Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2014; 6(5): 130-138
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i5.130
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i5.130
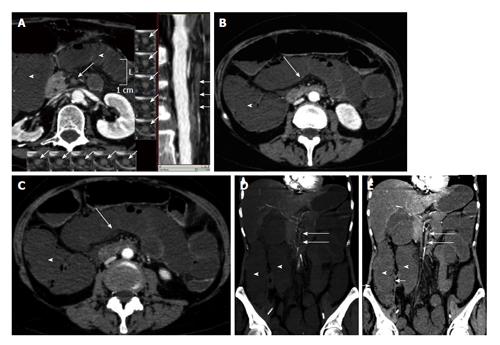
Figure 1 Arterial mesenteric ischemia.
A: Vessel probe in multiplanar (MPR) mode reconstructions showing bowel ischemia caused by the occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery (arrows). Bowel loop dilatation is associated (arrowheads); B and C: Computed tomography transverse scans show bowel wall dilatation (arrowheads) with loss of wall enhancement (arrows) in a case of arterial bowel ischemia diagnosed in the early stage; D: Coronal maximum intensity projection reconstruction; E: Coronal MPR reconstruction. Bowel ischemia caused by the occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery. Bowel loop dilatation (arrowheads) and parietal pneumatosis of the right colon (short arrows) are associated.
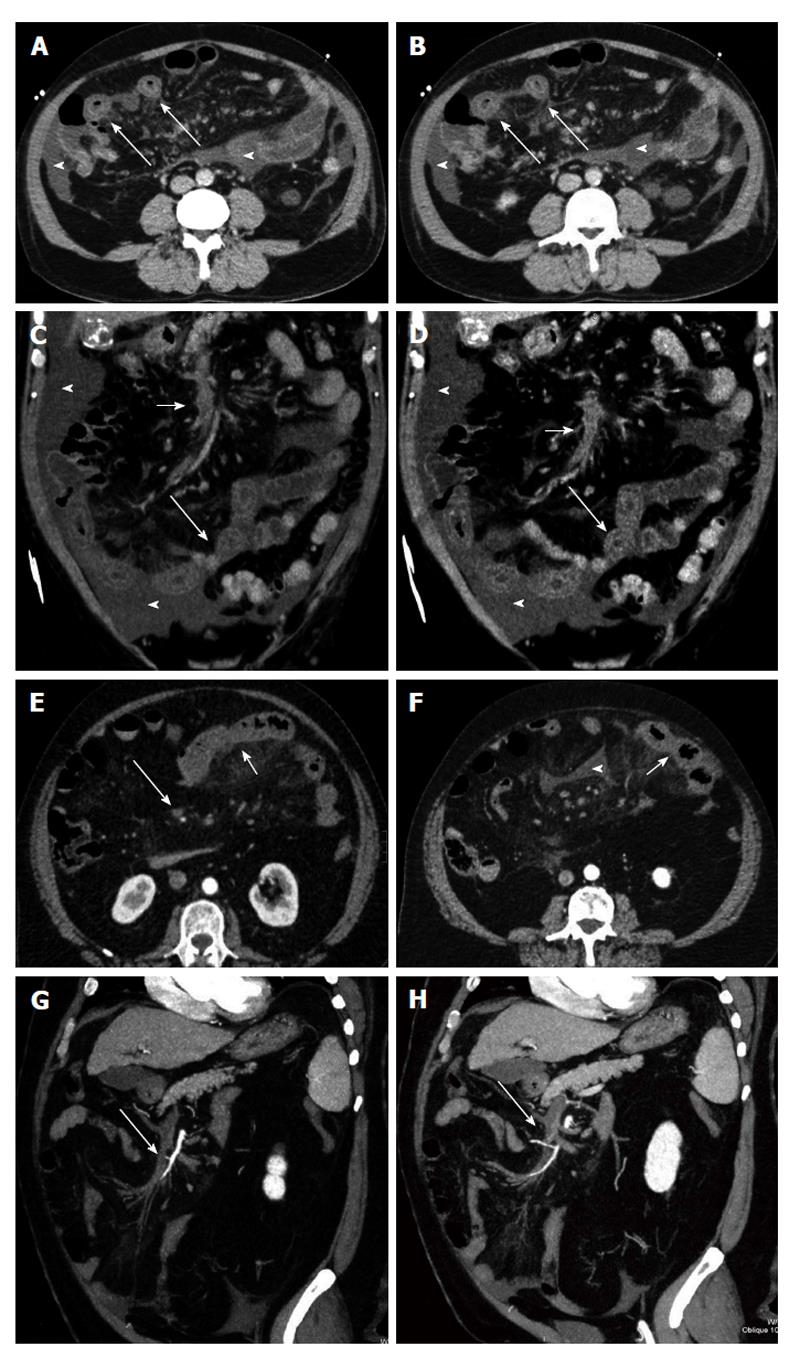
Figure 2 Venous mesenteric ischemia.
A and B: Transverse computed tomography (CT) scans; C and D: Coronal MPR reconstructions. Bowel ischemia caused by the occlusion of the superior mesenteric vein (short arrows). The target sign with concentric bowel wall thickening is well evident (long arrows). Ascites is associated (arrowheads); E and F: Transverse CT scans; G and H: Coronal curved multiplanar reconstructions. Bowel ischemia caused by the occlusion of the superior mesenteric vein (long arrows). The target sign with concentric bowel wall thickening is well evident (short arrows). Ascites is associated (arrowheads).
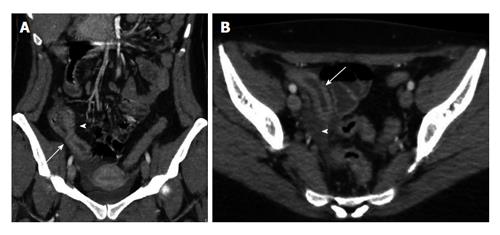
Figure 3 Crohn’s disease.
A: Computed tomography (CT) coronal reconstruction shows terminal ileal loop thickening with white attenuation pattern (arrow) and perivisceral vasa recta (arrowhead); B: Transverse CT scan shows thickening of the terminal ileal loop (arrow) associated with perivisceral endoperitoneal fluid (arrowhead).
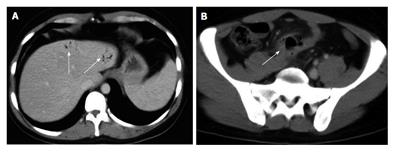
Figure 4 Intrahepatic portal air from diverticulitis.
A: Computed tomography transverse scan shows the presence of intrahepatic portal air (arrows); B: Pelvic sigmoid diverticulitis complicated by peridiverticular abscess (arrow).
- Citation: Moschetta M, Telegrafo M, Rella L, Stabile Ianora AA, Angelelli G. Multi-detector CT features of acute intestinal ischemia and their prognostic correlations. World J Radiol 2014; 6(5): 130-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i5/130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i5.130