INTRODUCTION
During the past few years, computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) has rapidly emerged as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography, particularly in patients at intermediate risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). Multicenter studies have confirmed the high predictive accuracy of CTCA, and further demonstrated comparable results to conventional angiography regarding the prediction of revascularization[1,2]. The high predictive accuracy of CTCA, and particularly its negative predictive value, has lead to the ongoing incorporation of the technique in the diagnostic work-up of patients with suspected CAD.
However, recent data suggesting that revascularization does not improve the prognosis of patients with intermediate coronary artery stenosis if the lesion does not impair flow during stress, renders mere anatomical assessment of coronary stenosis without myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) a very useful, albeit insufficient approach for clinical decision making[3,4]. In this regard, MPI has shown to be a useful and accurate tool in the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with CAD[5]. Until recently, CTCA was restricted to the anatomical assessment of coronary stenosis, whereas the functional significance of coronary lesions remained outside of its scope. Nevertheless, the kinetics of iodinated contrast is similar to gadolinium-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid used in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), allowing assessment of myocardial perfusion and viability by cardiac CT[6-14]. Accordingly, a number of studies confronted this limitation by demonstrating that myocardial perfusion during first-pass contrast-enhanced adenosine stress CTCA is feasible and related to microsphere-derived myocardial blood flow [15,16].
In parallel, owing to a volumetric acquisition and to ECG-triggering, CTCA allows submillimetric reconstructions from every possible angle at different time points of the cardiac cycle, consequently creating an optimal scenario for morphological and functional assessment, and enabling a wide array of non-coronary applications.
ASSESSMENT OF MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION WITH CT
It has been a long time since MPI was established as a reference standard for risk stratification and decision making in patients with CAD.
During the past 30 years, the field of MPI has been lead by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET), supported by robust evidence establishing that prognosis is highly related to the presence of inducible ischemia[5]. Nevertheless, these methods portray a number of inherent limitations, namely attenuation artifacts, expenses, ionizing radiation, and restricted availability of PET.
More recently, myocardial perfusion assessment using MRI has been established as an alternative to evaluate myocardial perfusion by means of an ionizing radiation free technique with superior spatial resolution, which allows discrimination between subendocardial and transmural infarction[17,18].
The rapidly evolving field of CTCA has lead to the exploration of non-coronary applications of CTCA[19]. The anatomical nature of CT has been one of the most debated limitations of CTCA for the purpose of evaluating patients with a high probability of CAD, thus significant efforts have been undertaken to attempt a simultaneous assessment of myocardial perfusion. Myocardial perfusion at rest has already been investigated in the past using electron beam CT[20]. The physiopathological substrate of this concept is similar to MRI with gadolinium, since both contrast media have similar kinetics. Accordingly, a conceptual congruence exists between MRI and CTCA regarding the assessment of myocardial perfusion and viability. In brief, during the first pass of iodinated contrast through the left ventricle, areas with diminished perfusion have a reduced delivery of contrast to the myocardium resulting in a characteristic hypoattenuation (Figure 1)[15]. The evaluation of myocardial perfusion defects at rest over the simultaneous assessment of coronary artery stenosis appears to be an interesting strategy for the assessment of patients with acute chest pain. It is noteworthy that myocardial perfusion at rest can be evaluated during conventional CTCA acquisitions, with no additional contrast administration or radiation dose required. Myocardial perfusion defects in first pass contrast-enhanced MDCT correlate closely with the presence of ischemic myocardium and myocardial necrosis, as determined by increases in troponin levels[15,22].
