Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2014; 6(10): 846-849
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.846
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.846
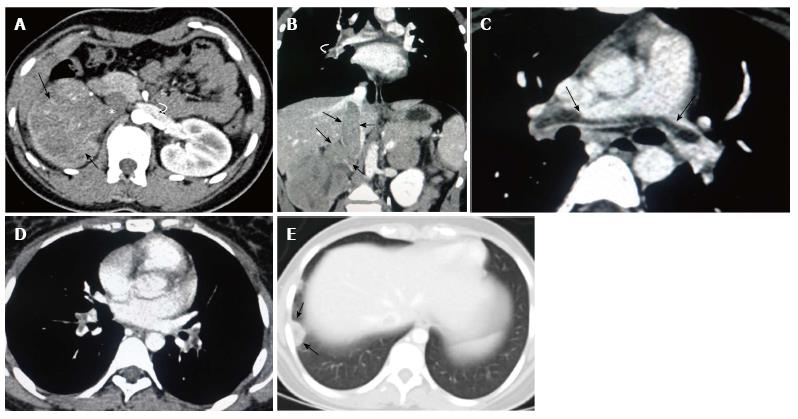
Figure 1 Contrast enhanced computed tomography of abdomen.
Corticomedullary phase (A) shows a heterogeneous enhancing mass (arrows) in the right kidney with invasion into the right renal vein and inferior vena cava (arrow head). Note normally opacified left renal vein (curved arrow); Coronal reconstructed image (B) shows the intraluminal tumoral filling defect causing expansion of the right renal vein and inferior vena cava (straight arrows) in continuity with primary renal mass. Tumor thrombus is also seen in right pulmonary artery (curved arrows); Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) of chest (C and D) shows saddle type filling defect (tumor thrombus) in the bifurcation of main pulmonary artery (arrows in C) and segmental branches of the bilateral pulmonary artery (arrows in D); Axial CECT of chest in lung window (E) shows wedge shaped patchy consolidation with central lucency in the subpleural region of the posterior segment in the right lower lobe (arrows) consistent with pulmonary infarct.
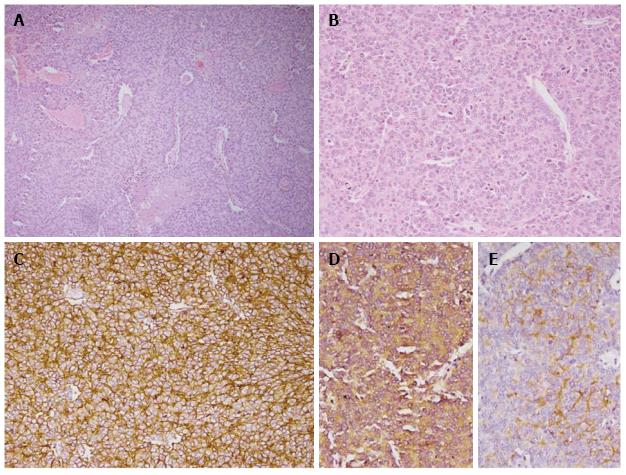
Figure 2 Photomicrograph showing tumor cells arranged in sheets with interspersed blood vessels and areas of necrosis (H and E × 100, A) with small to medium sized cells having round nuclei with stipple chromatin and moderate cytoplasm (H and E × 200, B).
Diffuse membranous immunopositivity for MIC 2 (IHC × 200, C), cytoplasmic immunopositivity for neuron specific enolase (NSE) (IHC × 200, D) and cytoplasmic immunopositivity for Synaptophysin (IHC × 200, E) were also seen. IHC: Immunohistochemistry.
- Citation: Chinnaa S, Das CJ, Sharma S, Singh P, Seth A, Purkait S, Mathur SR. Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney presenting with pulmonary tumor embolism: A case report. World J Radiol 2014; 6(10): 846-849
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i10/846.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.846