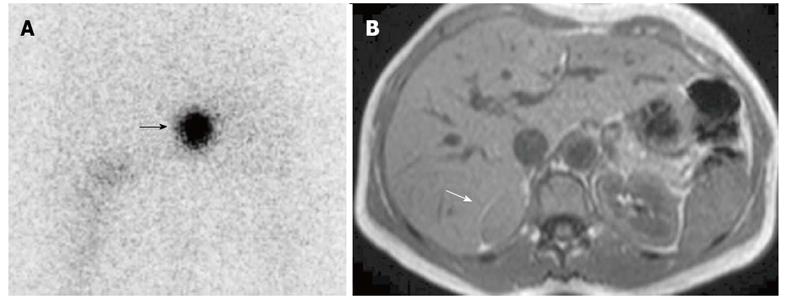
Figure 5 Right malignant hypersecreting pheochromocytoma.
A: Abdominal posterior scan of I-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy demonstrates abnormal (intense) focal uptake in the right adrenal (black arrow) where a large mass was detected by magnetic resonance (MR); no detectable tracer uptake in the left adrenal bed; B: T2-weighted axial MR with fat-suppression detects a large right adrenal lesion hyperintense compared to liver signal intensity (white arrow).
- Citation: Maurea S, Mainenti PP, Romeo V, Mollica C, Salvatore M. Nuclear imaging to characterize adrenal tumors: Comparison with MRI. World J Radiol 2014; 6(7): 493-501
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i7/493.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i7.493