Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2016; 8(7): 383-400
Published online Jul 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i7.383
Published online Jul 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i7.383
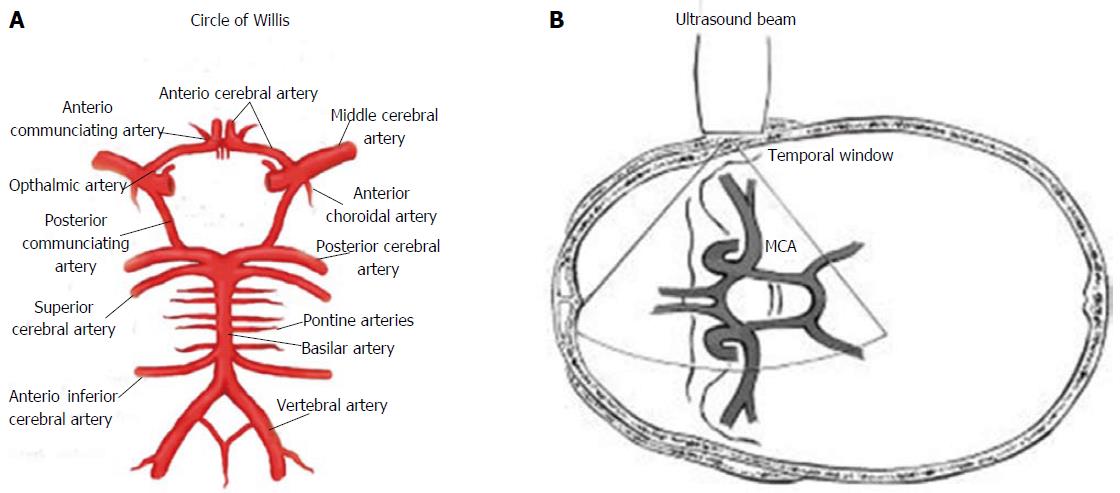
Figure 1 Circle of Willis and Ultrasonographic study by transcranial Doppler ultrasound.
A: Circle of Willis; B: Transmission of ultrasound beam through skull using pulsed Doppler sectorial probe with a 2.0-3.5 MHz emission frequency. Probe is positioned on temporal window. MCA: Middle cerebral artery.
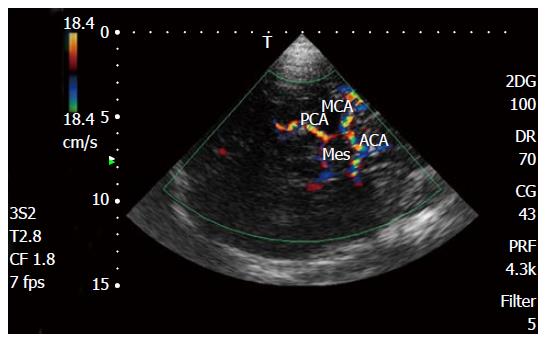
Figure 2 Transcranial Doppler color Doppler study of intracranial arteries.
MCA: Middle cerebral artery; PCA: Posterior cerebral artery; ACA: Anterior cerebral artery; Mes: Mesencephalon.
