Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2022; 14(6): 155-164
Published online Jun 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i6.155
Published online Jun 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i6.155
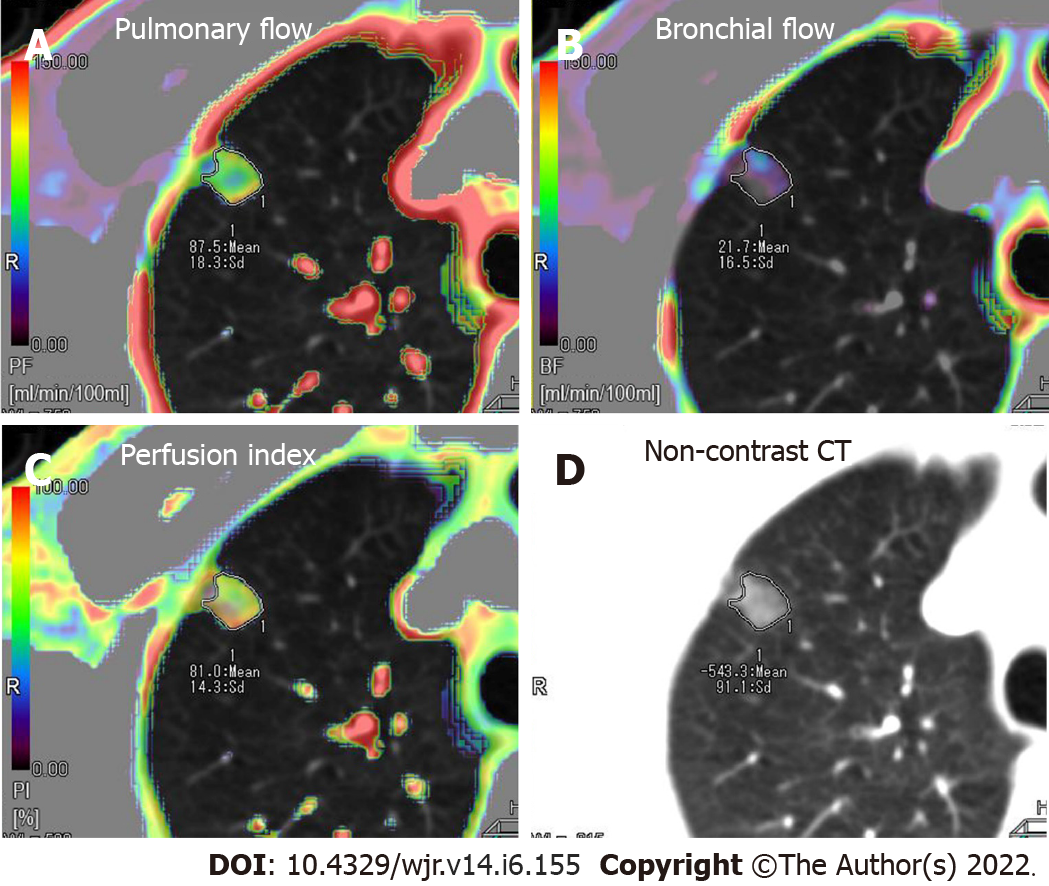
Figure 1 Axial colored perfusion maps in a 55-year-old male patient with pure ground-glass nodule carcinoma located in the right superior lung.
Dominant pulmonary flow (PF) along with subordinate bronchial flow (BF) was observed in the pure ground-glass nodule. A: Axial colored perfusion map of PF; B: Axial colored perfusion map of BF; C: Axial colored perfusion map of perfusion index; D: Axial non-contrast computed tomography.
