Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Jan 28, 2025; 17(1): 97255
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.97255
Published online Jan 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.97255
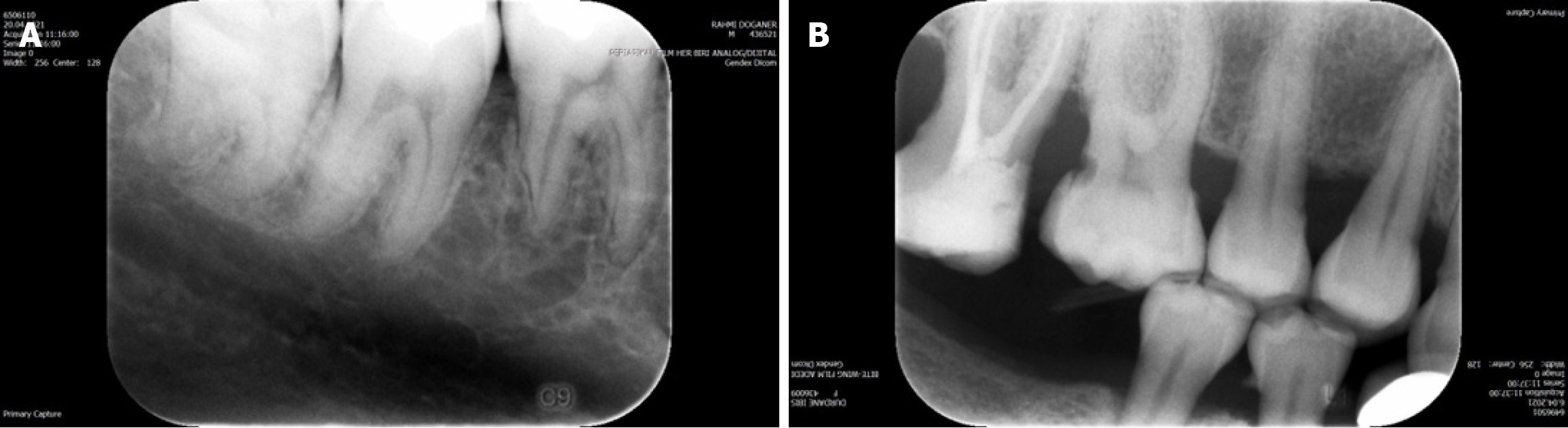
Figure 1 Periapical radiographic examination.
A: Periapical image taken from a patient with replacement external root resorption visible on the distal root surface of right mandibular first molar tooth. As can be seen, detailed root and bone structures were discernable but limited to a two-dimensional view; B: Bitewing image taken from a patient with alveolar bone destruction between the right maxillary first and second molar teeth along with a proximal caries on the distal surface of the first maxillary right molar.
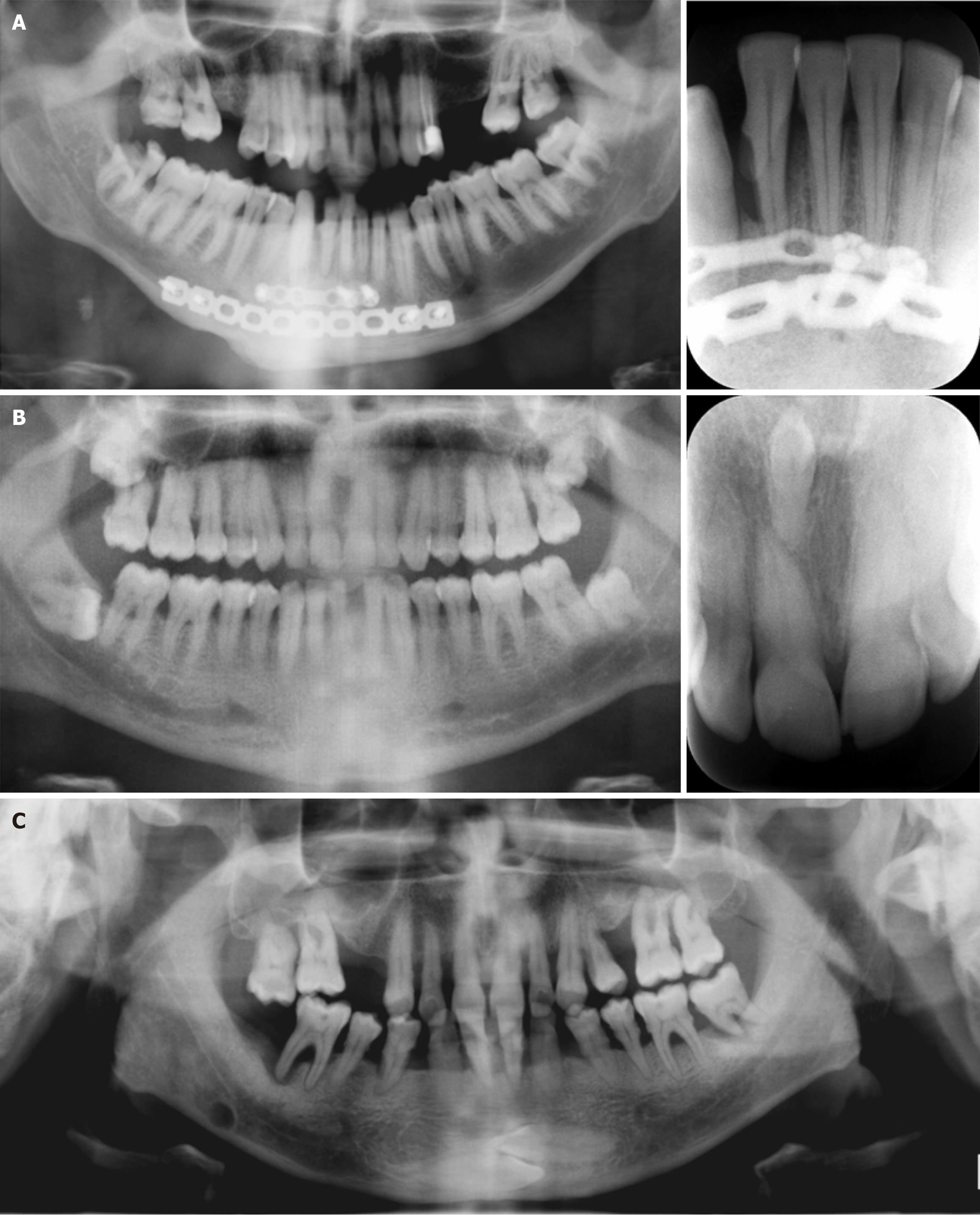
Figure 2 Panoramic images.
A: Patient with fixation screws and no visible alveolar bone defect in the mandibular anterior region on cropped panoramic radiography. Significant bone loss was evident around the right mandibular lateral incisor on cropped periapical radiography; B: A 35-year-old male patient with a vague radiopacity in the maxillary anterior region on cropped panoramic radiography. A clearly depicted inverted mesiodens tooth was evident between the maxillary incisors on cropped periapical radiography; C: Cropped panoramic image of a 55-year-old male patient with aggressive periodontitis and two horizontally impacted canine teeth visible on the mandibular anterior region. Also, a well-defined round Stafne bone cavity can be seen on the right mandibular region extending under the mandibular canal.