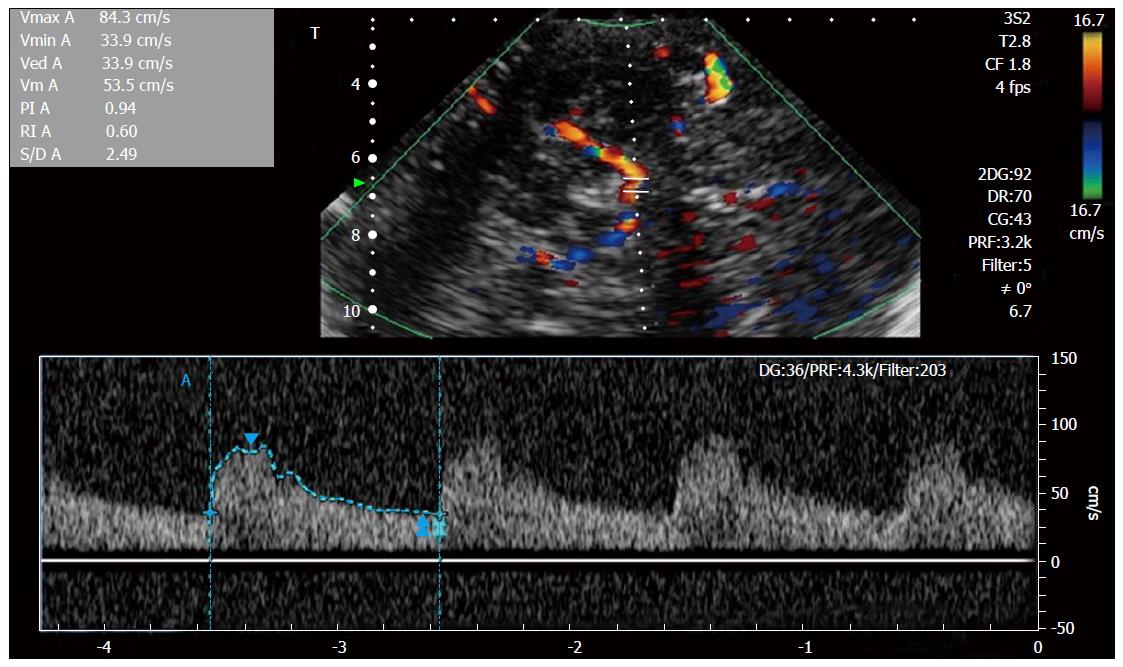
Figure 3 Transcranial Doppler spectral Doppler study of intracranial middle cerebral artery.
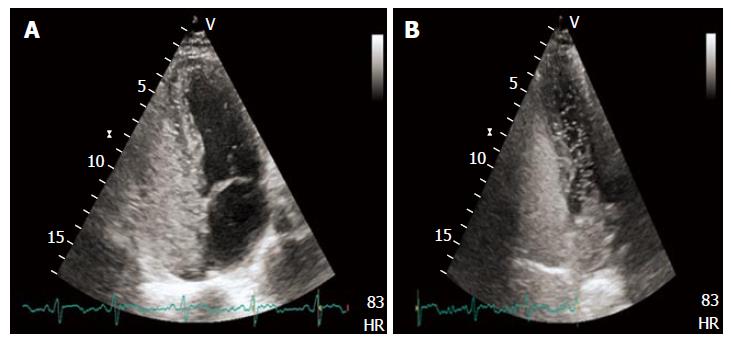
Figure 4 Transthoracic echocardiography showing high grade right to left shunt with evident micro-bubbles in the left heart after intravenous contrast administration (A and B).