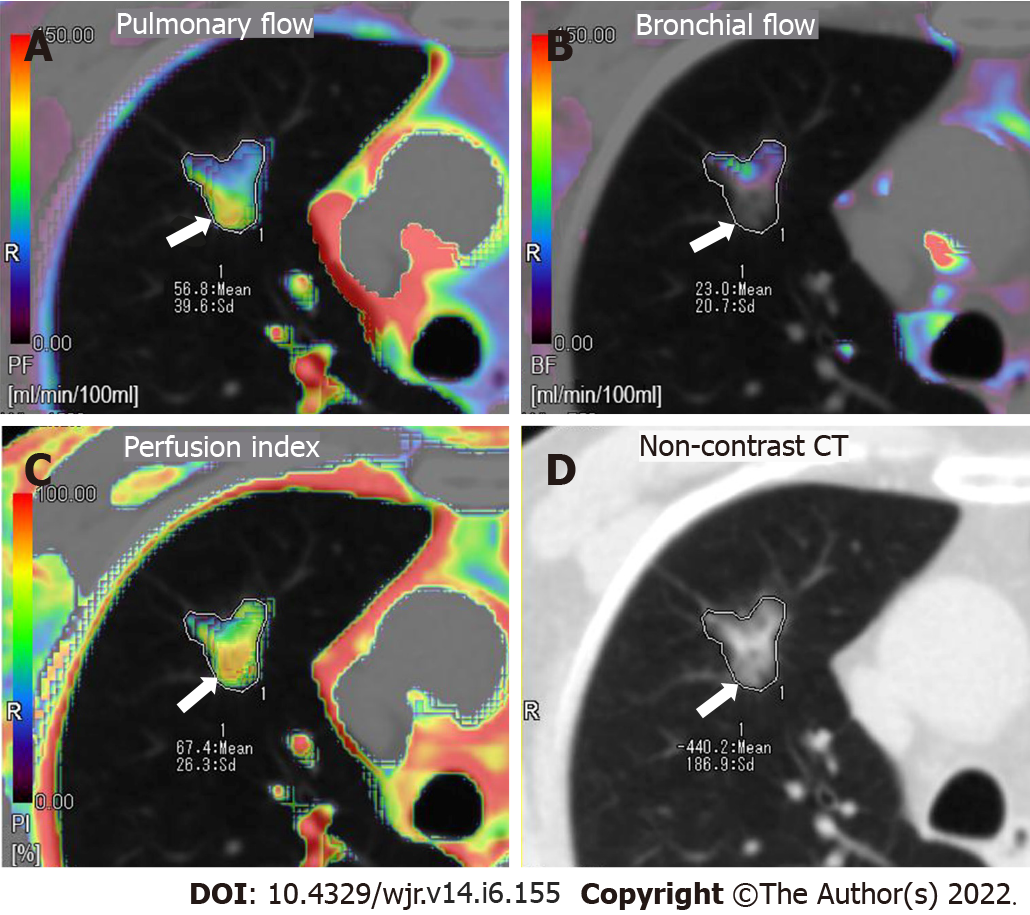
Figure 2 Axial colored perfusion maps in a 72-year-old male patient with mixed ground-glass nodule carcinoma located in the right superior lung.
The perfusion is heterogeneous throughout the lesion. Pulmonary flow (PF) is globally dominant, especially in the dorsal part of the lesion (arrow), which corresponds to the lower attenuation region of the mixed ground-glass nodule. A: Axial colored perfusion map of PF; B: Axial colored perfusion map of bronchial flow; C: Axial colored perfusion map of perfusion index; D: Axial non-contrast computed tomography.