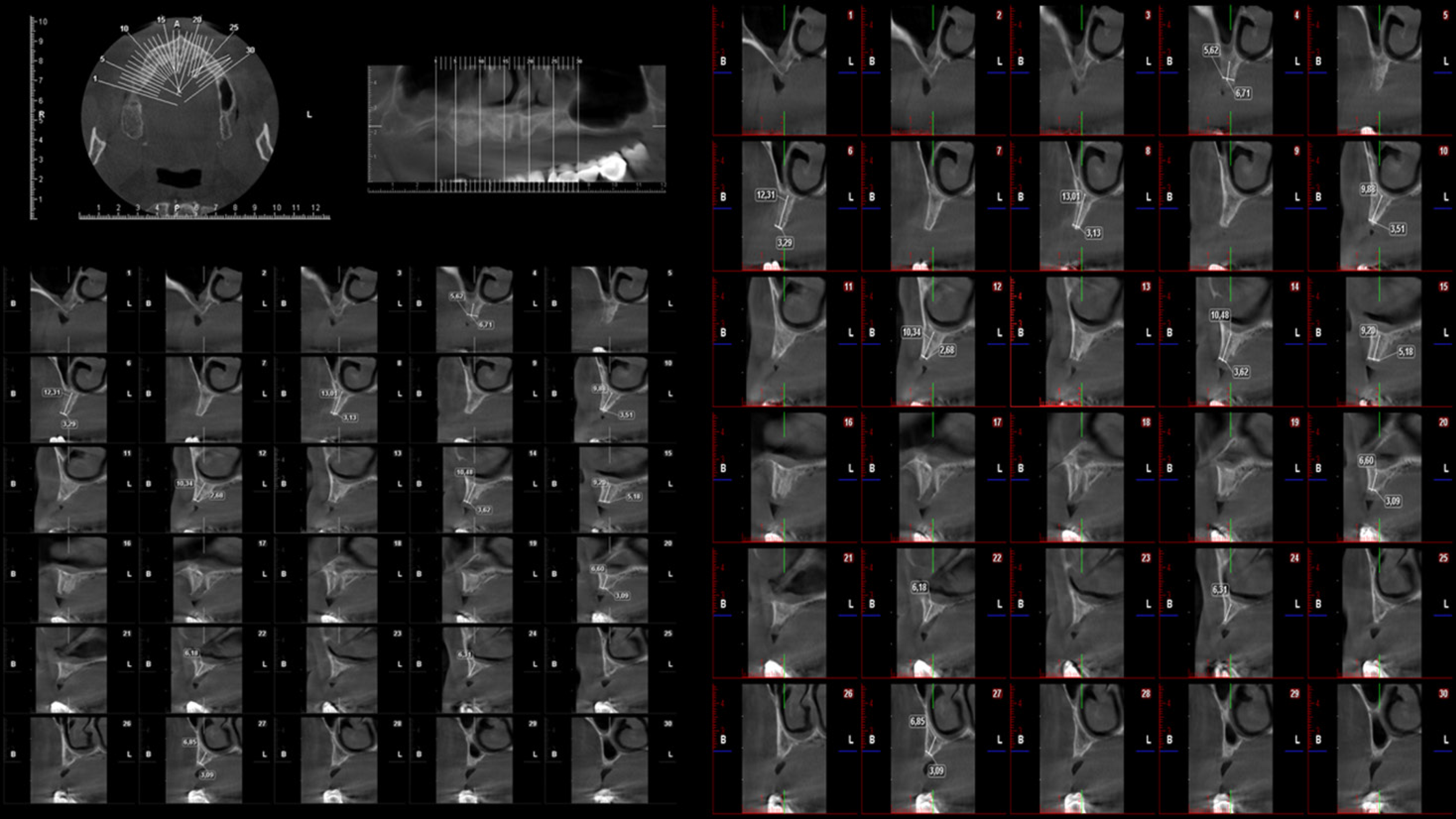
Figure 3 Multiplanar reformatted reconstruction images of a 60-year-old male patient requiring implant treatment referred for cone beam CT imaging.
Reformatted axial, panoramic, and cross-sectional images obtained at implant planning mode indicated severe maxillary bone resorption.
Figure 4 Diagnostic X-ray images of a 16-year-old female patient with histopathologically confirmed cemento-ossifying fibroma between the mandibular right premolar teeth.
A-D: Two-dimensional panoramic X-ray image (A), reformatted axial cone beam CT (CBCT) image (B), reformatted panoramic CBCT image (C), and reformatted cross-sectional CBCT images (D) showed a well-defined lesion. The mixed radiopacity degree of the inner structures of the lesion observed in different CBCT sections was not detectable on two-dimensional panoramic radiography.