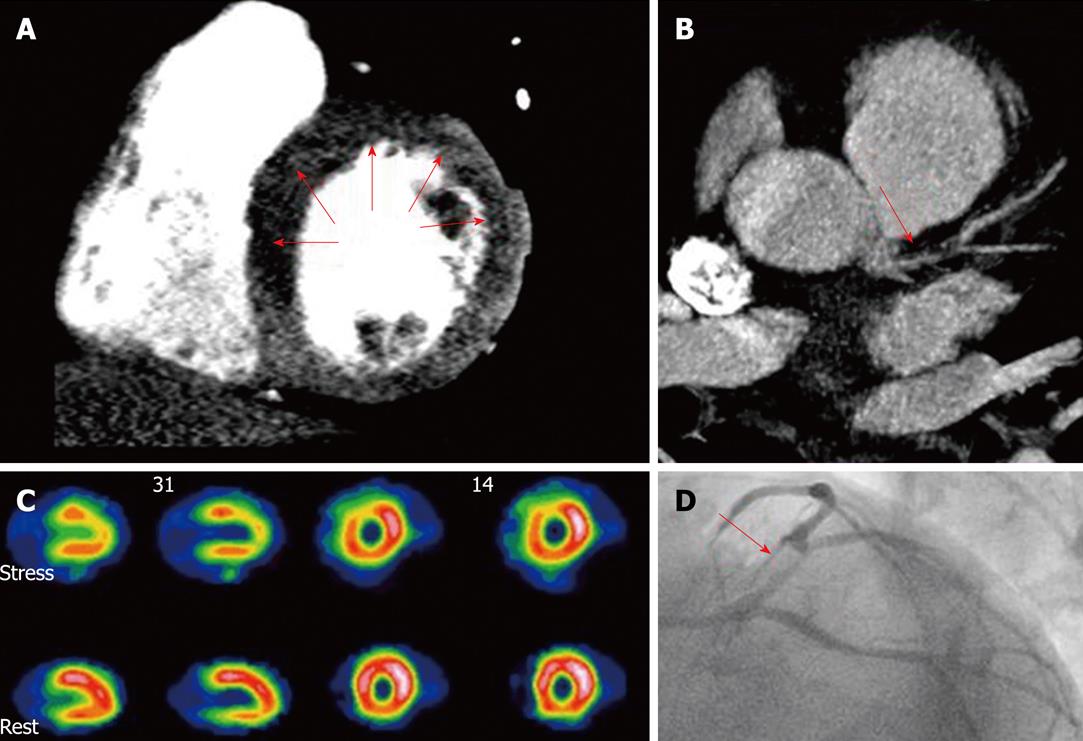
Figure 1 Combined assessment of myocardial perfusion at pharmacological (adenosine) stress and coronary angiography within a single-session cardiac computed tomography.
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) (panels A and B) showed diminished perfusion of the left ventricle anterior and septal wall (A, arrows) and a significant lesion at the proximal left anterior descending artery (B, arrow), findings confirmed by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (C) and invasive coronary angiography (D, arrow). A: CT perfusion (stress); B: Coronary CT angiography; C: SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging; D: Invasive angiography. With permission of Blankstein et al[21], J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 54: 1072-1084.
Since the assessment of myocardial perfusion by CTCA is based on the myocardial signal density, it is pivotal to determine the normal values of myocardial signal density and to identify potential mechanisms of misinterpretation of perfusion defects. A recent study that included consecutive asymptomatic patients without history of CAD and low pre-test likelihood, reported a mean myocardial signal density at the basal, mid and apical myocardium of 97.4 ± 17.3 Hounsfield units (HU), with significant differences between inferobasal and all American Heart Association segments. Indeed, the inferobasal segments commonly showed a considerable myocardial signal density drop mimicking perfusion defects, which appears to be attributed to beam hardening effect artifacts from the spine[23].
ASSESSMENT OF MYOCARDIAL VIABILITY BY CARDIAC CT
The ability to discriminate between dysfunctional but viable myocardium and necrotic myocardium has important clinical implications, regarding both clinical outcome and election of optimal therapeutical strategy. Indeed, a large meta-analysis demonstrated an 80% reduction in mortality in patients with CAD and left ventricular dysfunction with viable myocardium treated with revascularization, and no benefit for revascularization in patients without viability[24].
In the setting of acute myocardial infarction, the presence of microvascular obstruction and reduced capillary density lead to a delayed arrival of contrast to the infarct core during the first pass of iodinated contrast through the left ventricle. Likewise, those necrotic regions display a delayed enhancement of contrast, attributed mainly to an increment in the volume of distribution and to a delayed contrast wash-out (Figure 2)[6-14]. Both patterns are highly reproducible and have been extensively validated in animal and clinical studies, with good concordance with SPECT and MRI, although the contrast-to-noise ratio is significantly higher with MRI[6-14].