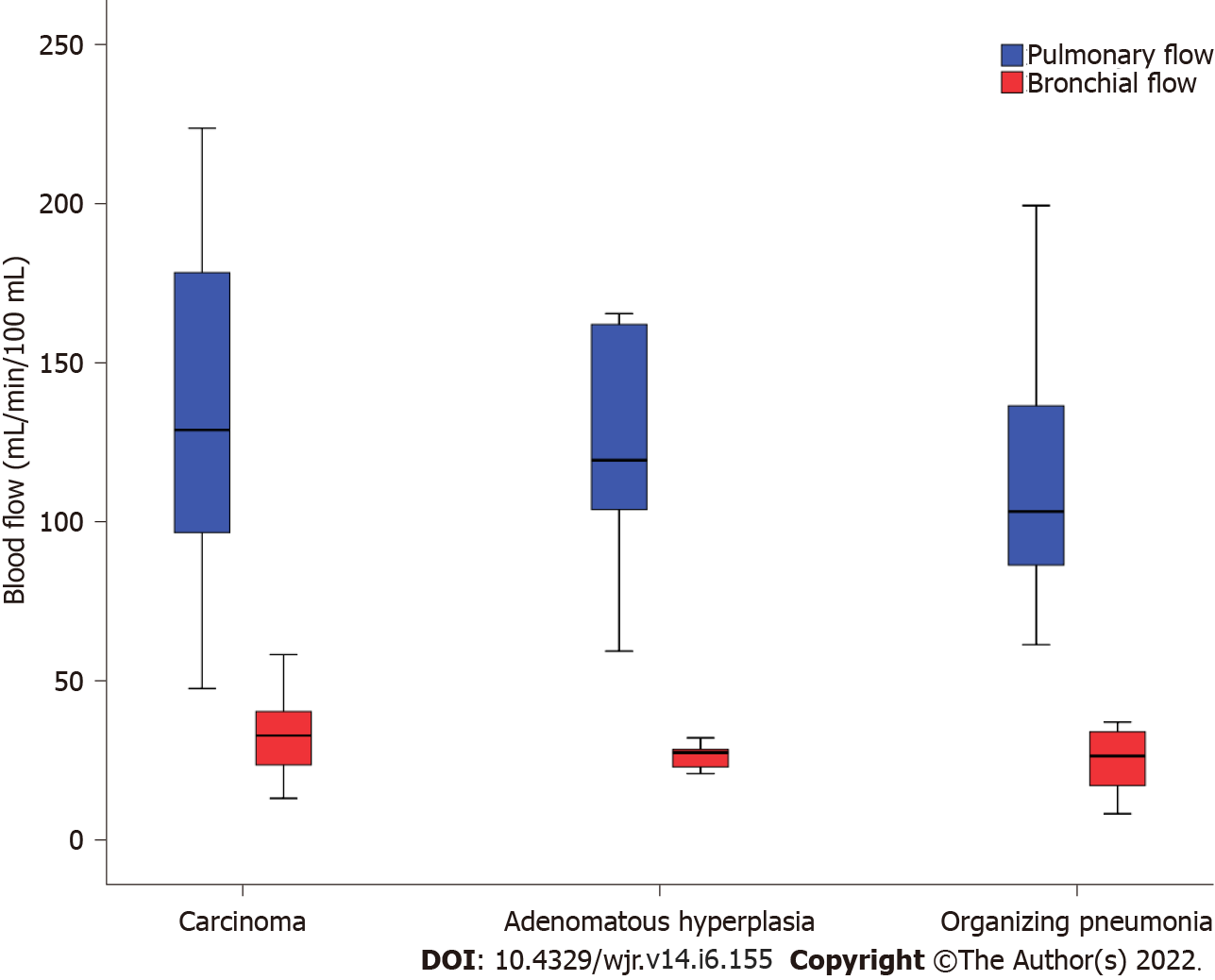
Figure 3 Box plot of perfusion parameters demonstrates dominant Pulmonary flow (PF) along with relatively low bronchial flow (BF) in carcinoma (n = 30), atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (n = 6) and organizing pneumonia (n = 11).
