Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2025; 17(5): 106333
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.106333
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.106333
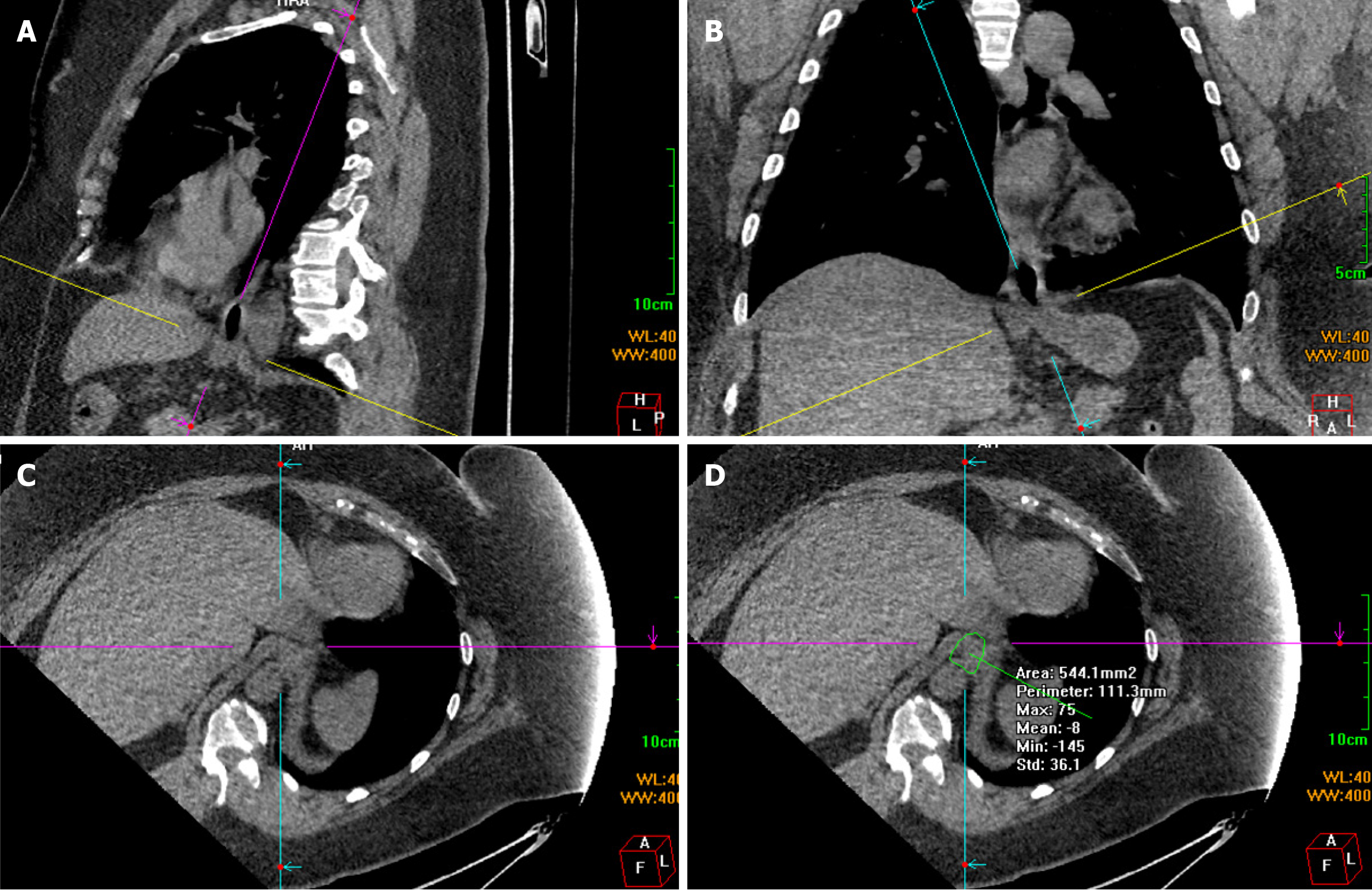
Figure 1 Esophageal hiatus measurement method.
A: For reconstructing the sagittal plane, select a slice passing through the center of the esophageal hiatus and move and rotate the locating line representing the axial plane (yellow) to intersect the anterior and posterior margins of the esophageal hiatus. This line generally slopes toward the spine. Consequently, the line representing the oblique sagittal plane (purple) is roughly parallel to the distal esophagus. The sagittal diameter is obtained by measuring the distance between the anterior and posterior margins; B: For reconstructing the coronal plane, move and rotate the yellow line to intersect the left and right margins of the esophageal hiatus. This line generally tilts downward toward the right. Consequently, the line representing the oblique coronal plane (blue) is roughly parallel to the distal esophagus. The transverse diameter is obtained by measuring the distance between the left and right margins; C: For the double oblique axis plane, the image presents a superior view of the esophageal hiatus from a perpendicular vantage point; D: A polygonal tool was used to manually define the inner margins of the hiatus, and the cross-sectional area of the esophageal hiatus was measured.
