Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2024; 16(11): 657-667
Published online Nov 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.657
Published online Nov 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.657
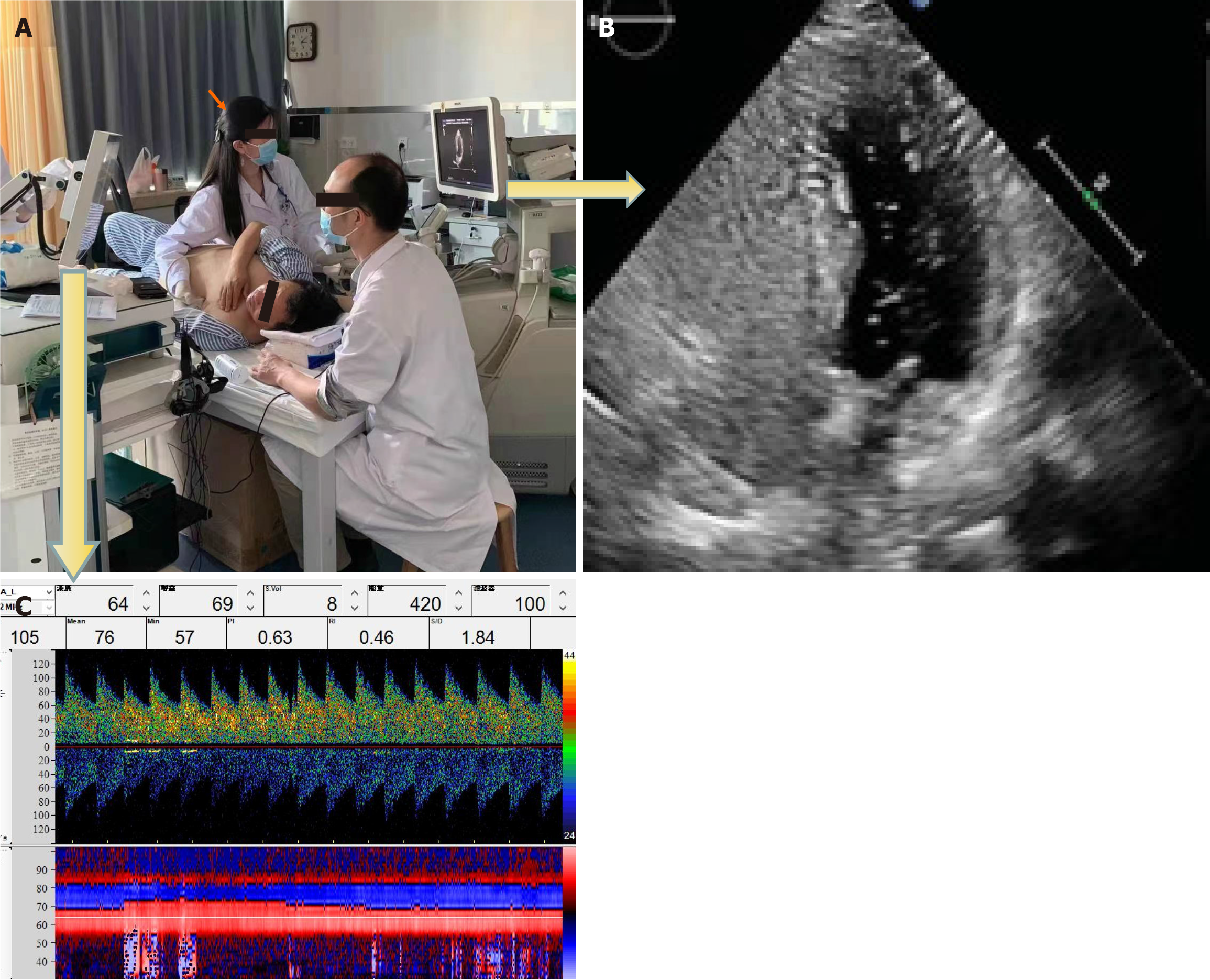
Figure 1 Synchronized contrast transcranial Doppler combined with contrast transthoracic echocardiography onsite inspection images.
A: Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) operator (orange arrow); B: TTE screen displaying the apical four-chamber view; C: Transcranial Doppler showing cerebral blood flow in the middle cerebral artery through the temporal window.
