Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2021; 13(10): 314-326
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i10.314
Published online Oct 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i10.314
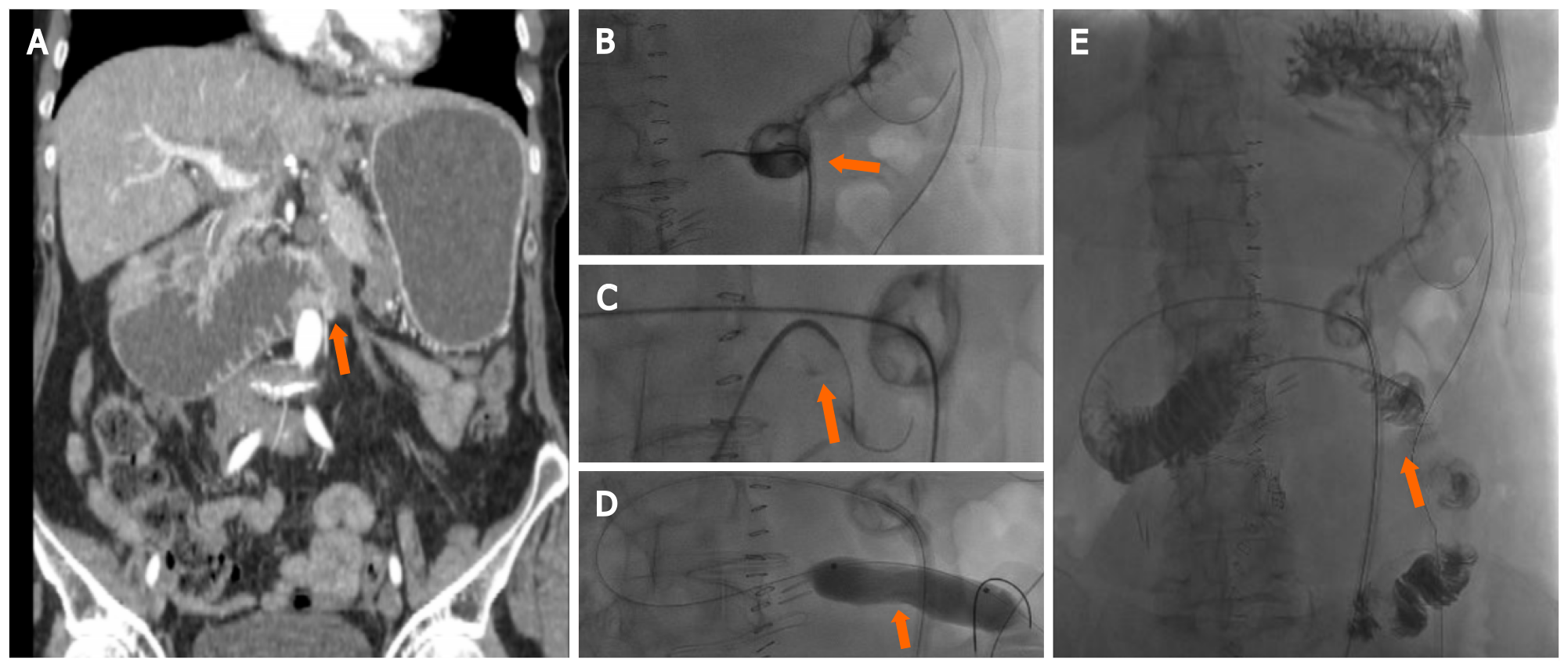
Figure 1 87-year-old female with distal duodenum/proximal jejunum Ca presents with severe recurrent melenas.
Endoscopic hemostasis failed in high risk surgical patients with hemodynamic instability and normal coagulation state, requiring embolization after transfusion and hemodynamic stabilization (stabilized blood pressure 90 mmHg with inotropes, HR: 110/min. Hb 6.4). A: Computed tomography-Angio: Two active bleeding sites at proximal jejunum (arrows); B: Selective digital subtraction angiography (DSA) from superior mesenteric artery depicting the bleeding sites (arrows); C: Selective catheterization of the feeding artery with microcatheter and two 3 mm micro coils deployed; D: Lesions are not depicted at final DSA.
Figure 2 Presacral collection following rectal surgery.
A: Axial computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrating a 4 cm × 3 cm presacral fluid collection (arrow), with small air bubbles; B: Patient in prone position, a Chiba needle is inserted with a trans-gluteal approach under CT guidance; C and D: Mip CT images and 3D Volume rendering reconstruction confirming the exact 8Fr drainage positioning.
Figure 3 Upper gastrointestinal cancers obstruction.
A: A 60 yr female with stage 4 ovarian cancer, with peritoneal carcinomatosis causing occlusion at the Treitz level (arrow); B and C: After percutaneous insertion of a decompressive gastrostomy, an angiografic catheter was advanced at the level of the occlusion and crossed using an hydrophilic guidewire (arrow); D and E: A ballon dilatation (18 mm × 6 cm) was performed (D, arrow) and a 5 fr catheter was left in place to ensure enteral nutrition (E, arrow).
Figure 4 Celiac plexus alcohol neurolysis.
In a patient with metastatic pancreatic cancer and non-controlled pain, an 18G Chiba needle (arrow) is inserted under computed tomography-guidance with a paravertebral approach; ethanol (95%–100%) is injected into the antecrural space after confirming the needle position with diluted iodinate contrast medium.
- Citation: Reitano E, de'Angelis N, Bianchi G, Laera L, Spiliopoulos S, Calbi R, Memeo R, Inchingolo R. Current trends and perspectives in interventional radiology for gastrointestinal cancers. World J Radiol 2021; 13(10): 314-326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v13/i10/314.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v13.i10.314