Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2017; 9(6): 531-538
Published online Jun 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i6.531
Published online Jun 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i6.531
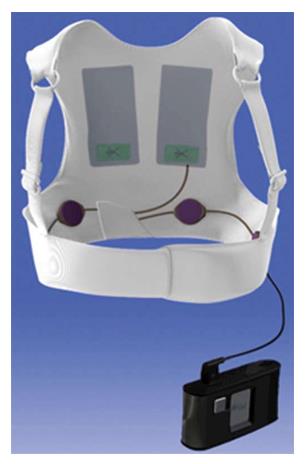
Figure 1 Wearable cardioverter defibrillator.
The two defibrillator electrodes are worn on the back of the garment, when the four monitoring electrodes are placed on the elastic belt around the chest. Both systems are connected to the monitor unit.
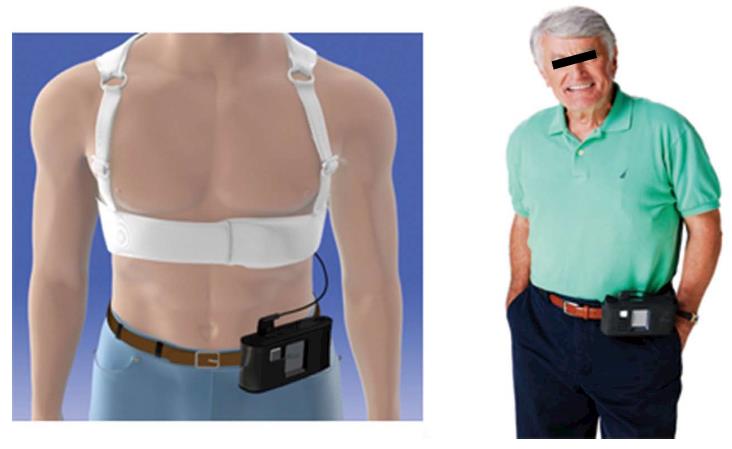
Figure 2 Wearable cardioverter defibrillator worn by a patient under clothes; monitor unit is worn on waist belt or in a holster.
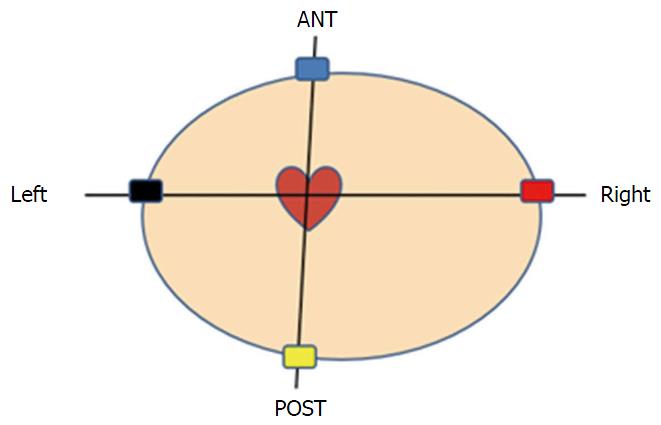
Figure 3 Four electrocardiographic electrodes position, and two left-right and front-back bipolar electrocardiographic vectors.
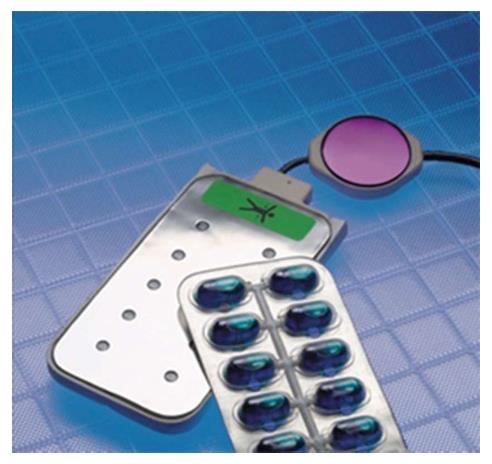
Figure 4 One defibrillator electrode with ten gel capsules inserted in, and one non-adhesive electrocardiogram electrode.
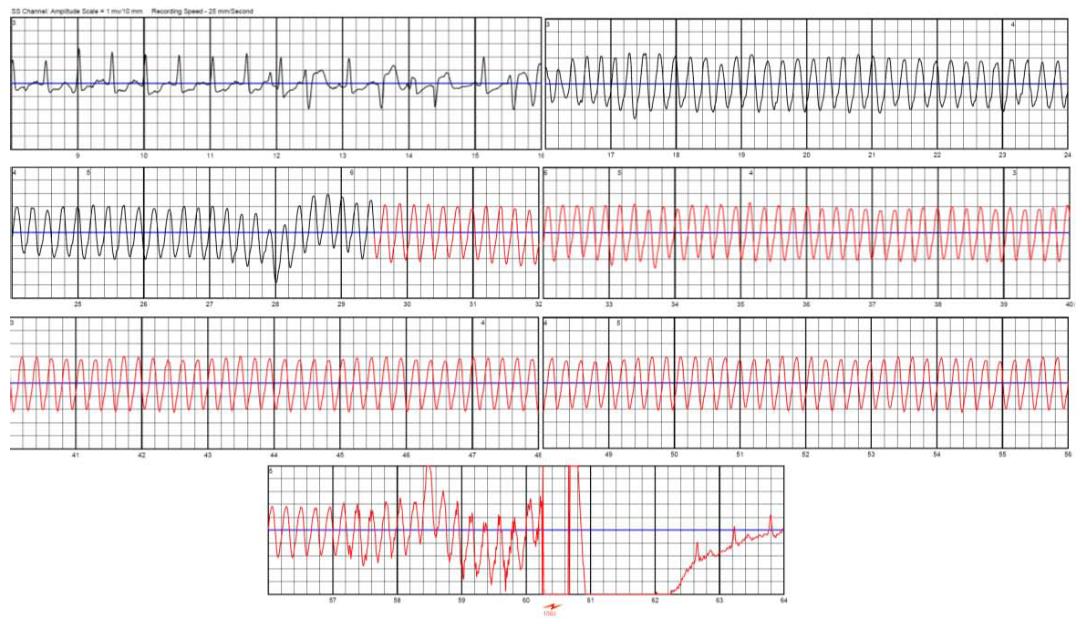
Figure 5 Ventricular tachycardia correctly diagnosed and treated by wearable cardioverter defibrillator.
Red line corresponds to sound signal. A 150-J defibrillation shock, automatically delivered by the device, terminated the arrhythmia.
- Citation: Barraud J, Cautela J, Orabona M, Pinto J, Missenard O, Laine M, Thuny F, Paganelli F, Bonello L, Peyrol M. Wearable cardioverter defibrillator: Bridge or alternative to implantation? World J Cardiol 2017; 9(6): 531-538
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i6/531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i6.531