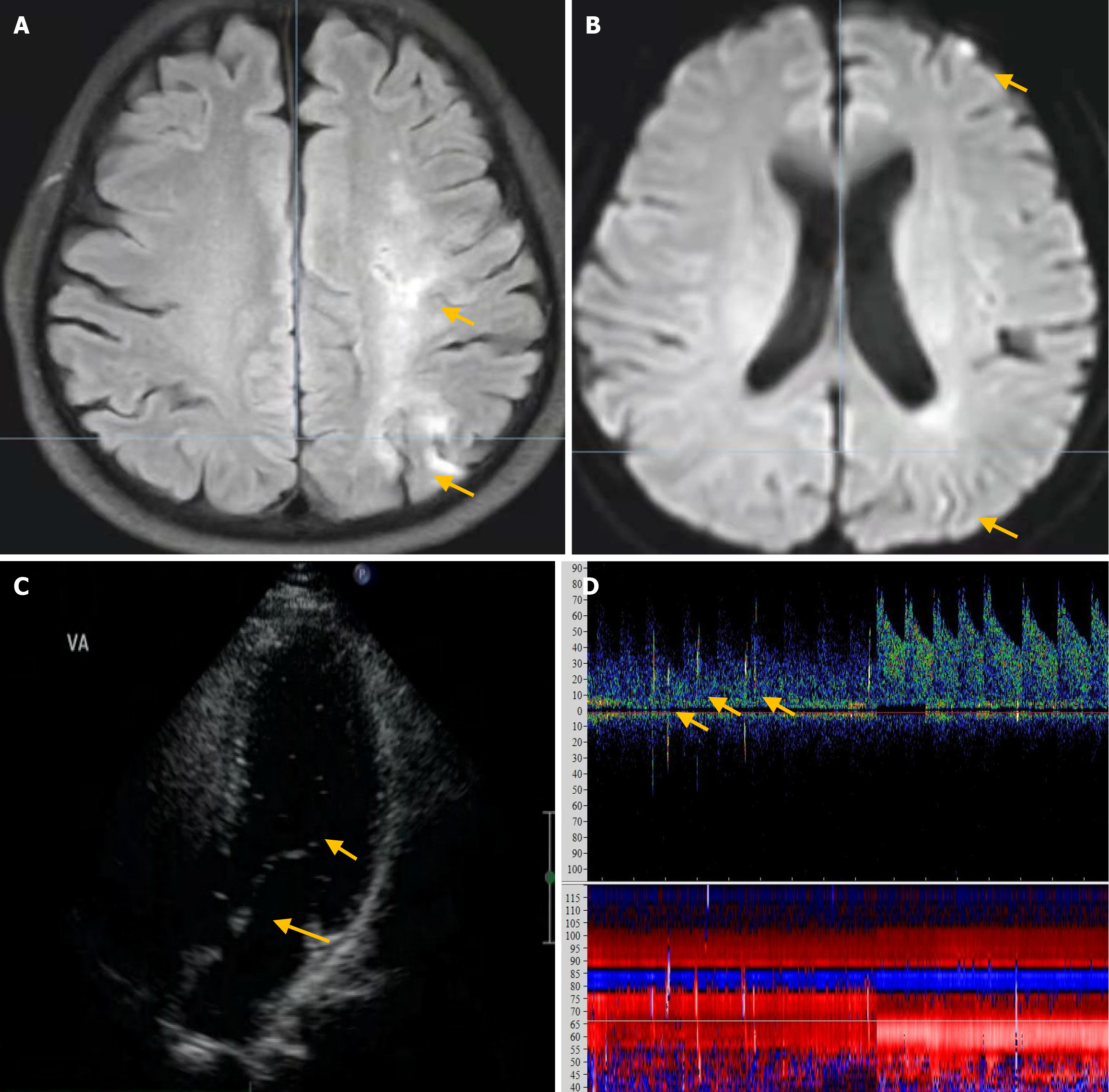
Figure 2 Brain magnetic resonance imaging revealing several infarcts located in the left occipital.
A: Arrow, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences and frontal lobes; B: Arrow, diffusion-weighted imaging, as well as in the subcortical white matter; C: Contrast transthoracic echocardiography shows 11–30 microbubbles both at rest and during the Valsalva maneuver (VM); D: The contrast transcranial Doppler only detects approximately five microbubbles after the VM.