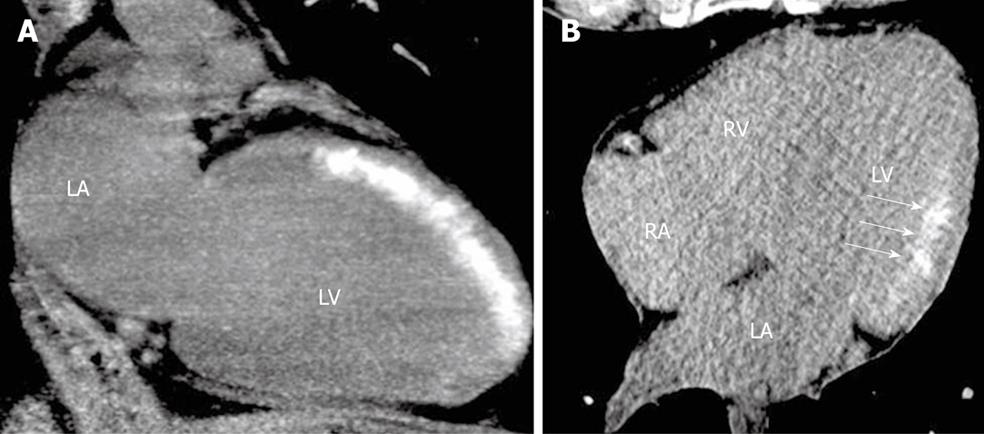
Figure 2 Early assessment of myocardial viability immediately after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with anterior (A) and inferolateral (B) ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction.
Delayed enhancement of iodinated contrast administrated during percutaneous coronary intervention is observed using non-contrast enhanced cardiac computed tomography, without heart rate control and using a low dose-saving protocol. Discrimination between transmural (A) and subendocardial (B, arrows) extent of the irreversible myocardial damage (delayed enhancement) can be achieved using this technique. LA: Left atrium; LV: Left ventricle; RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle.
An emergent clinical application of delayed enhancement using cardiac CT is for early assessment of myocardial viability in the setting of ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI). A recent study that explored this concept in STEMI patients undergoing non-contrast cardiac CT immediately after primary percutaneous coronary intervention, demonstrated that although door-to-balloon target times were accomplished and optimal epicardial results (TIMI 3) were obtained, myocardial delayed enhancement (Figure 2) was detected in half of the patients. Similarly, even though 6-mo clinical outcome did not differ significantly, the presence of myocardial delayed enhancement was related to poor microvascular flow, greater enzyme elevation, worse left ventricular function, and a higher incidence of complications during hospitalization[14]. It should be noted that this application of the technique uses the contrast administrated during the invasive procedure, thereby precluding the need for contrast administration during the CT scan. In addition, since coronary assessment is not required and contrast enhancement is usually readily evident if present, β-blockers are not required and radiation dose can be significantly reduced up to 5.5 mSv using retrospective gating acquisitions. Indeed, Chang et al[25] recently demonstrated good agreement between retrospective and prospective ECG-gated delayed enhancement CT regarding infarct size estimation, enabling a further significant decrease in radiation dose (930.1 ± 62.2 mGyXcm vs 42.4 ± 2.3 mGyXcm, P < 0.001).
Finally, it should be stressed that delayed enhancement studies also allow evaluation of the presence of microvascular obstruction, an independent predictor of events after acute myocardial infarction, as hypoattenuated regions within an area of delayed enhancement[13,26].
The transmural extension of the delayed enhancement is significantly related to the likelihood of improvement in regional function after revascularization[27]. In parallel to cardiac MRI, the spatial resolution of CT allows the ability to discriminate between transmural and subendocardial infarcts using delayed enhancement CT (Figure 2)[14].
ASSESSMENT OF CHRONIC MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION SEQUELAE BY CARDIAC CT
Cardiac CT also allows an accurate evaluation of characteristics of chronic myocardial infarction and its sequelae (Figure 3). It is worth mentioning there is a higher prevalence of apical thrombus detected with CT compared to echocardiography[28], with the difference possibly attributed to a higher spatial resolution and to the ability to evaluate the entire cardiac volume without “window” restrictions. Indeed, Carlsson et al[29] demonstrated a similar diagnostic accuracy of CT and MR in detecting heterogeneous microinfarcts in a swine model.