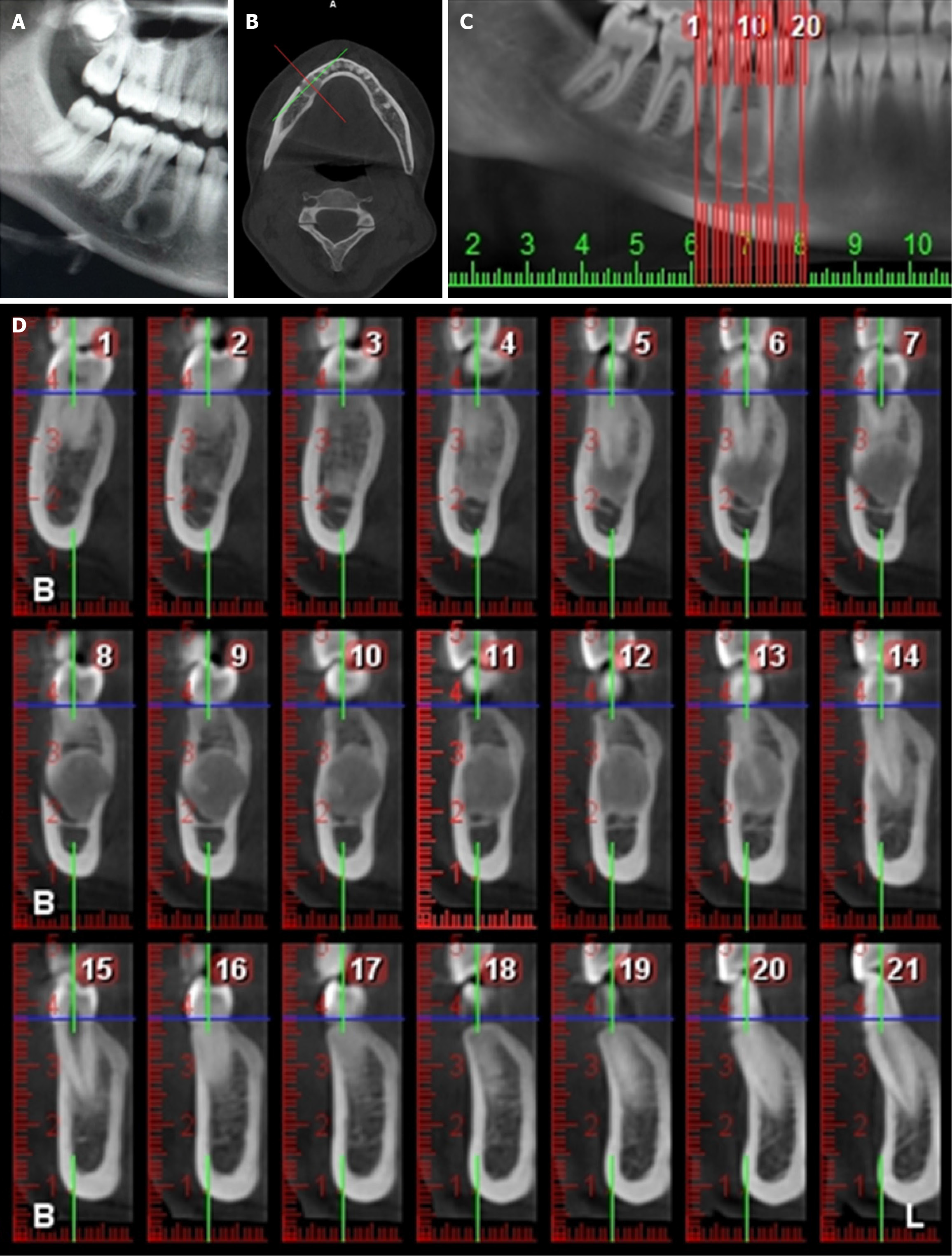
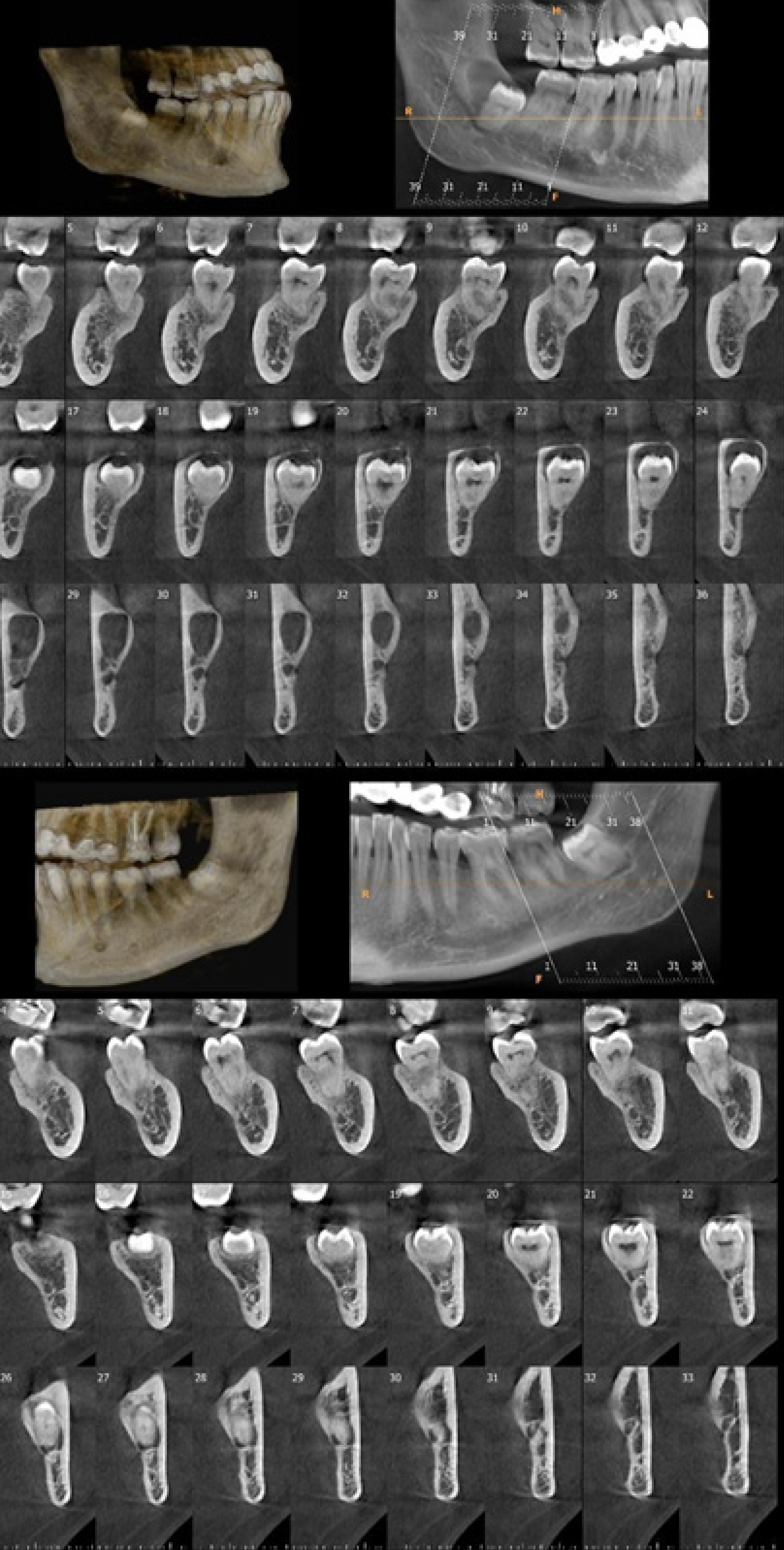
Figure 5 Cone beam CT images of mandibular right (upper image) and left (lower image) third molar teeth of a 25-year-old female patient referred for persistent pain on both retromolar sides.
Three-dimensional bone model, panoramic, and cross-sectional images showed a dentigerous cyst related to the mandibular right third molar tooth and direct contact of mandibular left third molar tooth root with mandibular canal.