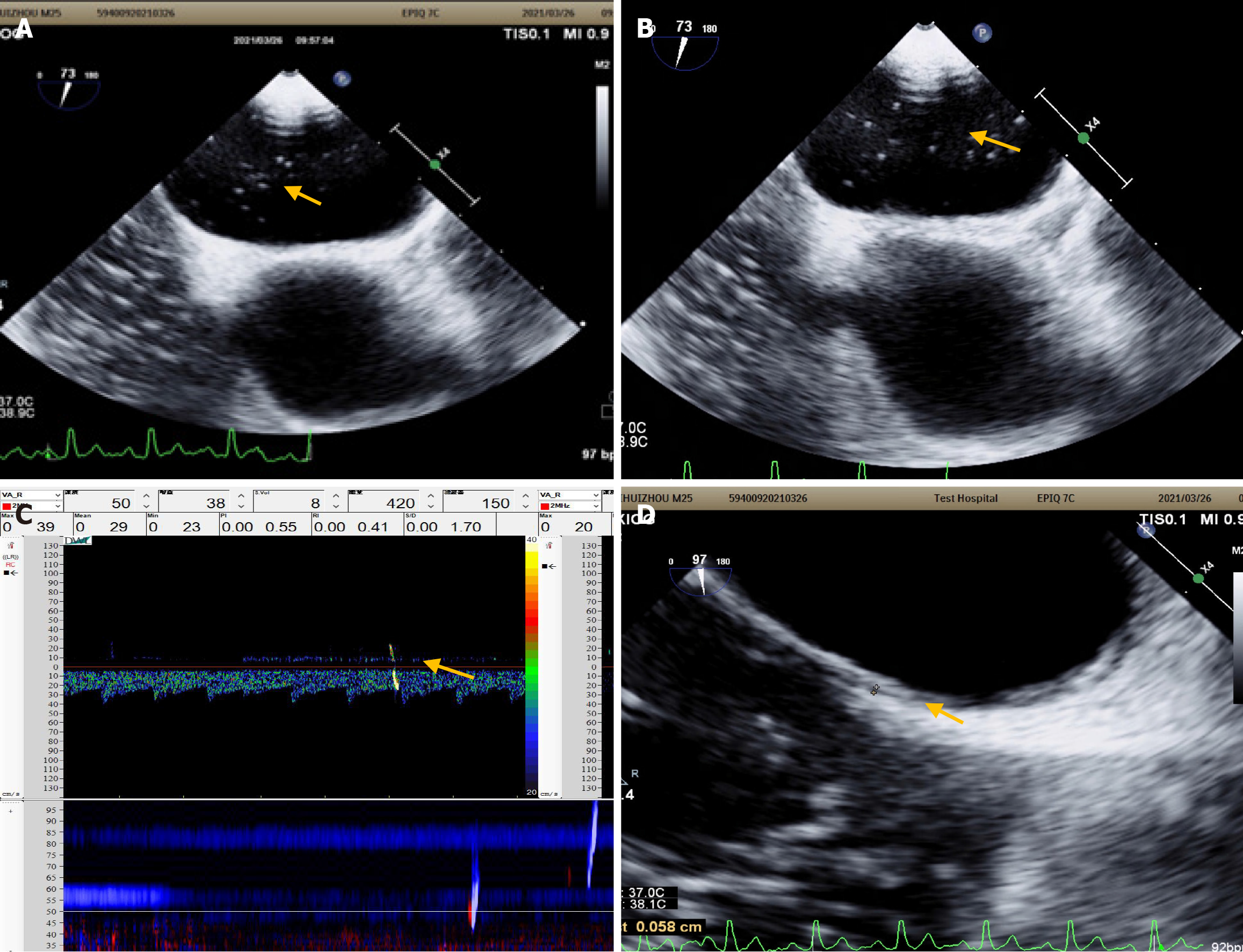
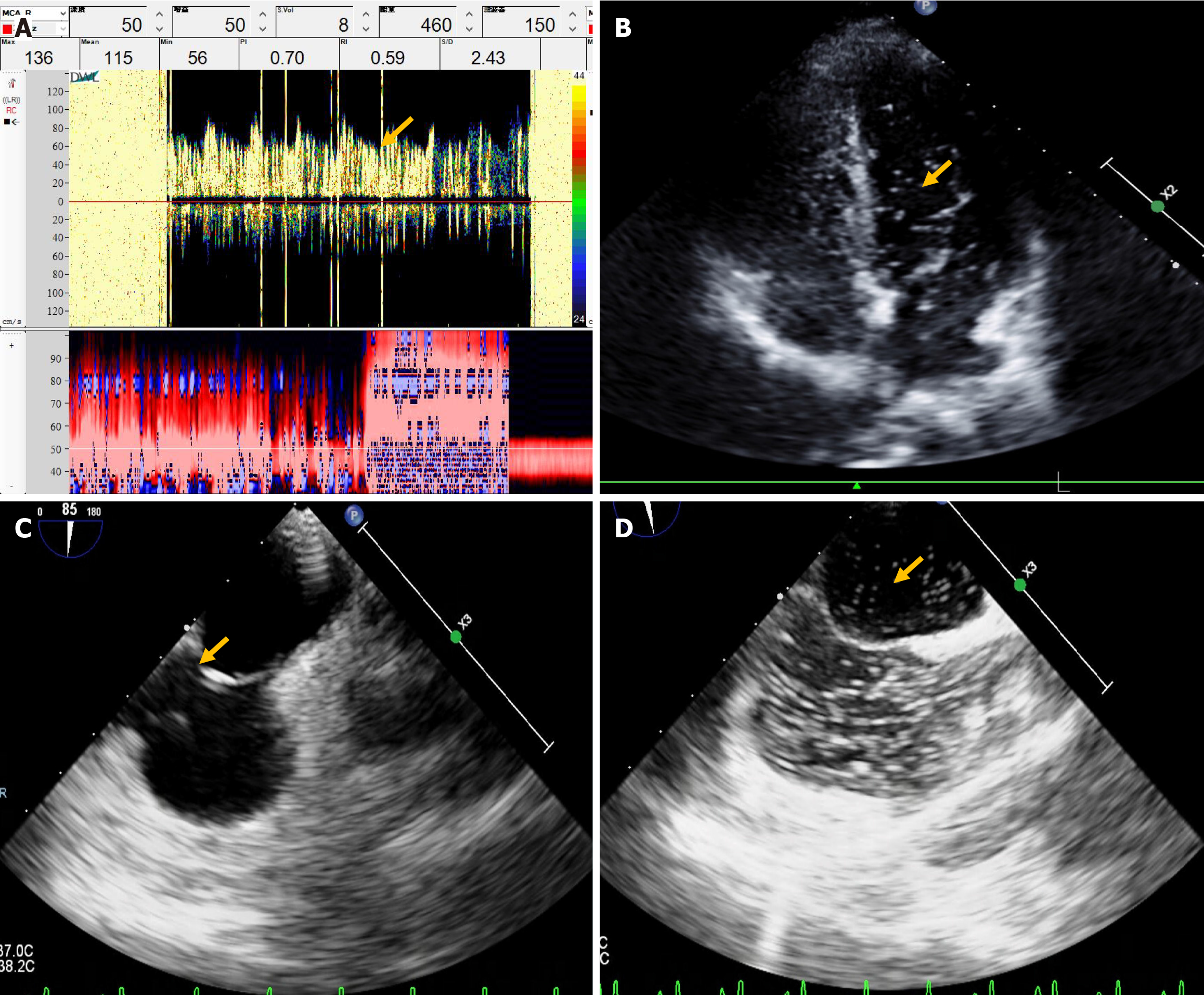
Figure 3 Comparison of transthoracic echocardiography at rest.
A: At rest, a moderate right-to-left shunt (RLS) is observed on contrast transthoracic echocardiography; B: A large RLS (> 30 microbubbles) is observed following the Valsalva maneuver (VM); C: Contrast transcranial Doppler only detects a small RLS during VM; D: Enhanced transesophageal ultrasonography identifies a patent foramen ovale (arrow).