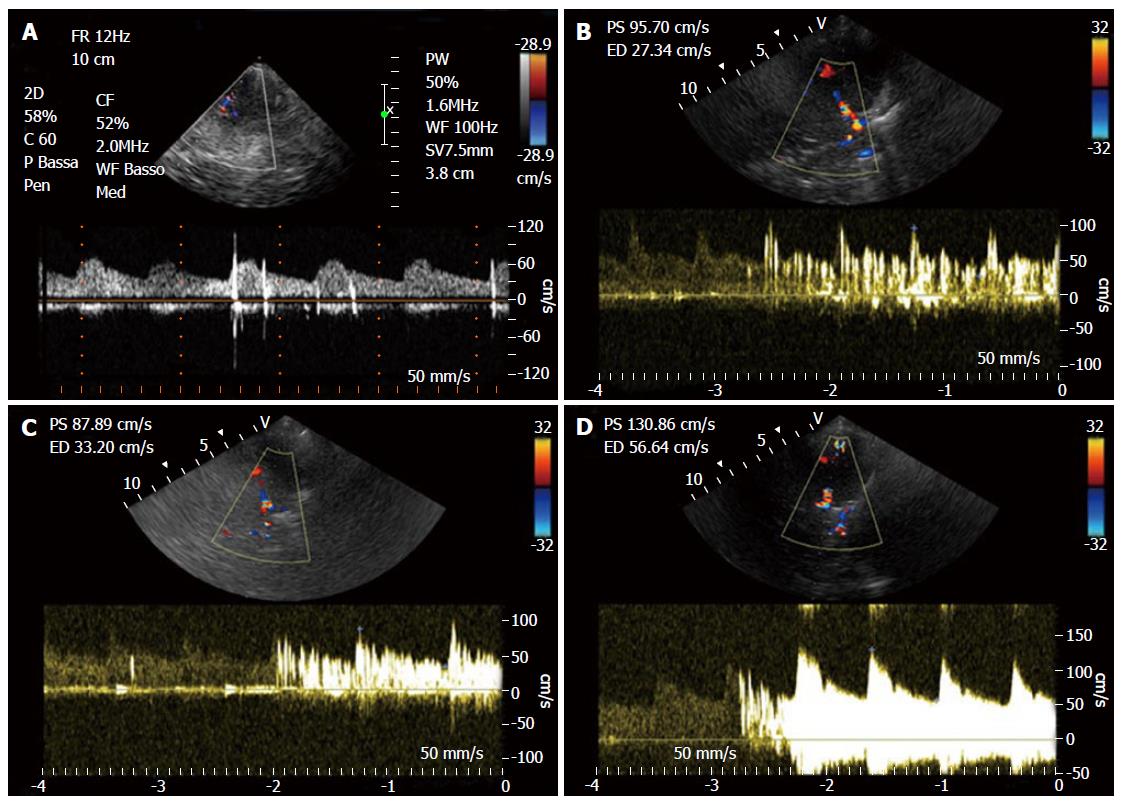
Figure 5 Right to left shunt with microembolic signals.
A: Low grade shunt; B: Moderate grade shunt; C: High grade shunt (shower); D: Curtain effect.
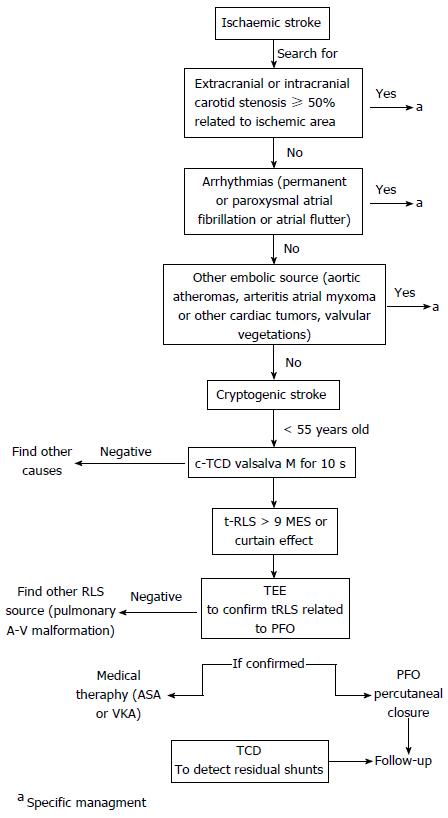
Figure 6 Contrast enhanced transcranial Doppler as a first line screening tool in the setting of a cryptogenic ischemic stroke.
TCD: Transcranial Doppler; c-TCD: Contrast enhanced TCD; TEE: Transesophageal echocardiography; RLS: Right-to-left shunting; PFO: Patent foramen ovale; ASA: Atrial septal aneurysm; MES: Microembolic signals; VKA: Vitamin K antagonist.
- Citation: D’Andrea A, Conte M, Cavallaro M, Scarafile R, Riegler L, Cocchia R, Pezzullo E, Carbone A, Natale F, Santoro G, Caso P, Russo MG, Bossone E, Calabrò R. Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography: From methodology to major clinical applications. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(7): 383-400
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i7/383.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i7.383