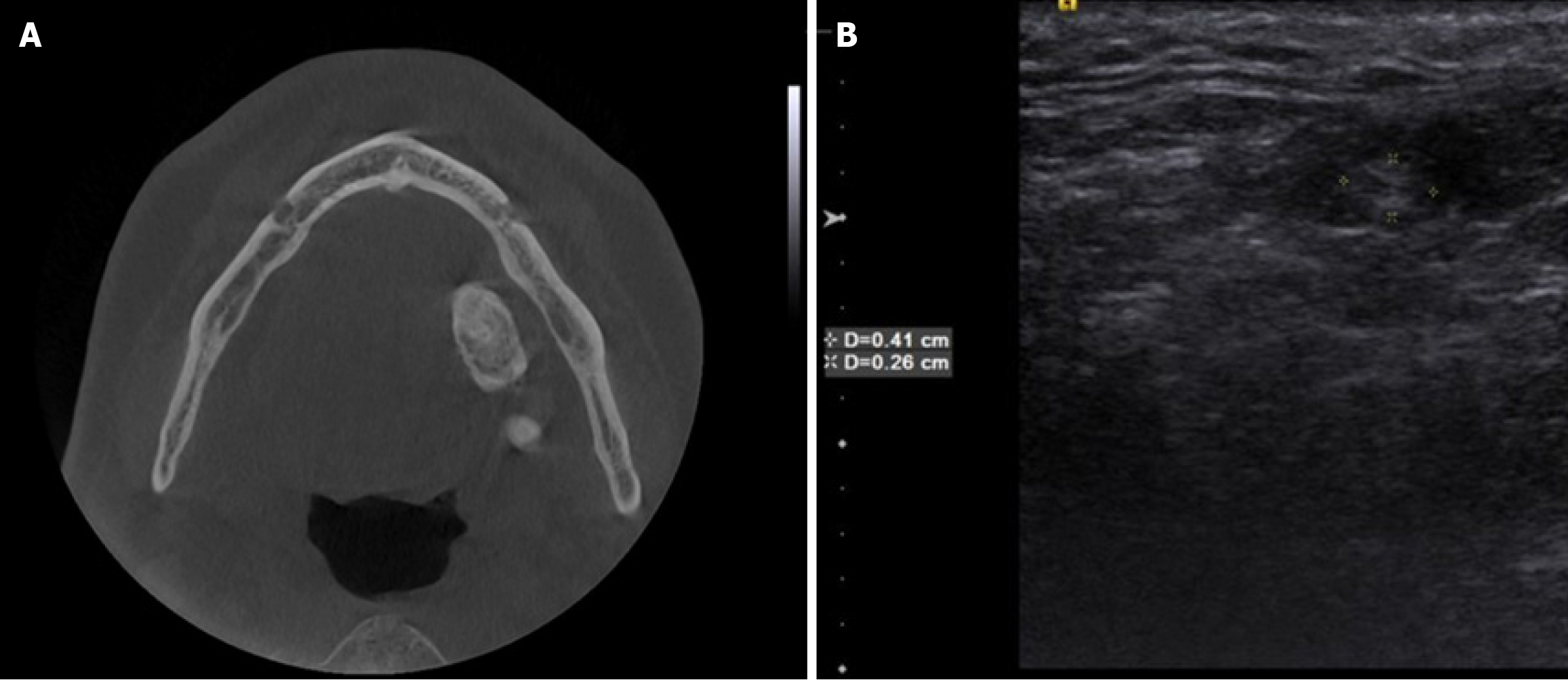
Figure 6 Axial cone beam CT and ultrasonographic measurement images.
A and B: Axial cone beam CT (A) and ultrasonographic measurement (B) images of a 25-year-old female patient referred to our clinic with the complaints of pain and swelling of the cheek after meals. The radiopaque lesion on cone beam CT and hyperechoic lesion on ultrasound images in the submandibular region were suggestive of a submandibular sialolithiasis.