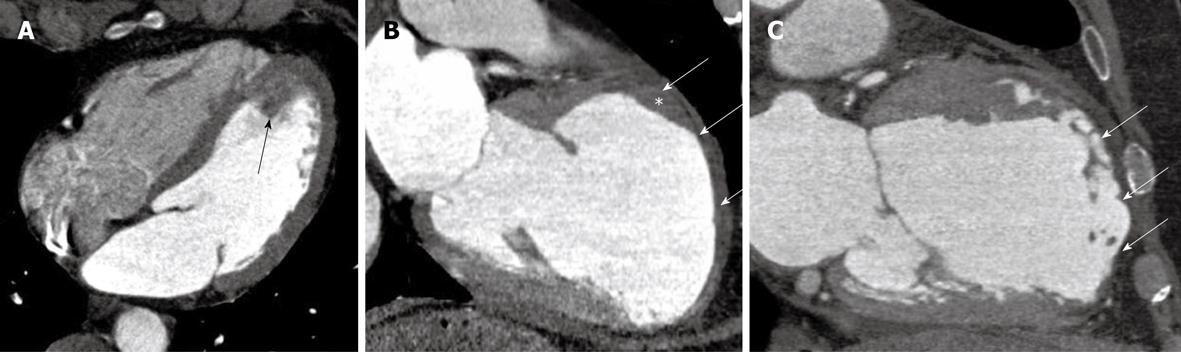
Figure 3 Acute and chronic sequelae of myocardial infarction.
A: A four-chamber view of a patient with acute chest pain and an occluded mid left descending coronary artery. A fresh, mobile, pedunculated thrombus is observed at the left ventricular apex (arrow); B: A two chamber view of a patient with recent onset heart failure and history of previous myocardial infarction. A left ventricle aneurysm is detected at the anterior wall, with significant wall thinning, pericardial effusion (arrows) and a fixed thrombus (*); C: An anterior wall chronic myocardial infarction, with significant wall thinning and lipomatous metaplasia (arrows).
On the other hand, chronic myocardial infarction characterization using CTCA has revisited the concept of lipomatous metaplasia. Despite the fact that adipose tissue can be easily detected using histopathology, the presence of myocardial fat replacing scar tissue remained unreported until 1997[30]. Recently, Su et al[31] demonstrated the presence of adipose tissue in 84% of evaluated chronic myocardial infarctions. Furthermore, using specific sequences to detect fat, a magnetic resonance study identified adipose tissue in 78% of infarcts older than 6 mo[32].
CT has the ability to discriminate between air, water, fat and bone, with fat presenting a density of approximately -120 HU. Consequently, a number of studies have recently been carried out to explore the characterization of chronic myocardial infarction using CTCA. These studies have confirmed the notion that infarcted tissue is gradually replaced by adipose tissue, although attenuation levels (HU) are usually slightly higher than those of pericardial fat, indicating possibly a compound of adipose tissue, fibrosis, and myocardial fibers within the infarct core[28,33]. Overall, these results countermine the longstanding concept of myocardial scar, whose Latin origin is derived from the production and contraction of fibrous tissue.
The high prevalence of adipose tissue in myocardial infarction represents a possibility to attempt identification of chronic MI by means of CT without the addition of contrast media. This has been recently explored using conventional coronary calcium scoring acquisitions, showing a sensitivity and specificity of 66% and 100%, respectively, for the detection of chronic myocardial infarction (Figure 3). The presence of lipomatous metaplasia seems to be highly related to the infarct age. We have recently shown that patients with myocardial hypoenhancement on contrast CT had older infarcts than did patients without hypoenhancement (24 mo, interquartile range, 12-48 mo vs 6 mo, interquartile range, 3-33 mo, P = 0.04). Similar results were found with non-contrast CT (36 mo, interquartile range, 13-60 mo vs 11 mo, interquartile range, 4-24 mo, P < 0.001)[28].
COMBINED ASSESSMENT OF CORONARY ANATOMY AND STRESS MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION: ONE-STOP SHOP?