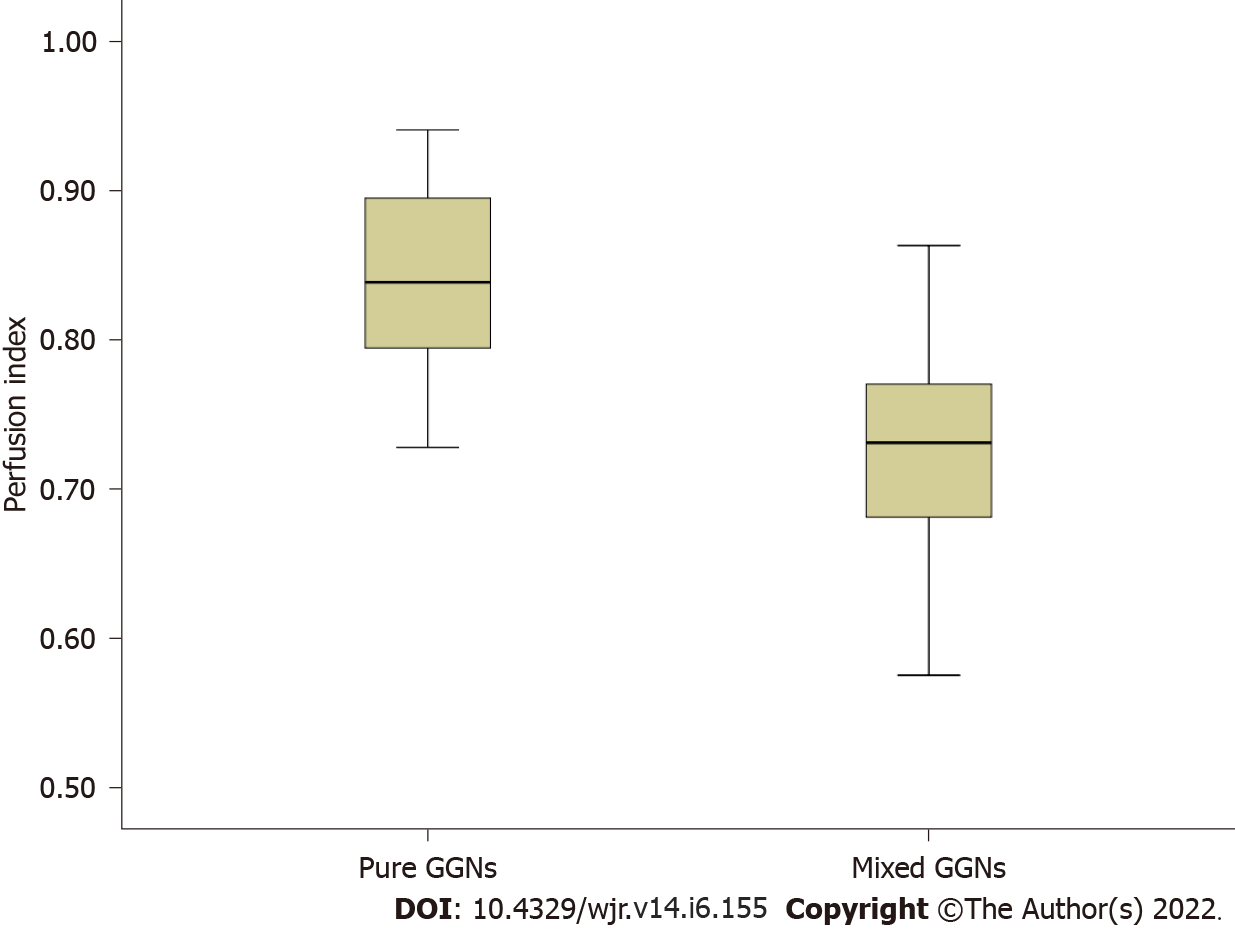
Figure 4 Box plot of perfusion index [= pulmonary flow/(pulmonary flow + bronchial flow)] demonstrates dominant pulmonary flow along with subordinate bronchial flow in pure ground-glass nodule carcinoma (n = 16) and a weakened pulmonary flow along with an enhanced bronchial flow in mixed ground-glass nodule carcinoma.