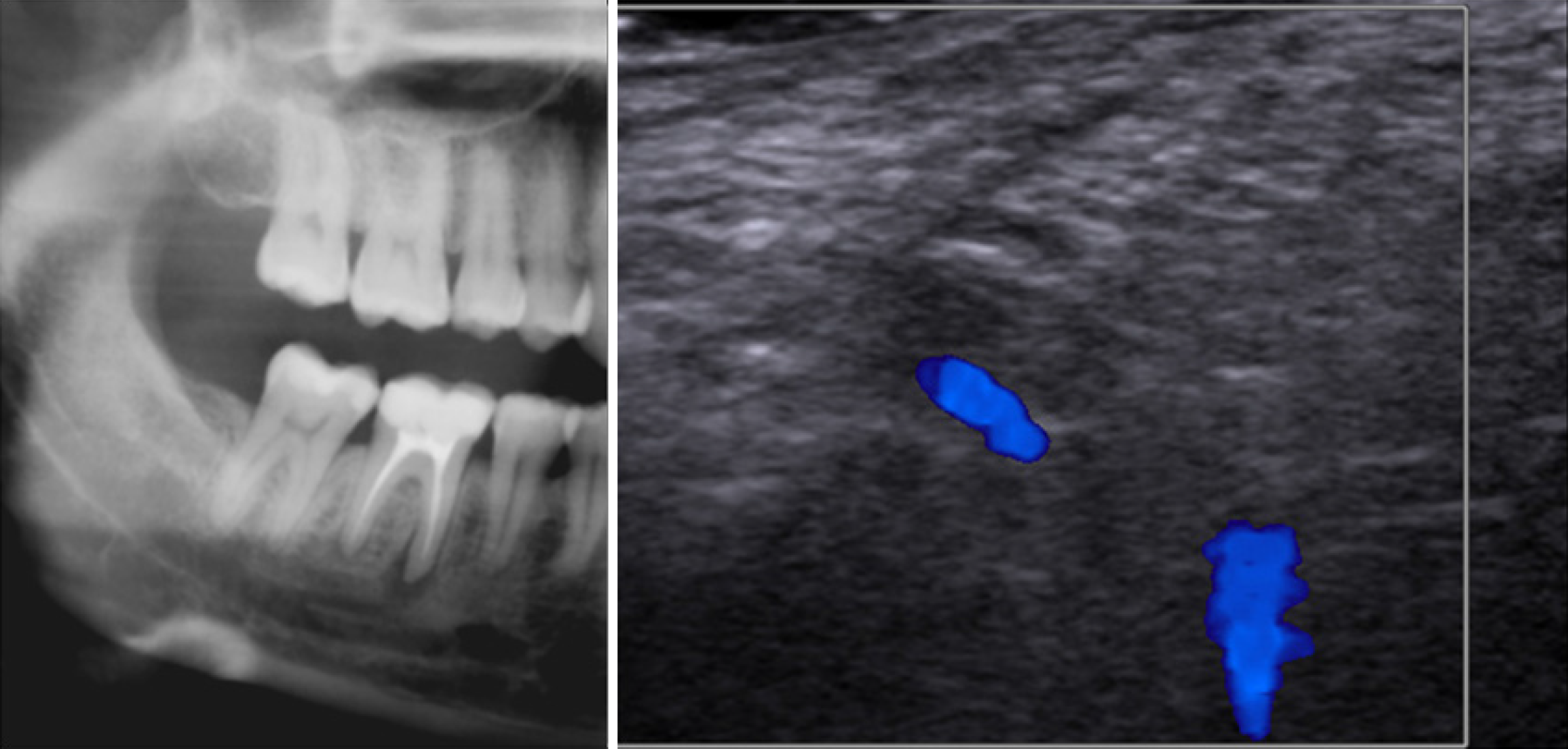
Figure 7 Cropped panoramic radiography (left) and laser doppler ultrasonographic image of a 30-year-old female patient referred for slight percussion sensitivity in the right mandibular first molar region.
On panoramic radiography, a well-defined radiolucent lesion on the mesial root of the first mandibular right molar was observed. Laser Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation revealed that there was blood flow in the region suggestive of a granuloma, which was proved by histopathological examination.
