Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Mar 26, 2017; 9(3): 200-206
Published online Mar 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i3.200
Published online Mar 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i3.200
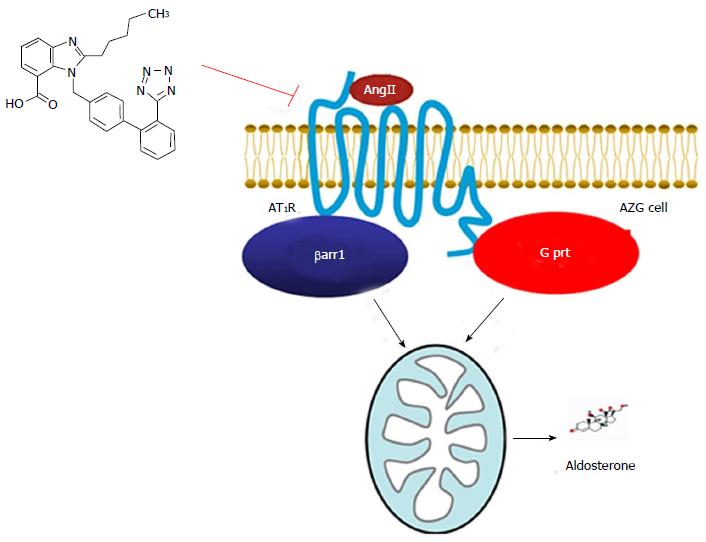
Figure 1 Angiotensin II type 1 receptor and aldosterone production.
Schematic representation of the parallel G prt- and βarr1-mediated, AngII-bound AT1R signaling cascades that converge on mitochondrial aldosterone synthesis in adrenocortical zona glomerulosa (AZG) cells. The structure of the proposed AT1R antagonist (2-pentyl-1-({4-[2-(2H-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl}methyl)-1H-1,3-benzodiazole-7-carboxylic acid)[40], discussed in the text, capable of suppressing both pathways equally well, is also shown (upper left corner). See text for details. G prt: Gq protein; βarr1: β-arrestin1; AngII: Angiotensin II; AT1R: AngII type 1 receptor.
- Citation: Lymperopoulos A, Aukszi B. Angiotensin receptor blocker drugs and inhibition of adrenal beta-arrestin-1-dependent aldosterone production: Implications for heart failure therapy. World J Cardiol 2017; 9(3): 200-206
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i3/200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i3.200