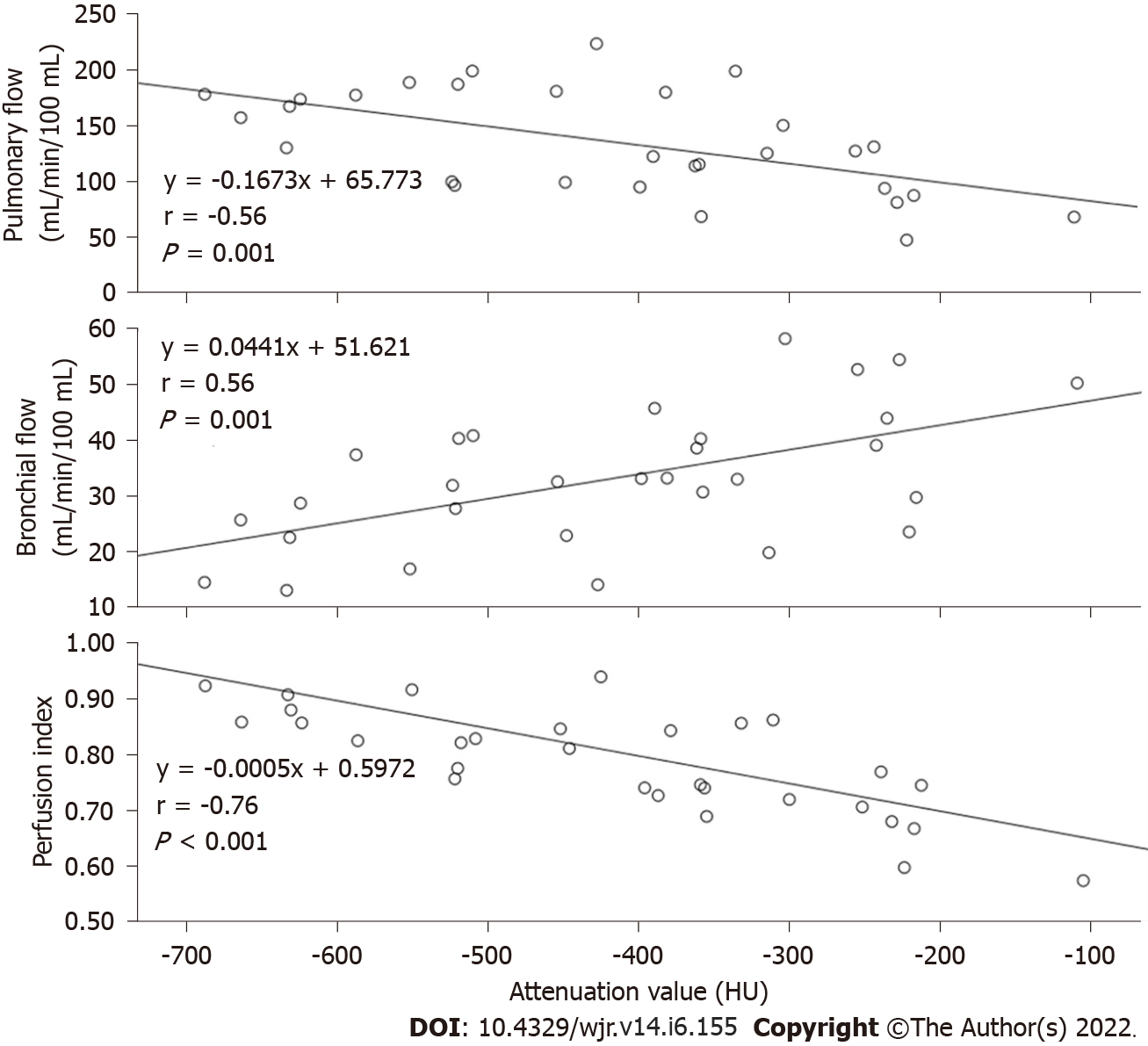
Figure 5 Plots of the Pearson correlation between the attenuation values of the ground-glass nodule carcinoma and the three perfusion parameters.
The HU of the GGN carcinoma correlates negatively, positively and negatively with the pulmonary flow (PF), bronchial flow (BF) and the perfusion index (PI), respectively. A: Correlation between the HU of ground-glass nodule (GGN) carcinoma and PF; B: Correlation between the HU of GGN carcinoma and BF; C: Correlation between the HU of GGN carcinoma and PI.
- Citation: Wang C, Wu N, Zhang Z, Zhang LX, Yuan XD. Evaluation of the dual vascular supply patterns in ground-glass nodules with a dynamic volume computed tomography. World J Radiol 2022; 14(6): 155-164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v14/i6/155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v14.i6.155