Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2018; 10(10): 135-142
Published online Oct 28, 2018. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v10.i10.135
Published online Oct 28, 2018. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v10.i10.135
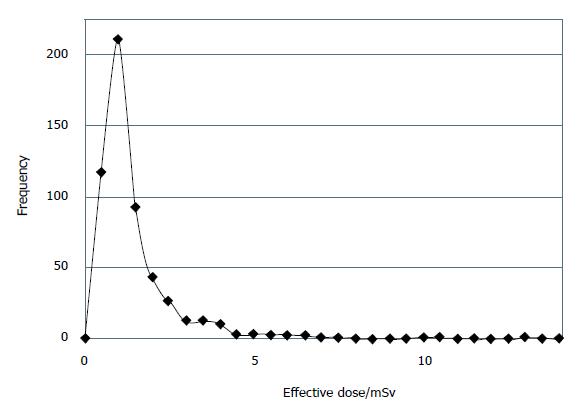
Figure 1 Distribution of effective doses for patients undergoing coronary computed tomography angiography.
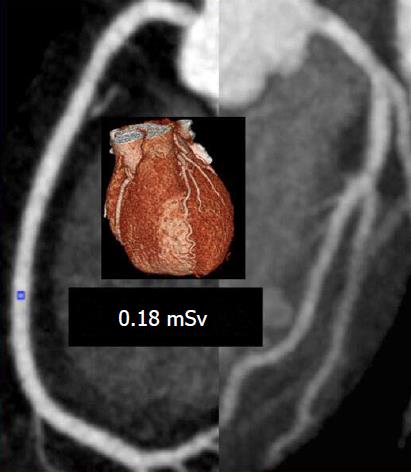
Figure 2 Coronary computed tomography angiography examination with image quality score 4 performed in a 52 years old female patient with heart rate of 56 bpm with a dose of 0.
18 mSv.
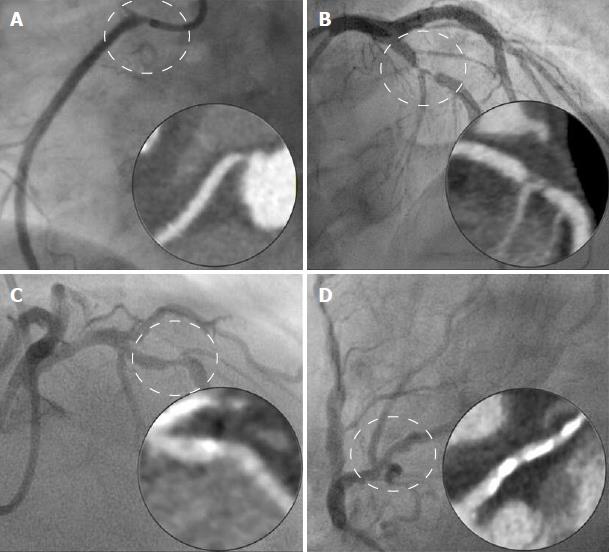
Figure 3 Examples of correlation of coronary computed tomography angiography with invasive angiography.
A: Correct identification of ostial stenosis in right coronary; B: Correct identification of significant stenosis in left anterior descending coronary; C: Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) incorrectly classifies lesion as not significant (subsequently proven to be haemodynamically significant with fractional flow reserve); D: CCTA incorrectly identifies a significant lesion in circumflex coronary due to artefact from extensive calcification.
- Citation: Richards CE, Dorman S, John P, Davies A, Evans S, Ninan T, Martin D, Kannoly S, Roberts-Davies G, Ramsey M, Obaid DR. Low-radiation and high image quality coronary computed tomography angiography in “real-world” unselected patients. World J Radiol 2018; 10(10): 135-142
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v10/i10/135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v10.i10.135