Recently, two invasive studies that evaluated the coronary reserve flow have stressed the importance of functional assessment by showing that revascularization of patients with intermediate lesions does not confer a significant clinical benefit if stenoses are not flow limiting during stress[3,4]. In the same line, Meijboom et al[34] demonstrated that both conventional angiography and CTCA show a poor correlation with coronary flow reserve (r = -0.30 and r = -0.32, respectively), rendering a diagnostic accuracy of 67% and 71%, respectively. These findings represent a challenge for non-invasive imaging techniques and warrant the search for a “one-stop shop” tool that would allow a combined assessment of the coronary anatomy and of the functional significance of coronary lesions. Even with the advent of dual source CT scanners, diffuse calcification is commonly related to a significant drop in positive predictive values, reinforcing the need for functional assessment by MPI[35]. As aforementioned, CTCA allows the evaluation of myocardial perfusion at rest. In addition, recent advances in multidetector-row CT have allowed a simultaneous assessment of coronary imaging and MPI during pharmacological stress with adenosine. A seminal study using a canine model of left anterior descendent artery stenosis demonstrated a myocardial blood flow in stenosed vs remote territories of 2.54 ± 0.93 mL/g per min and 8.94 ± 5.74 mL/g per min, respectively (P < 0.05) during adenosine infusion, with a myocardial signal density (HU) of 92.3 ± 39.5 HU in stenosed vs 180.4 ± 41.9 HU in remote territories (P < 0.001)[15].
More recently, Blankstein et al[21] have shown the feasibility of the combined (sequentially during the same procedure) morphological-functional approach: (1) adenosine-stress myocardial perfusion; (2) rest myocardial perfusion; (3) coronary angiography (simultaneous with rest perfusion); and (4) delayed enhancement 7 min post-contrast. This combined approach has been carried out with an effective radiation dose of 12.7 mSv, similar to that observed with SPECT in the same study. Adenosine-stress myocardial perfusion yielded a 79% and 80% sensitivity and specificity, respectively, to detect > 50% diameter stenoses by conventional angiography; whereas SPECT showed a sensitivity and specificity of 67% and 83%, respectively. In turn, using > 70% diameter stenoses as a reference standard, adenosine-stress myocardial perfusion yielded an 86% and 68% sensitivity and specificity, respectively, whereas SPECT showed a sensitivity and specificity of 73% and 73%, respectively. It should be stressed that this study included a high risk population, with a high prevalence of previous MI (35%), previous revascularization (38%), diabetes (32%), hypertension (88%), dyslipidemia (85%) and obesity (41%)[21].
With the advent of new generation dual source CT scanners, cardiac acquisitions can be accomplished within a single heart beat, allowing a substantial reduction in radiation exposure. Rocha-Filho et al[36] recently demonstrated that adding stress CT perfusion to coronary CT angiography during a single session has a significant incremental value for the detection of hemodynamically significant CAD, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve increasing from 0.77 to 0.90 (P < 0.005). Interestingly, this was achieved at an acceptable mean effective radiation exposure of 11.8 mSv.
It should be stressed that such a combined approach might gain relevance particularly in patients with a high probability of CAD with diffusely calcified vessels.
CLINICAL PERSPECTIVE
During the past decade, CTCA has evolved as the non-invasive diagnostic tool with the highest diagnostic performance to detect coronary artery stenosis, particularly driven by its ability to exclude CAD. A number of investigators have subsequently established its ability to predict revascularization, its significant prognostic value over clinical risk factors, and the excellent prognosis of a negative study. In spite of these accomplishments, two main limitations have limited the incorporation of CTCA as a clinically established tool in diagnostic algorithms: radiation dose and lack of functional assessment hampering accurate assessment in patients with diffusely calcified vessels.
As mentioned previously, several investigators have convincingly demonstrated the ability of cardiac CT to evaluate myocardial perfusion, myocardial viability and the sequelae of chronic myocardial infarction. Indeed, cardiac CT might appear in the near future as a potential one-stop shop diagnostic tool.
Concerns regarding radiation exposure and potential association of the procedure with the risk of cancer represent other limitations of the technique, although such assumptions are based on Monte-Carlo simulations without demonstration of cause-effect[37]. In addition, the lifetime-risk of cancer attributable to CTCA is similar to the risk related to a stress-rest SPECT or a chest or abdomen CT[38]. It is noteworthy, though, that the currently widely established application of prospective ECG gating acquisitions allows a significant reduction in radiation doses to as low as 1-3 mSv[39]. Furthermore, the recent incorporation of high pitch spiral scanners achieves effective radiation doses up to 1-2 mSv[40].
Peer reviewers: Antony Leslie Innasimuthu, MD, MRCP, Presbyterian-Shadyside Program, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, 5230 Center Ave, Pittsburgh, PA 15232, United States; Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD, Cardiology Division, Heart Center, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 712 Eonjuro, Gangnam-gu, 135-720 Seoul, South Korea
S- Editor Cheng JX L- Editor Lutze M E- Editor Zheng XM