Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2022; 14(8): 249-255
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i8.249
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i8.249
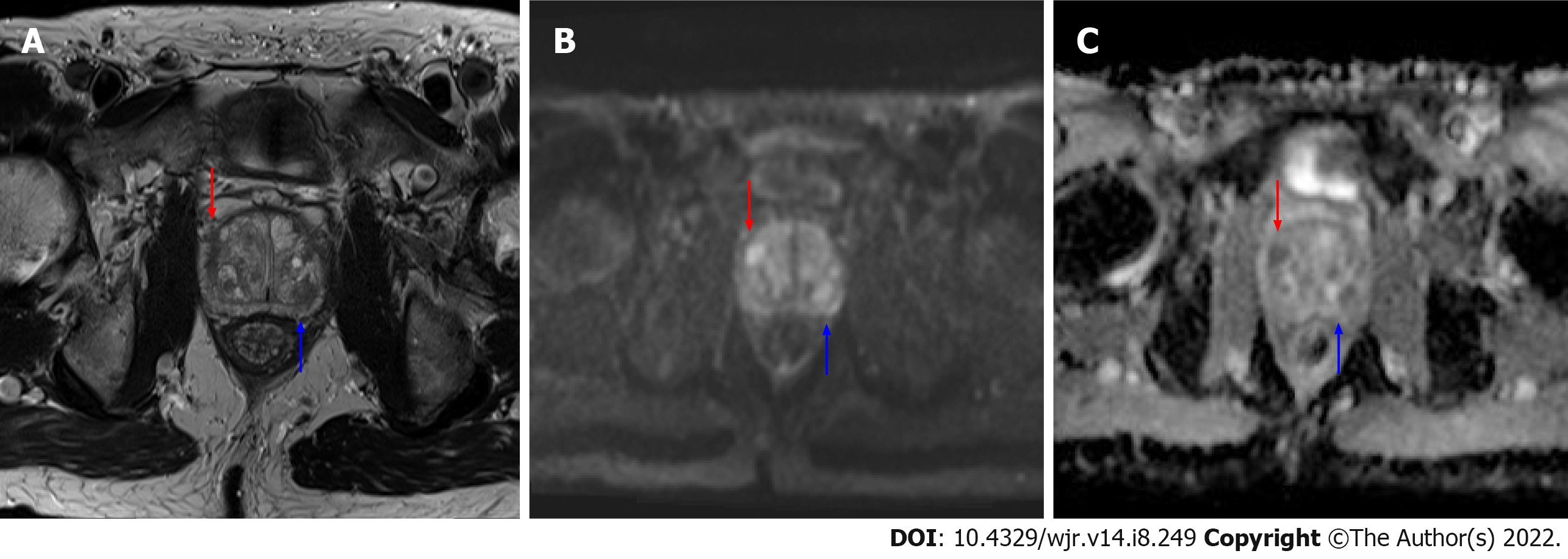
Figure 1 Axial magnetic resonance imaging images of the prostate.
A: T2 weighted image; B: b1200 diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) image; C: Calculated apparent dispersion coefficient (ADC) image. A mostly encapsulated T2-hypointense transitional zone lesion is demonstrated in the left posterior central gland, measuring 10 mm (blue arrows) with focal moderate low ADC, high DWI signal, designated prostate imaging reporting and data system (PI-RADS) 3 per PI-RADS version 2.1. An additional 8 mm PI-RADS 4 Lesion of the anterior right transitional zone is present (red arrow), demonstrating non-circumscribed moderate T2 hypointensity and marked focal ADC hypointensity and DWI hyperintensity.
Figure 2 Sample structured report for prostate lesion reporting with integrated risk calculator reporting.
The calculated percent risk of clinically significant prostate cancer is included in the lesion evaluation findings with recommendations for biopsy or observation in the conclusion. csPCa: Clinically significant prostate cancer; DRE: Digital rectal exam; DWI: Diffusion weighted imaging; PI-RADS: Prostate imaging reporting and data system; PSA: Prostate specific antigen.
- Citation: Gupta K, Perchik JD, Fang AM, Porter KK, Rais-Bahrami S. Augmenting prostate magnetic resonance imaging reporting to incorporate diagnostic recommendations based upon clinical risk calculators. World J Radiol 2022; 14(8): 249-255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v14/i8/249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v14.i8.249