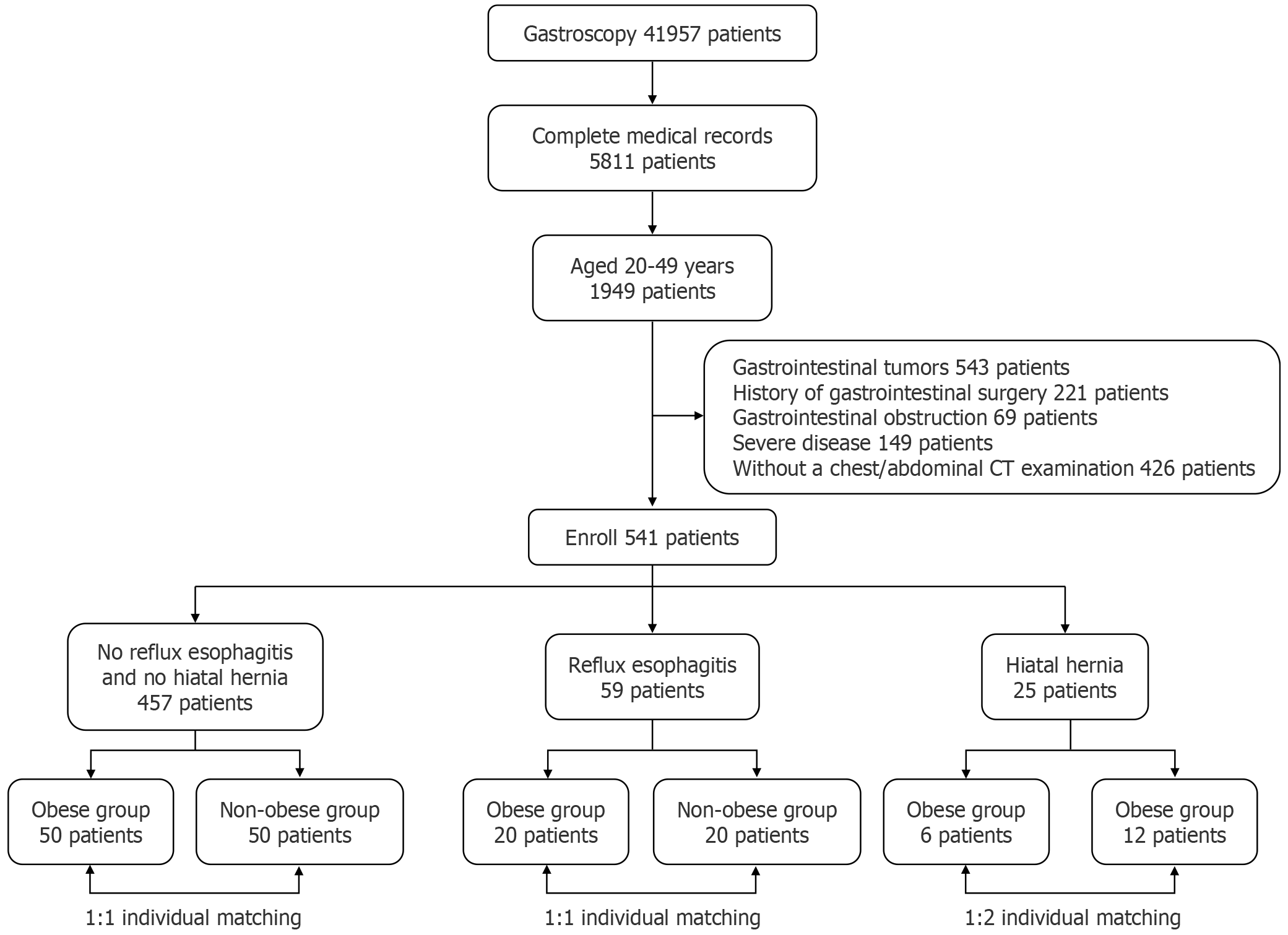
Figure 2 Patient selection flowchart.
Patients were screened and grouped based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. CT: Computed tomography.