Figure 8
Open mouth sagittal T1 magnetic resonance image of a 65-year-old female patient with pain and limitation during chewing suggested anterior disc displacement without reduction.
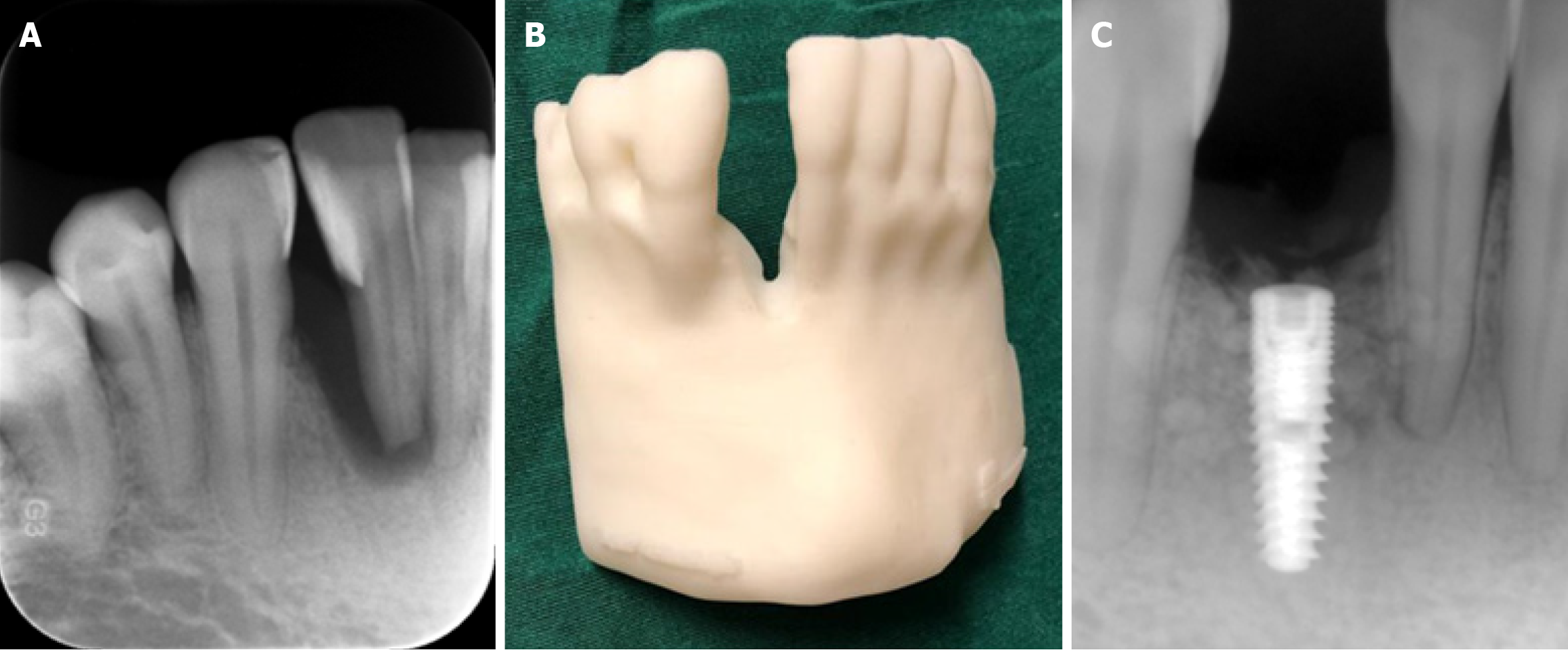
Figure 9 Cone beam CT images.
A-C: Intraoral periapical image (A) and three-dimensional printed bone model (B) of a patient from cone beam CT data obtained in order to assess right mandibular anterior lateral tooth for implant placement; C: According to diagnostic images and the three-dimensional bone model, an implant was successfully placed in the anterior lateral incisor region of the patient as can be seen from the postoperative periapical image.
- Citation: Kamburoğlu K. Trends in dentomaxillofacial radiology. World J Radiol 2025; 17(1): 97255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i1/97255.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i1.97255