Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2017; 9(12): 853-857
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i12.853
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i12.853
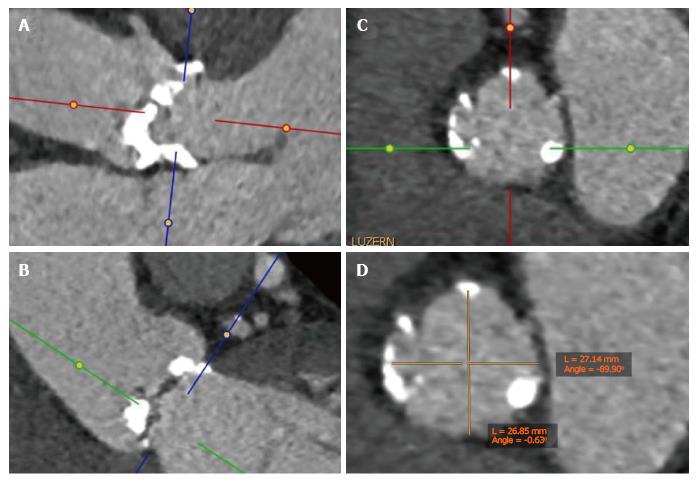
Figure 1 Example of a multiplanar reconstruction of the aortic annulus.
A and B: Double-oblique MSCT images at the basal insertion of the calcified native cusps; C: Double-oblique reconstruction at the level of the aortic annulus. The aortic valve leaflets are just barely visible at the level of the ventriculoarterial junction; D: Measurement of the short and long diameter at the level of the aortic annulus. MSCT: Multislice computed tomography.
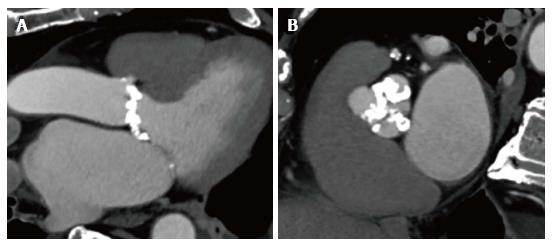
Figure 2 Cardiac multislice computed tomography showing a patient with heavy calcifications extending into the left ventricular outflow tract and a shallow sinus.
This anatomy is associated with increased risk for annular rupture in patients undergoing TAVI with a balloon expandable valve. A: Three chamber view of the heart showing a patient with heavy calcification extending from the aortic annulus into the LVOT and a shallow sinus; B: Short axis view of the aortic valve showing heavy calcified aortic leaflets. LVOT: Left ventricular outflow tract; TAVI: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
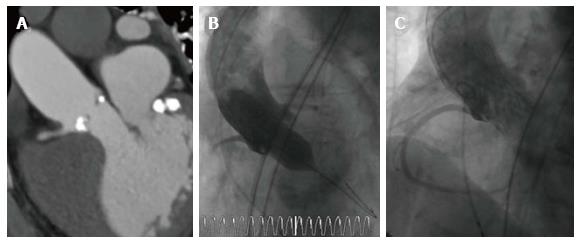
Figure 3 Patient undergoing transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation with a very low ostium of the right coronary artery.
A: Patient with a very low ostium of the right coronary artery but potentially a large enough sinus valsalva for TAVI; B: Balloonvalvuloplasty with simultaneous injection of contrast media to estimate the risk for coronary obstruction; C: Successful implantation of an Evolut R. Supraannular injection shows a patent right coronary artery. TAVI: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
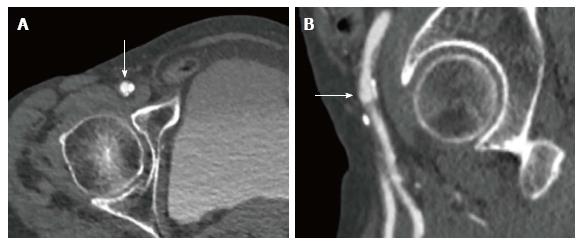
Figure 4 Multislice computed tomography showing calcified right common femoral artery in a patient undergoing transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
A: Right common femoral artery with an arrow pointing at the ideal puncture site above the calcification; B: Right common femoral artery with an arrow pointing at the ideal puncture site above the height of bifurcation of the common femoral artery in relationship to the femoral head.
- Citation: Brinkert M, Toggweiler S. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation operators - get involved in imaging! World J Cardiol 2017; 9(12): 853-857
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i12/853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i12.853