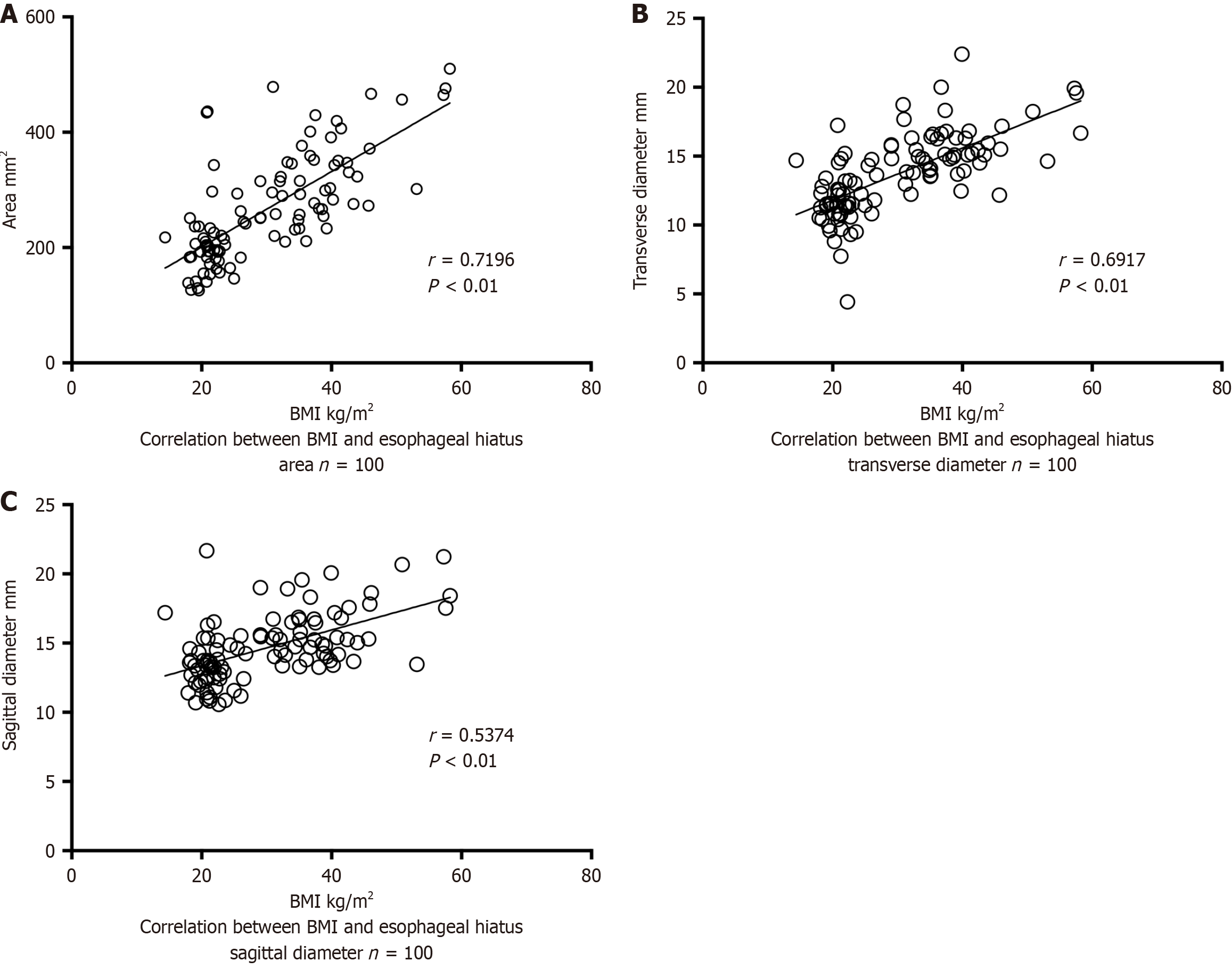
Figure 3 Spearman’s correlation test between body mass index and esophageal hiatus size.
A: Correlation between body mass index (BMI) and esophageal hiatus area with a correlation coefficient of 0.72 (P < 0.01), showing a linear positive correlation of moderate intensity; B: Correlation between BMI and esophageal hiatus transverse diameter with a correlation coefficient of 0.69 (P < 0.01), showing a linear positive correlation of moderate intensity; C: Correlation between BMI and esophageal hiatus sagittal diameter with a correlation coefficient of 0.54 (P < 0.01), showing a linear positive correlation of moderate intensity. BMI: Body mass index.
- Citation: Qi Z, Shi XC, Yan WM, Bai RX. Association of esophageal hiatus size with reflux esophagitis and type I hiatal hernia in patients with obesity. World J Radiol 2025; 17(5): 106333
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i5/106333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.106333