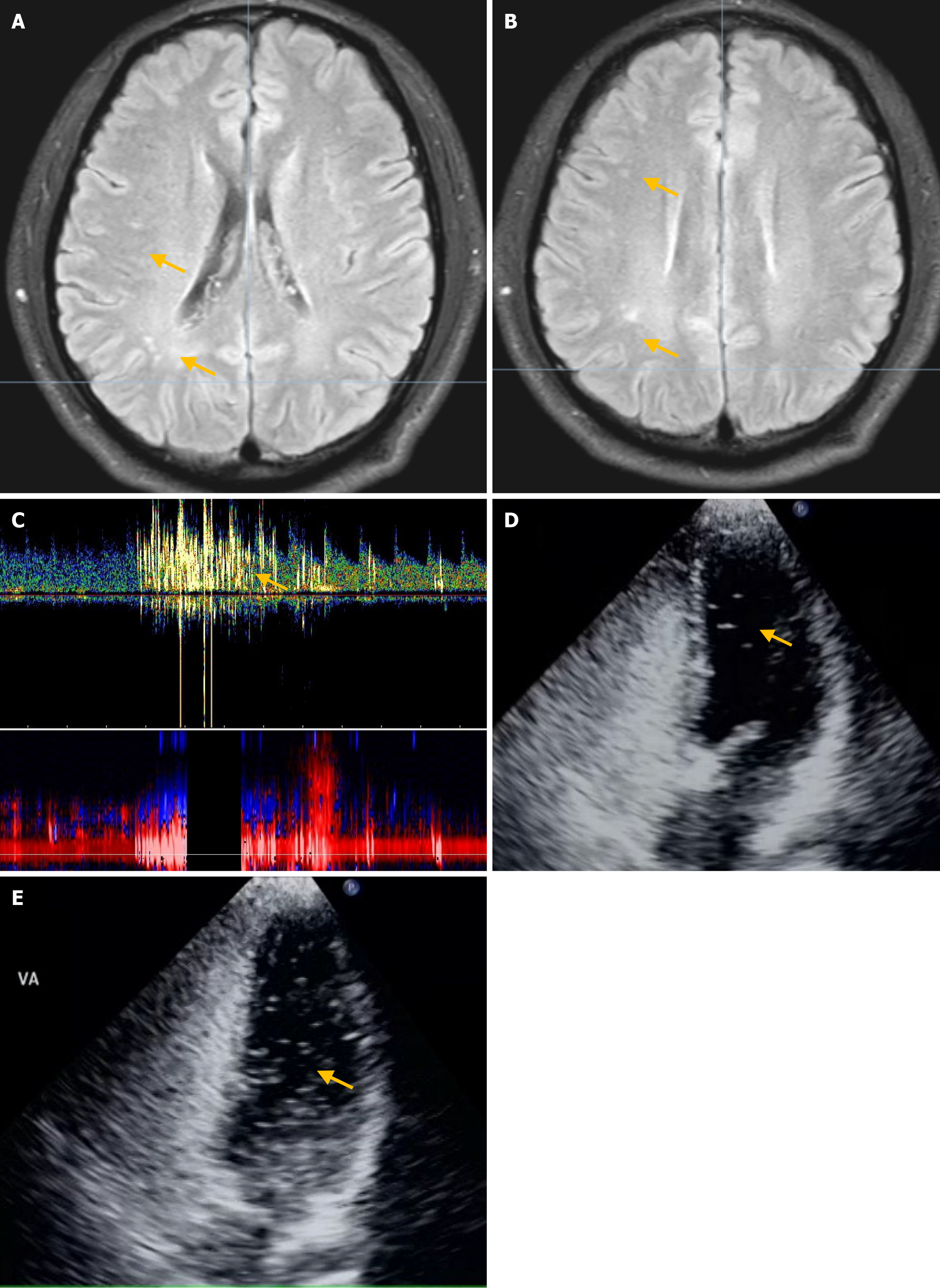
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
A and B: Brain magnetic resonance imaging identified a few small ischemic foci in bilateral subcortical areas (arrows); C: At rest, contrast transcranial Doppler shows a small right-to-left shunt (RLS), whereas after the Valsalva maneuver (VM) it shows a large RLS; D and E: Contrast transthoracic echocardiography shows a small and a moderate RLS at rest and after the VM, respectively.
Figure 5 Contrast transthoracic echocardiography.
A: Contrast transthoracic echocardiography showing a small right-to-left shunt (RLS) at rest and during the Valsalva maneuver (VM); B: Contrast transcranial Doppler identifies a small RLS at rest and a large RLS during VM; C and D: Enhanced transesophageal ultrasonography revealing a patent foramen ovale (arrow) with a large presence of microbubbles (arrow).
- Citation: Yao MJ, Zhao YY, Deng SP, Xiong HH, Wang J, Ren LJ, Cao LM. Right-to-left shunt detection via synchronized contrast transcranial Doppler combined with contrast transthoracic echocardiography: A preliminary study. World J Radiol 2024; 16(11): 657-667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i11/657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.657